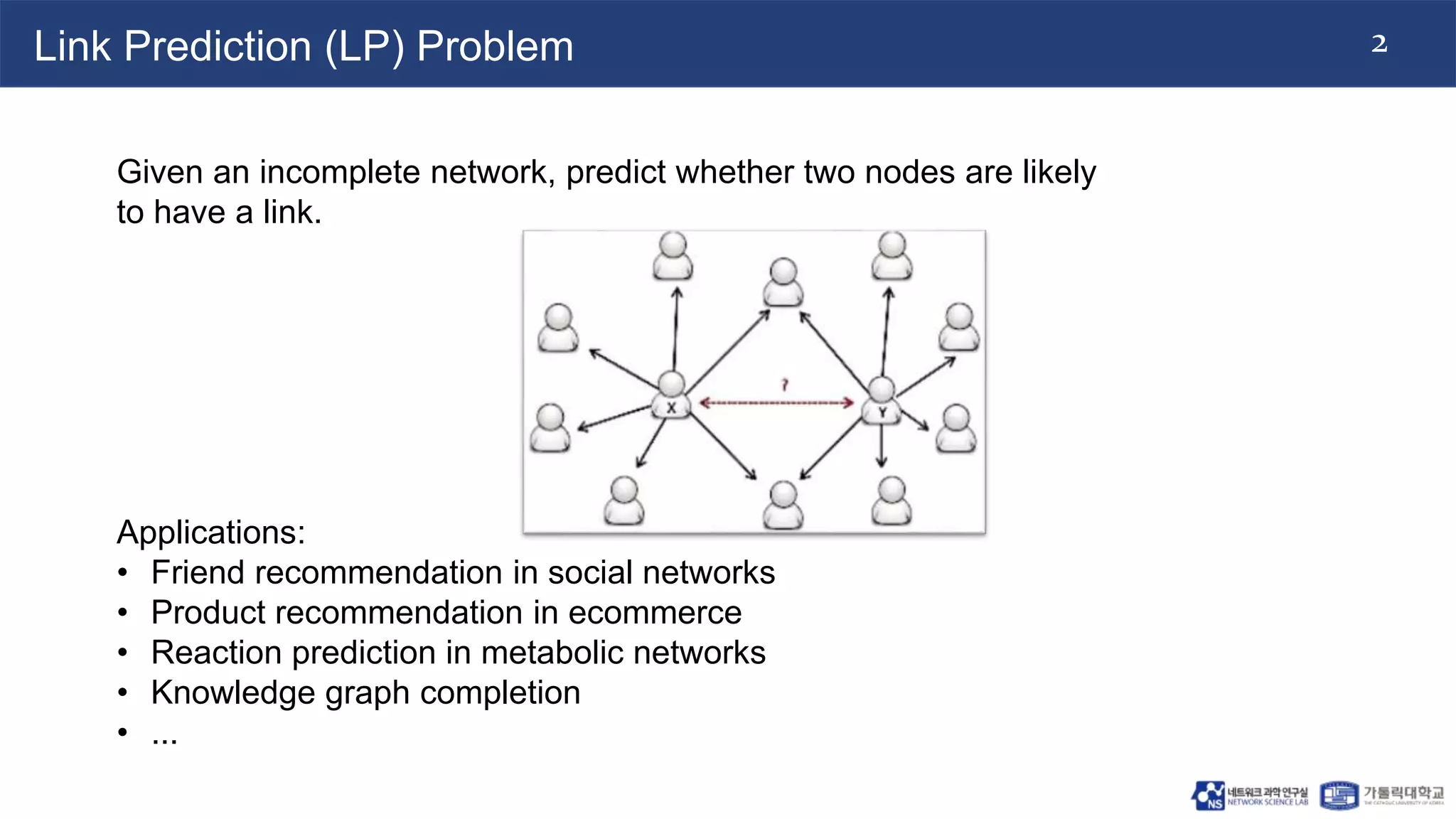
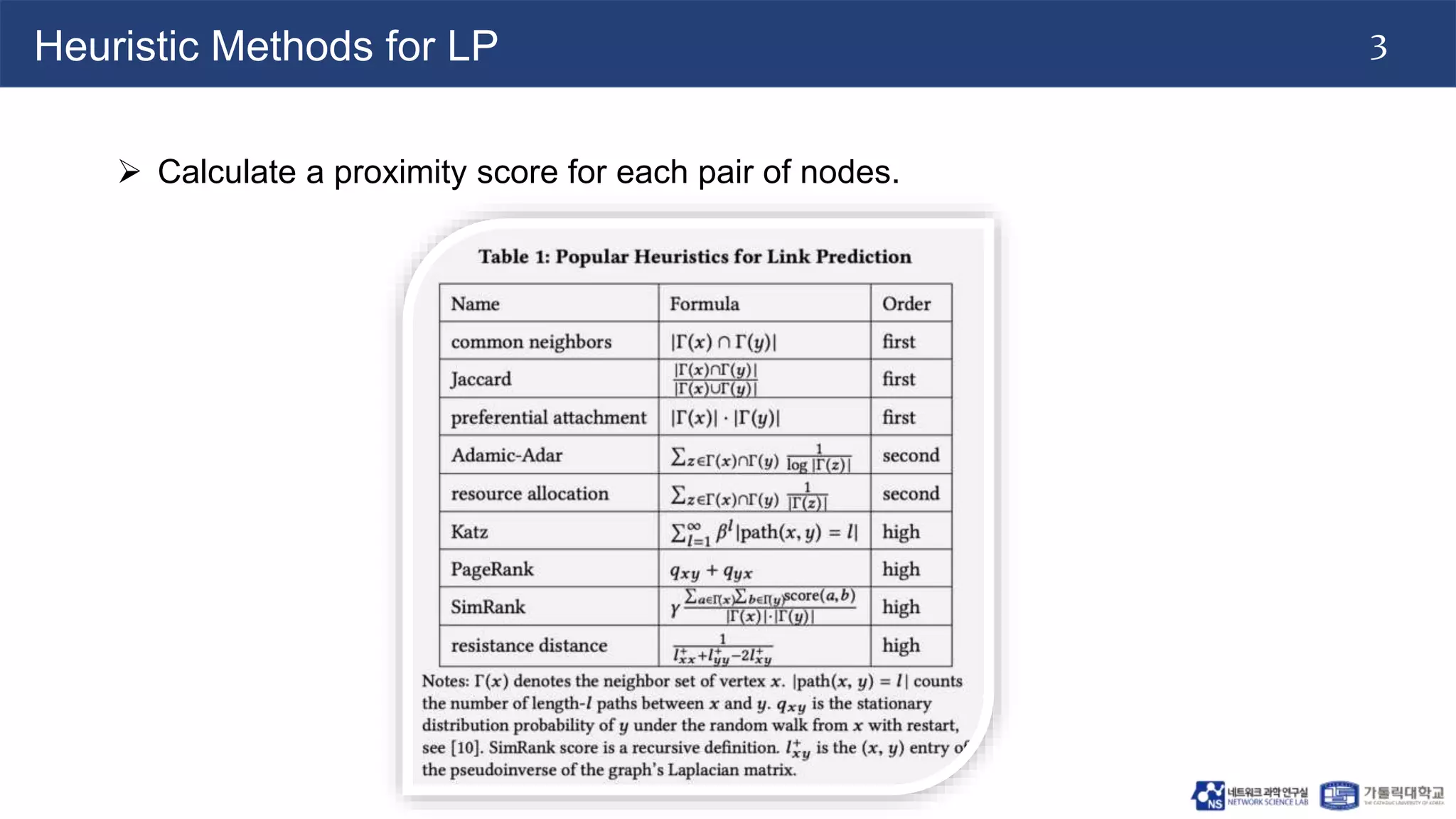
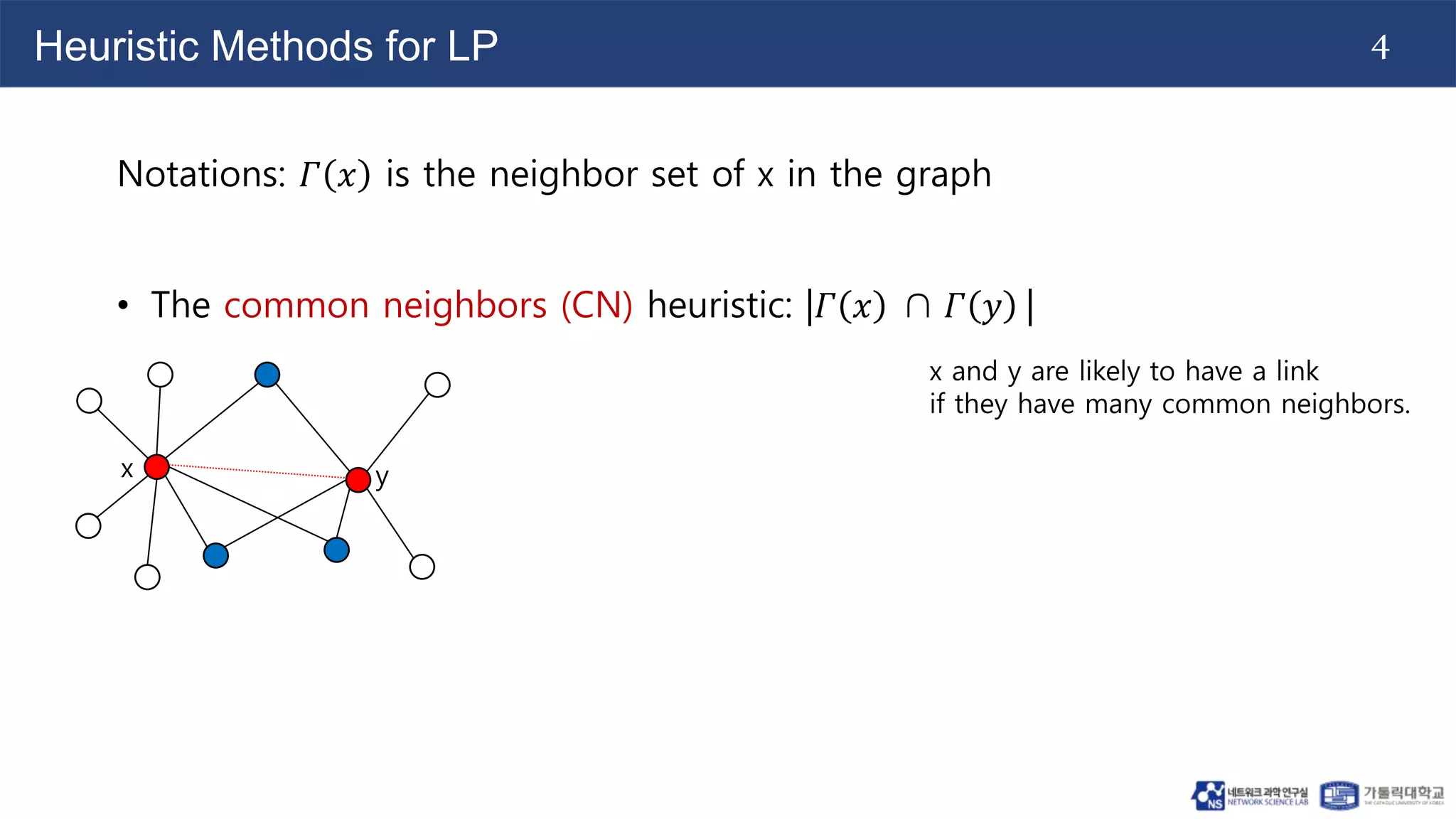
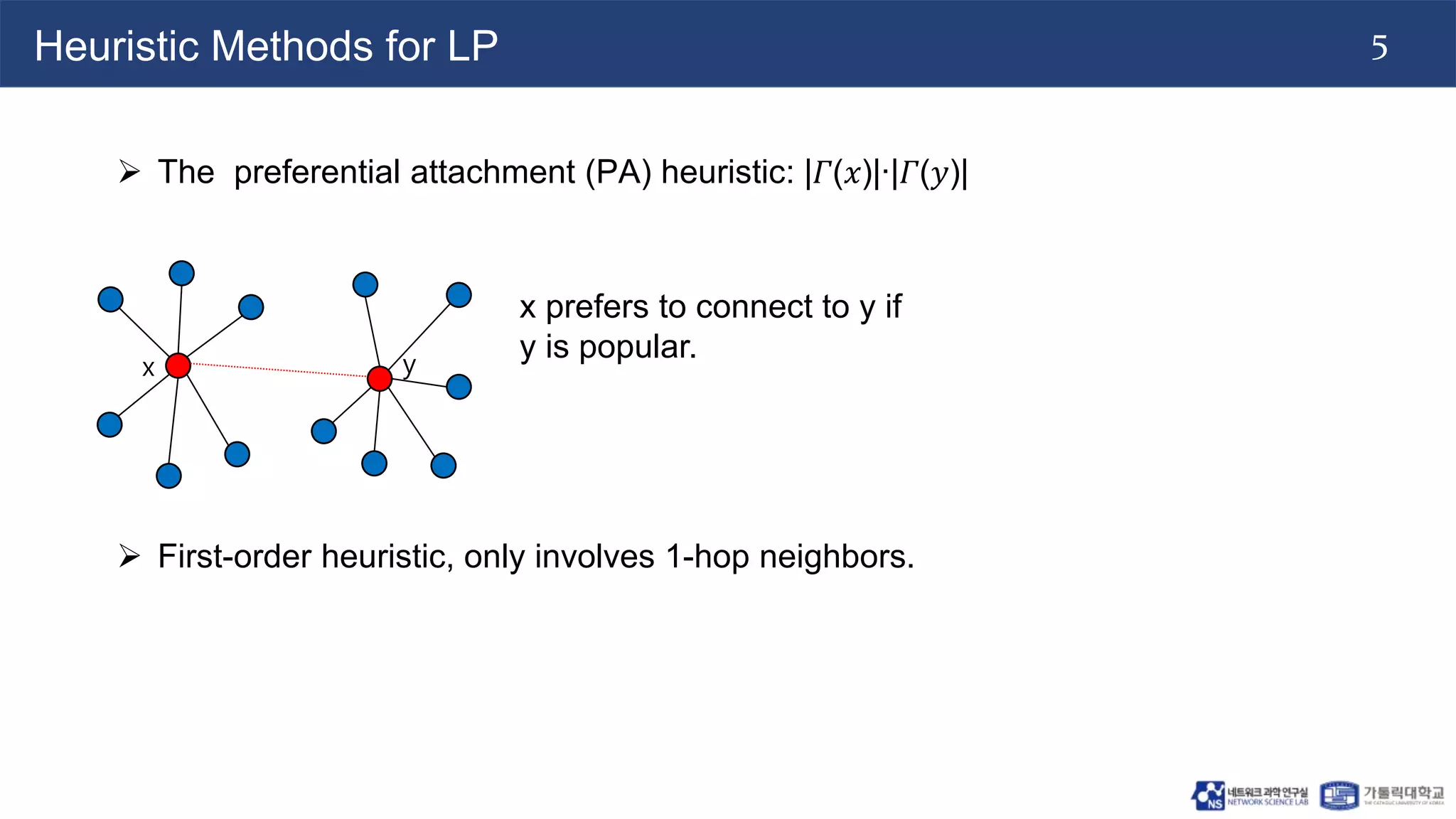
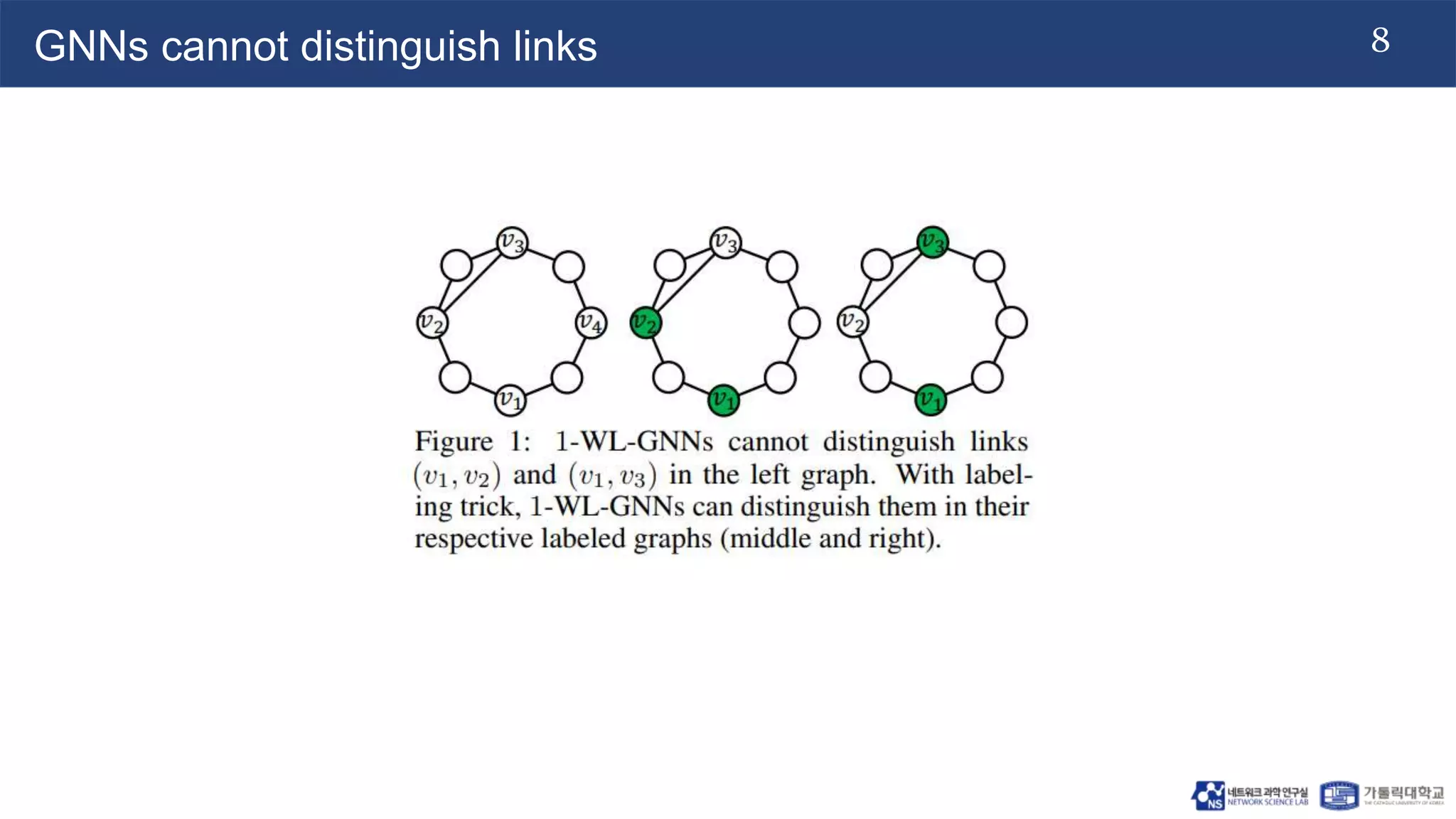
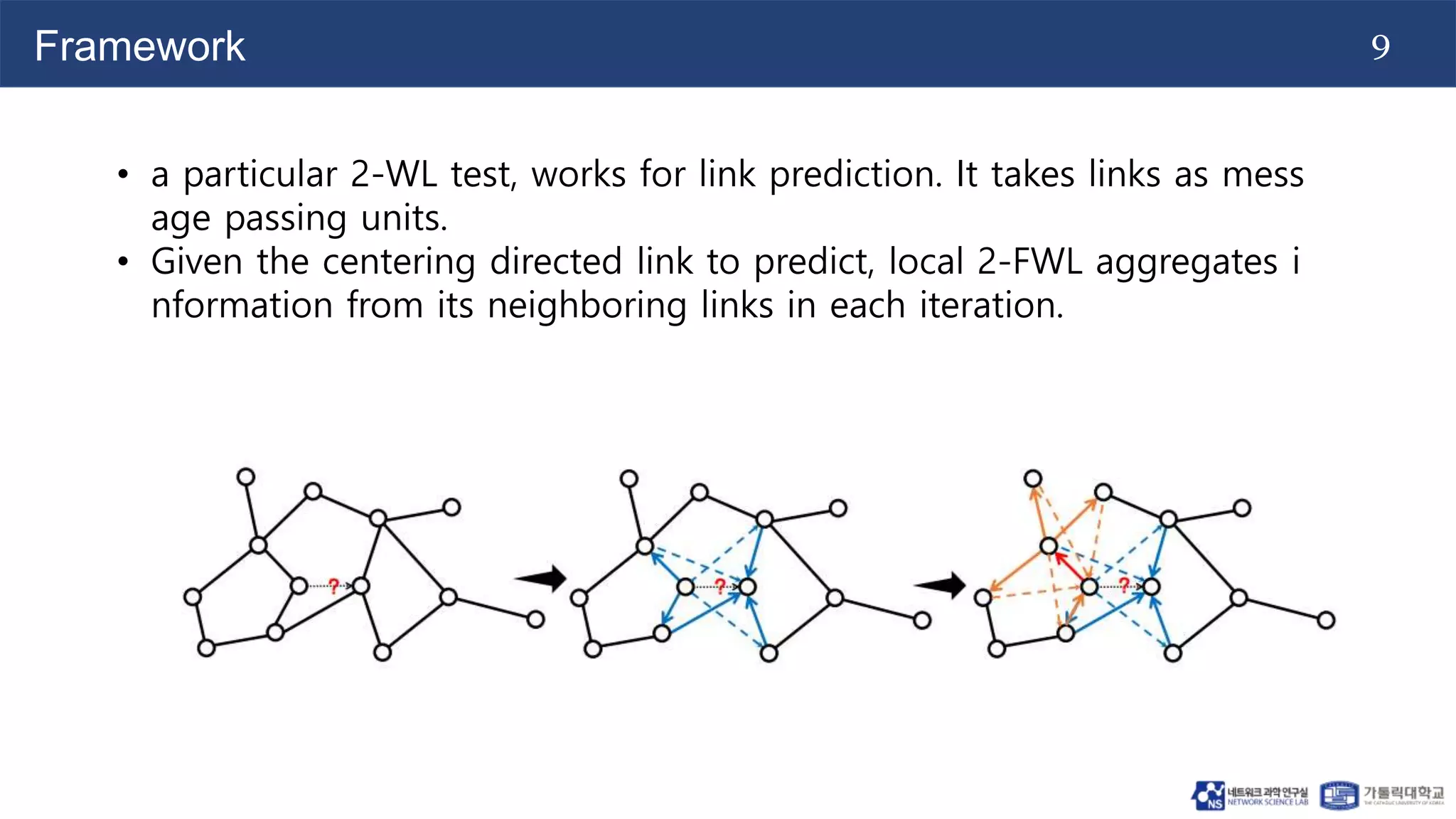
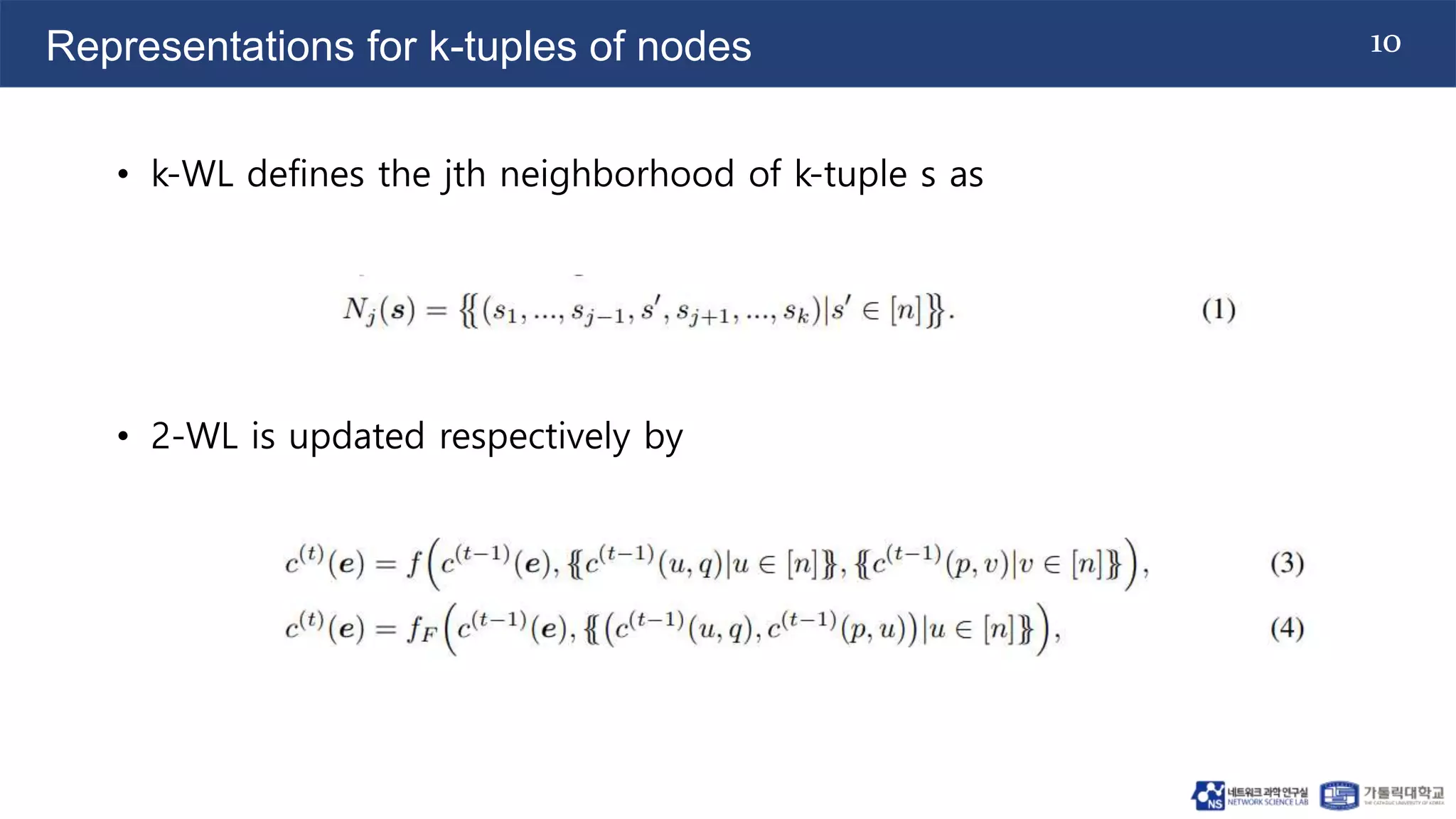
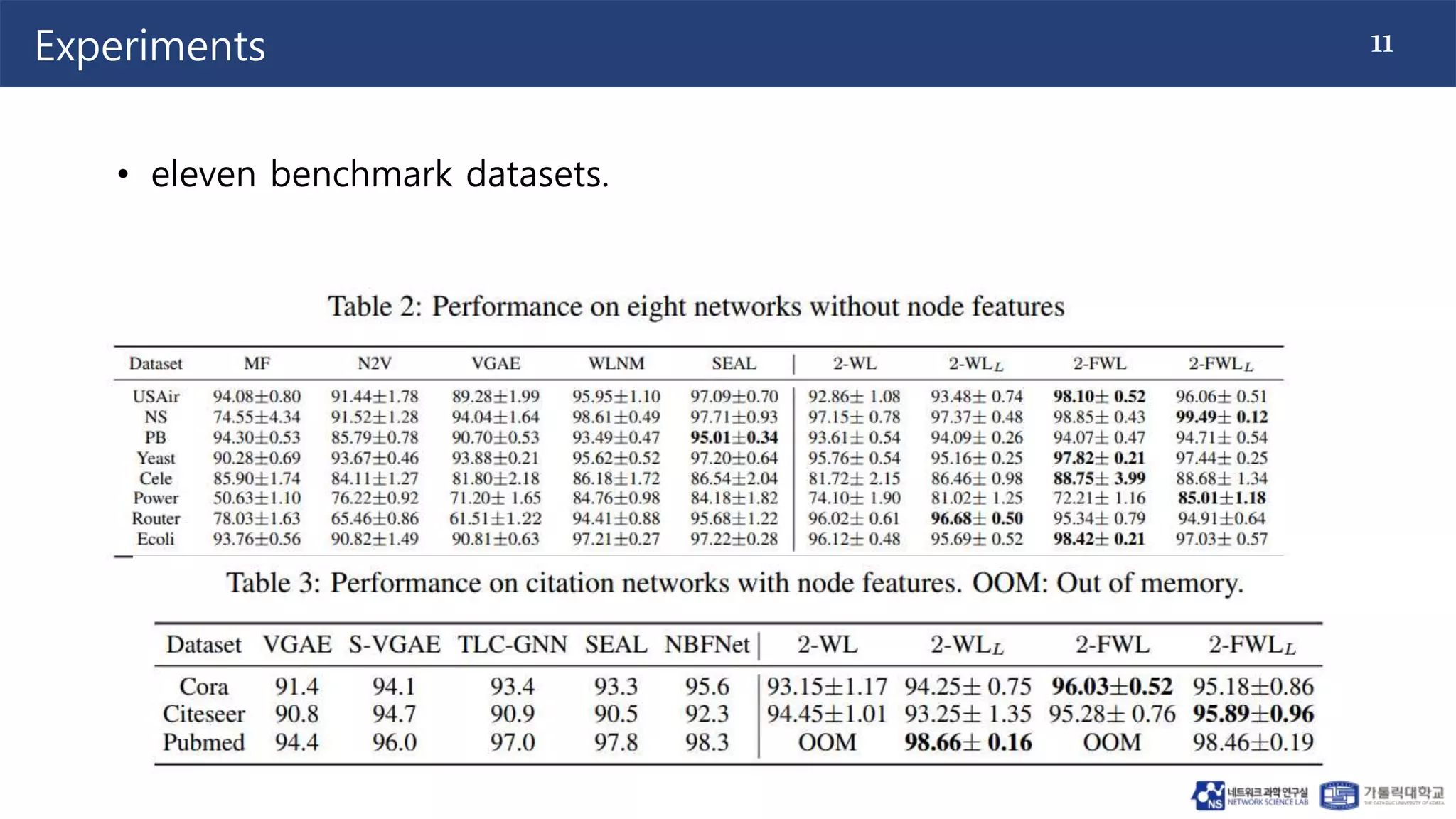
The document discusses the use of two-dimensional Weisfeiler-Lehman graph neural networks (2-WL GNNs) for link prediction in various applications like social networks and e-commerce. It highlights the limitations of traditional heuristic methods in link prediction, emphasizing the need for a neural network model that learns features directly from the graph. The 2-WL GNNs demonstrated superior performance compared to traditional methods across eleven benchmark datasets.