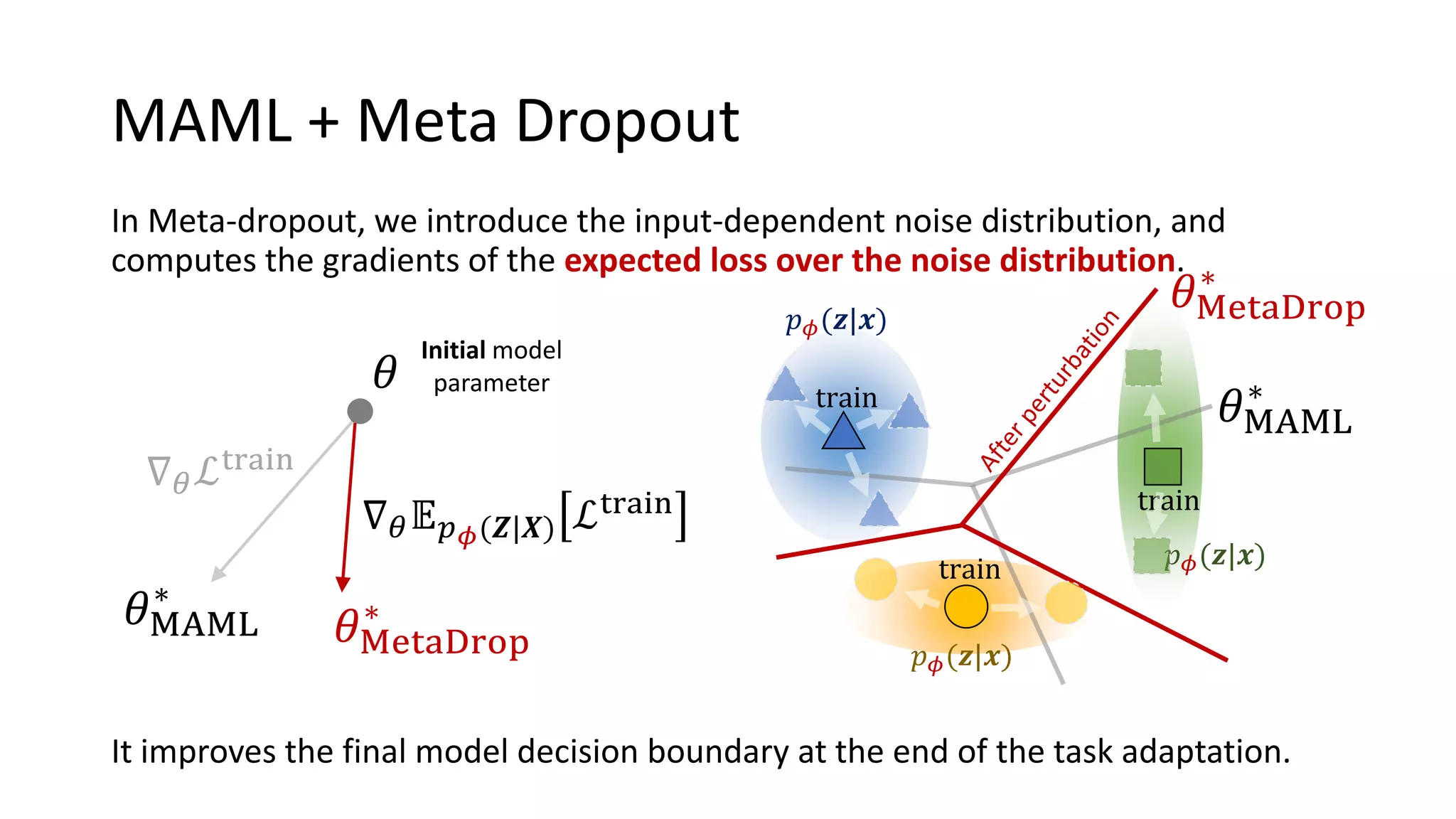
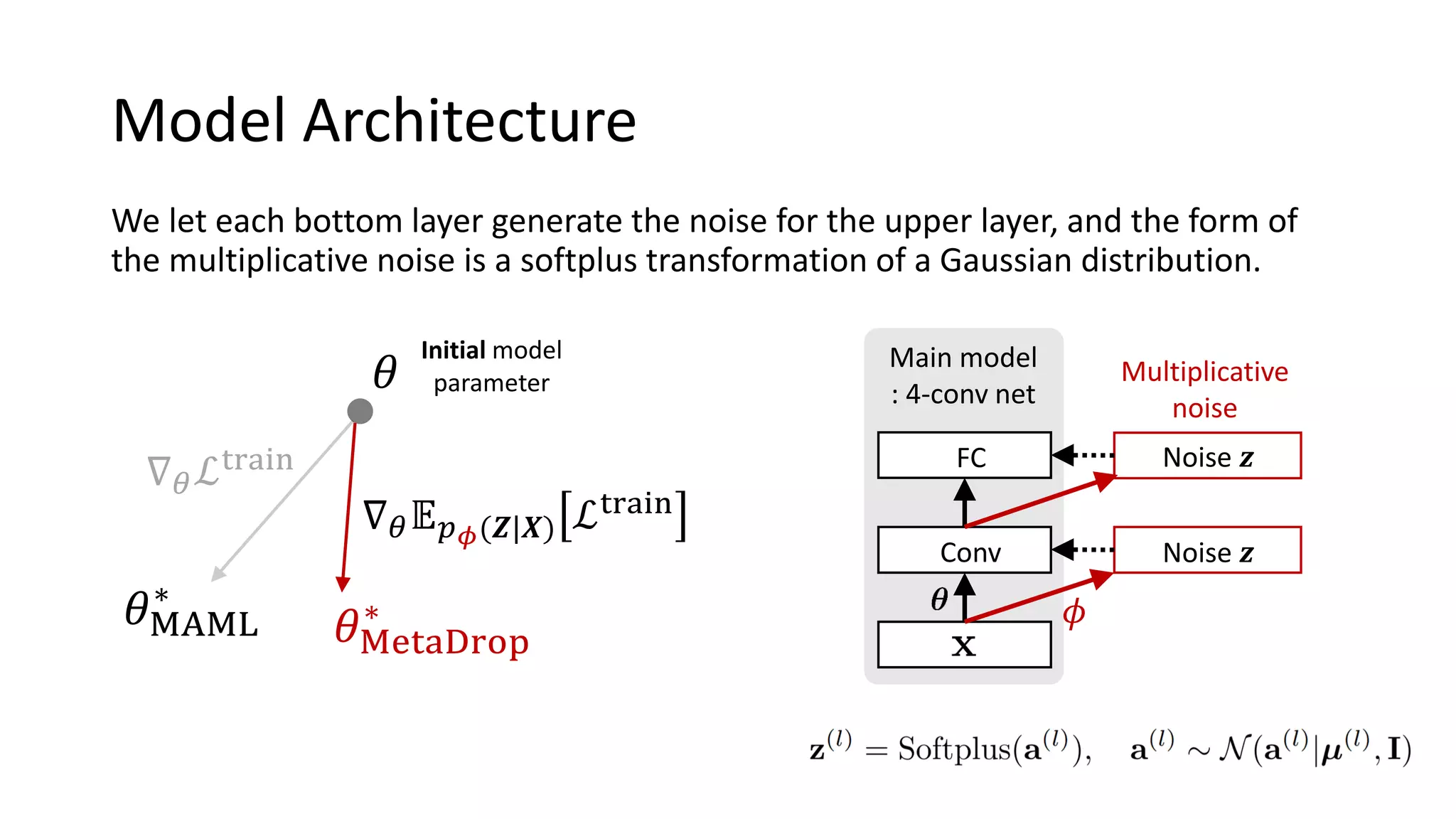
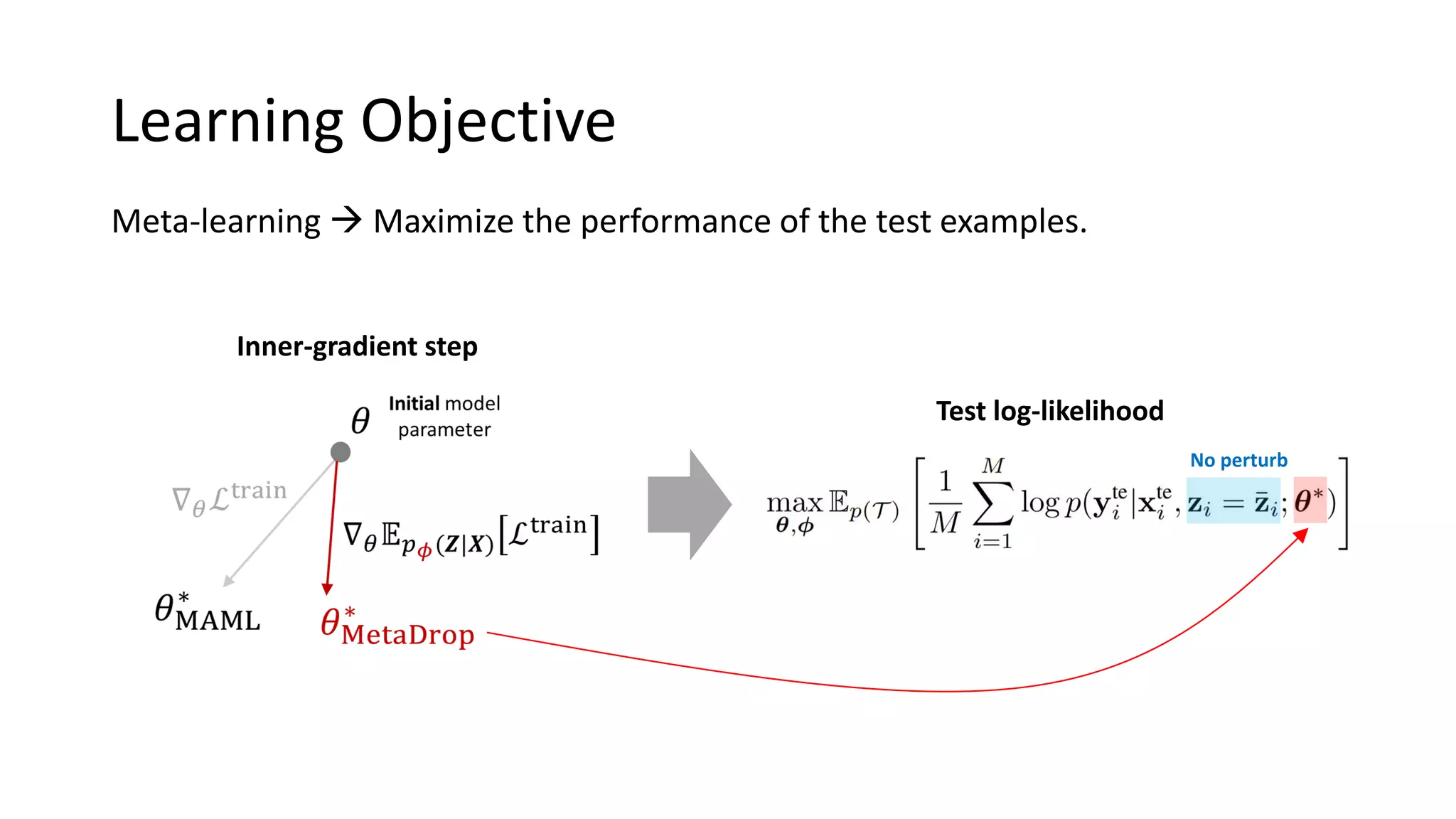
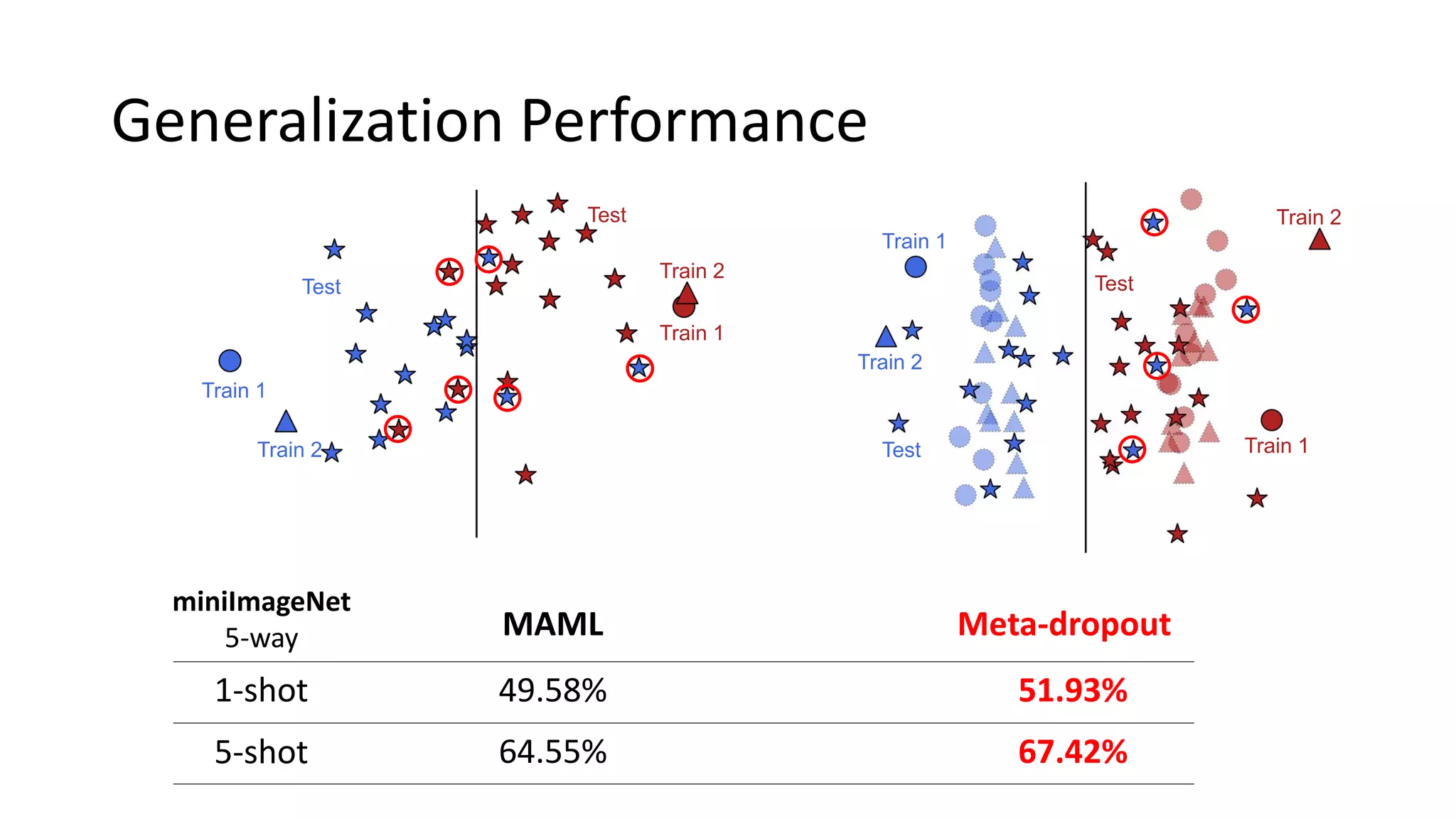
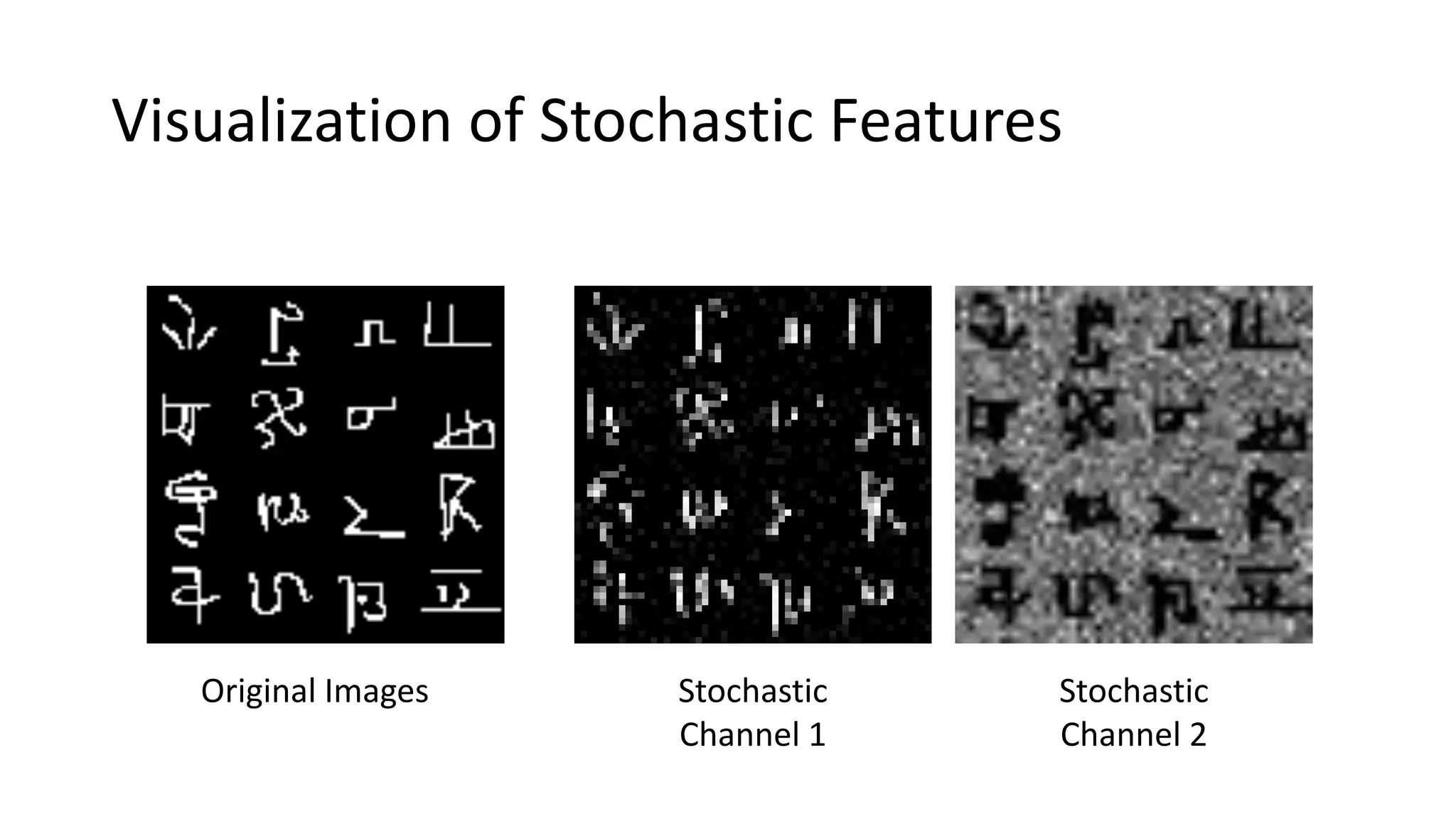
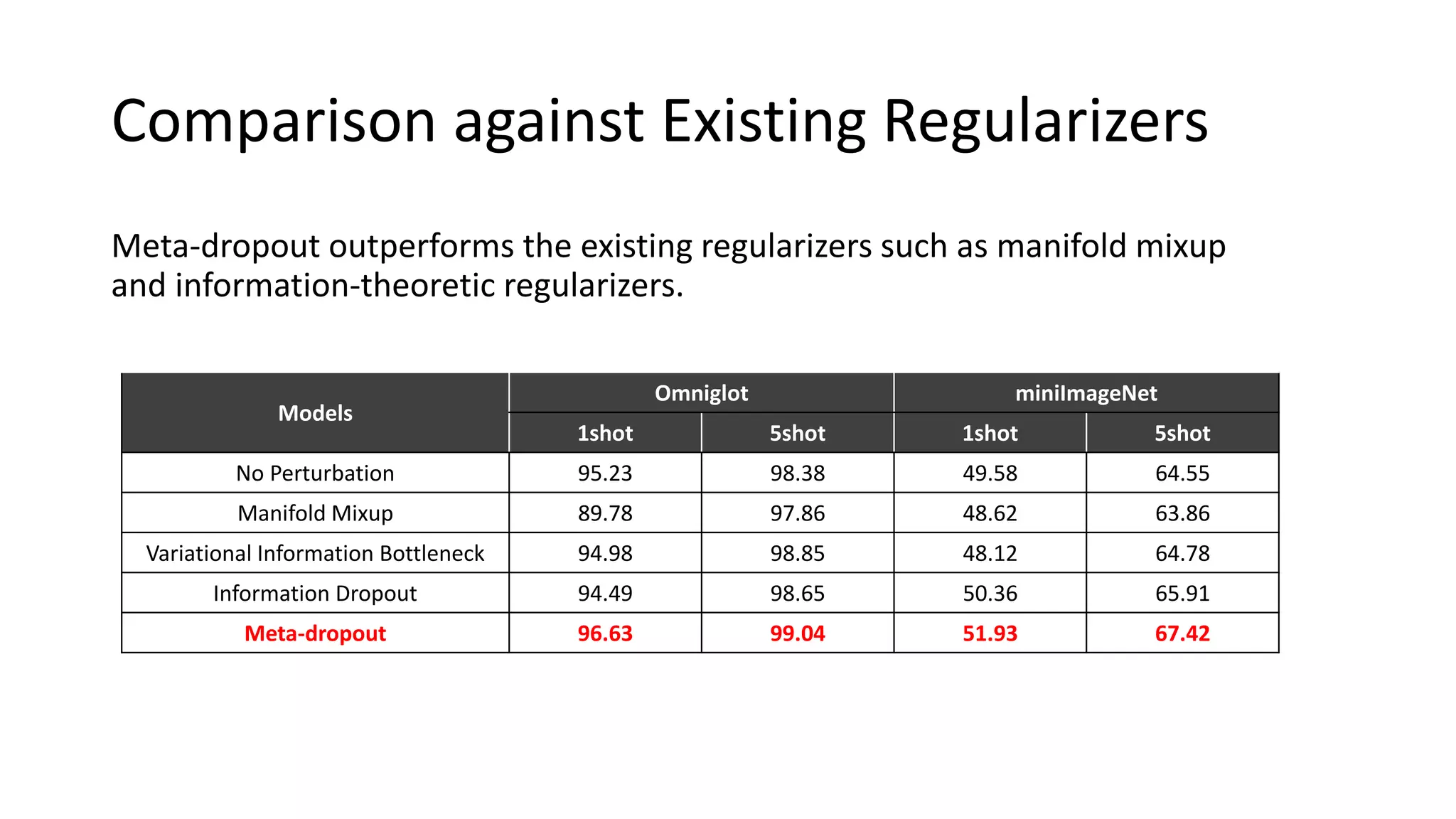
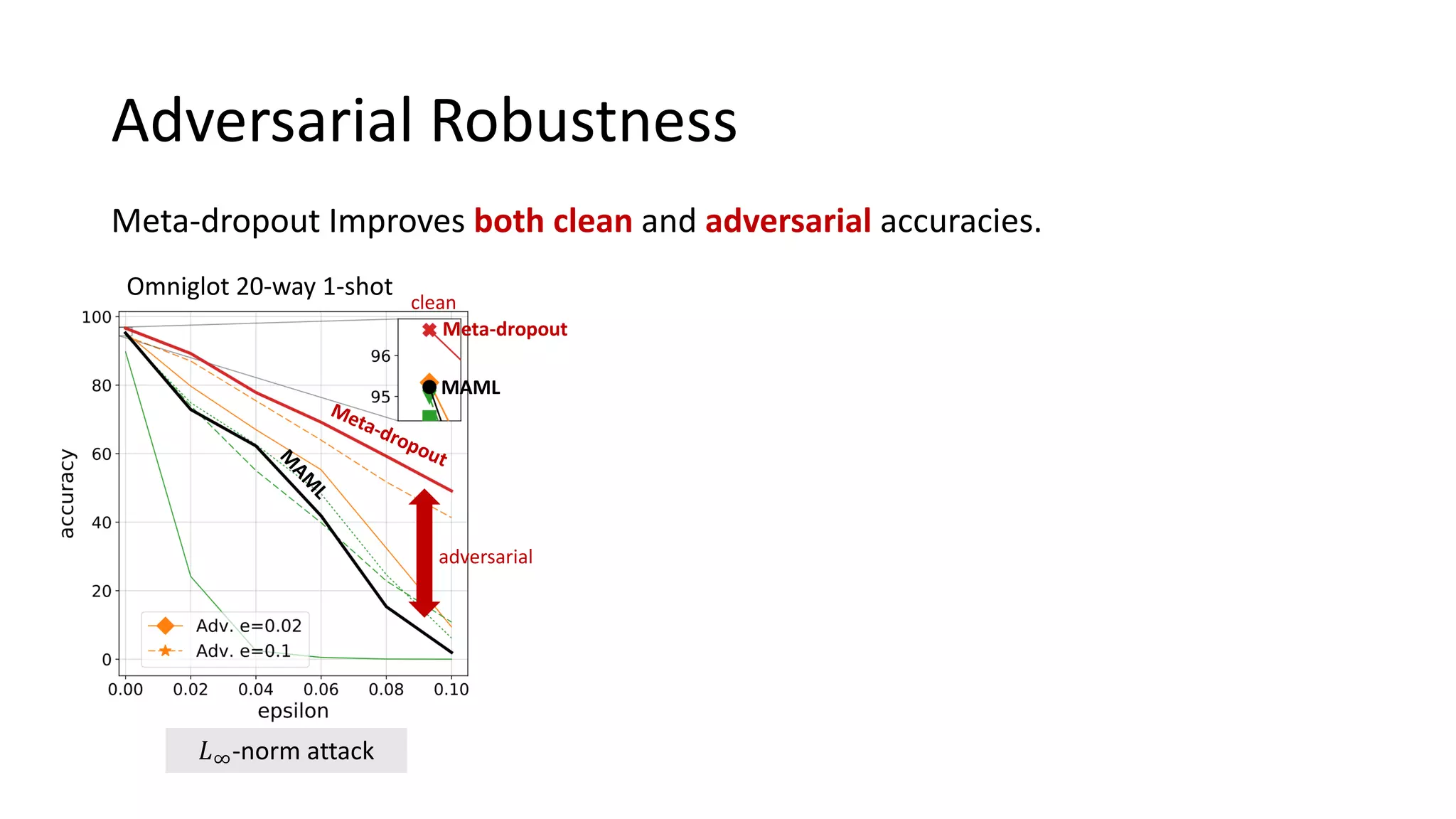
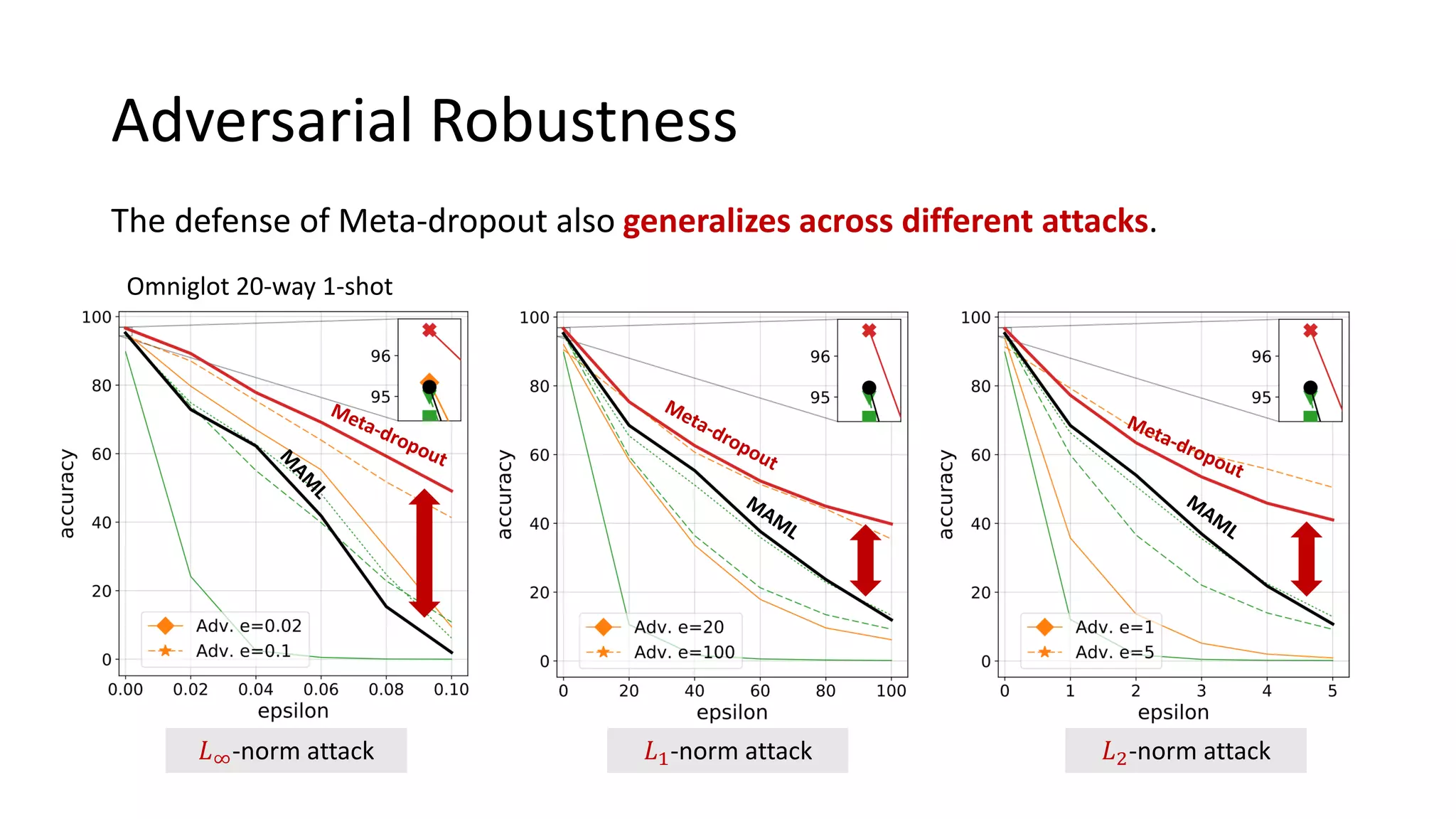
This document presents a method called meta-dropout, which learns to perturb latent features in an input-dependent manner to enhance generalization in few-shot learning. Through a meta-learning framework, the approach improves decision boundaries and outperforms existing regularizers in both clean and adversarial settings. The findings demonstrate that meta-dropout can effectively increase model performance across various tasks and resistance to adversarial attacks.

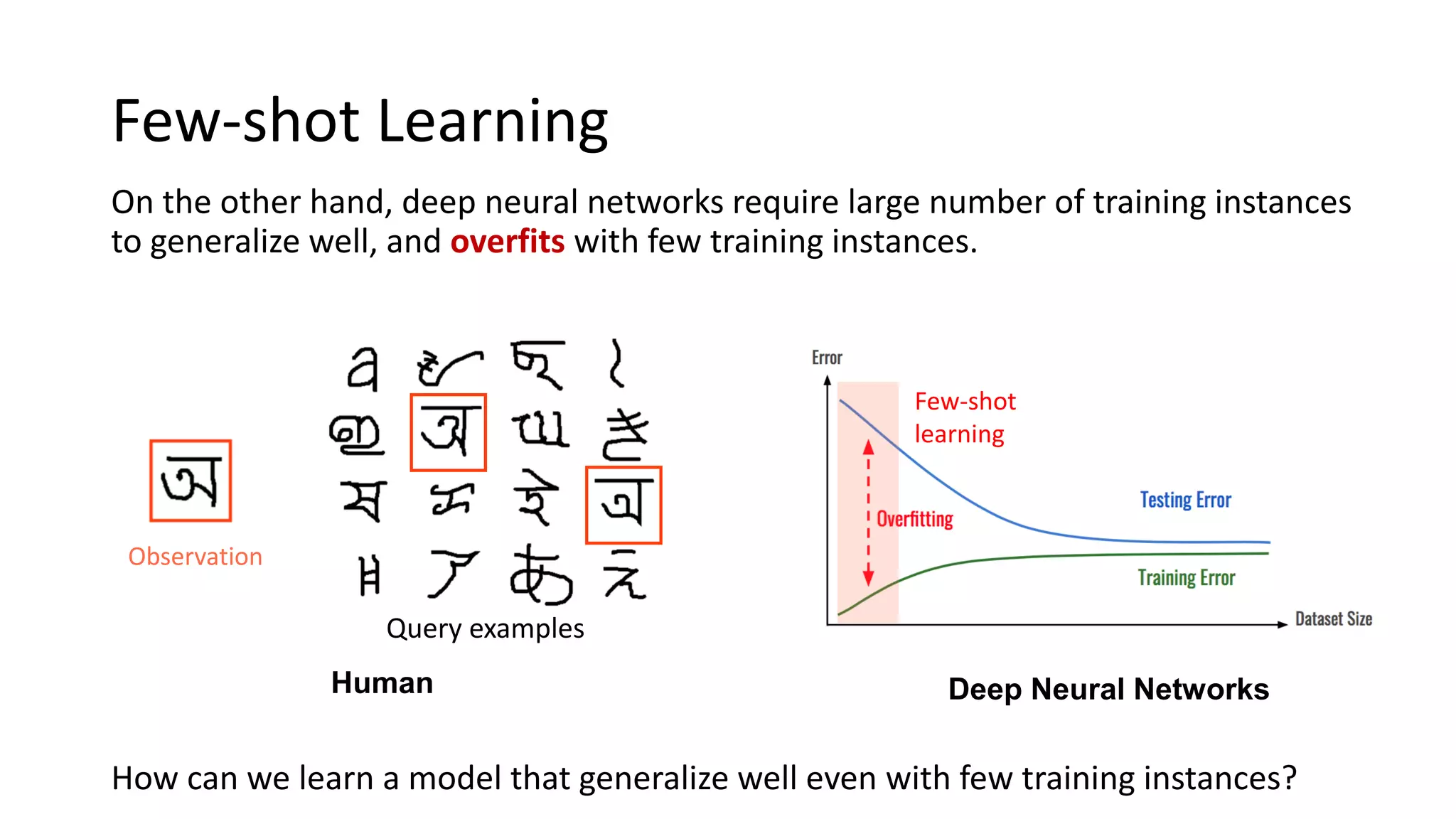
![Few-shot Learning
Humans can generalize even with a single observation of a class.
[Lake et al. 11] One shot Learning of Simple Visual Concepts, CogSci 2011
Observation
Query examples
Human](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metadropoutlearningtoperturbfeaturesforgeneralization-200529022020/75/Meta-Dropout-Learning-to-Perturb-Latent-Features-for-Generalization-2-2048.jpg)
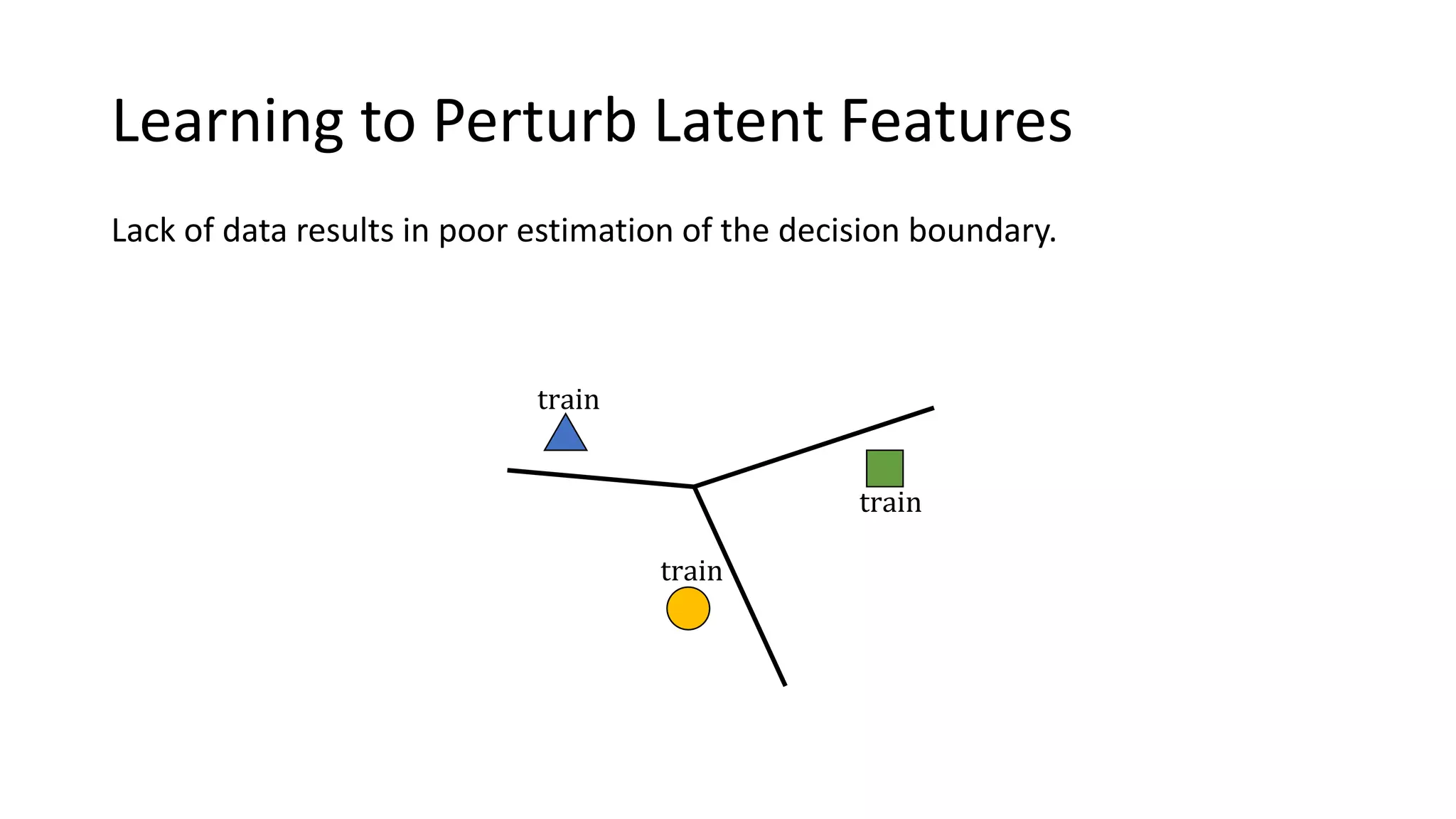
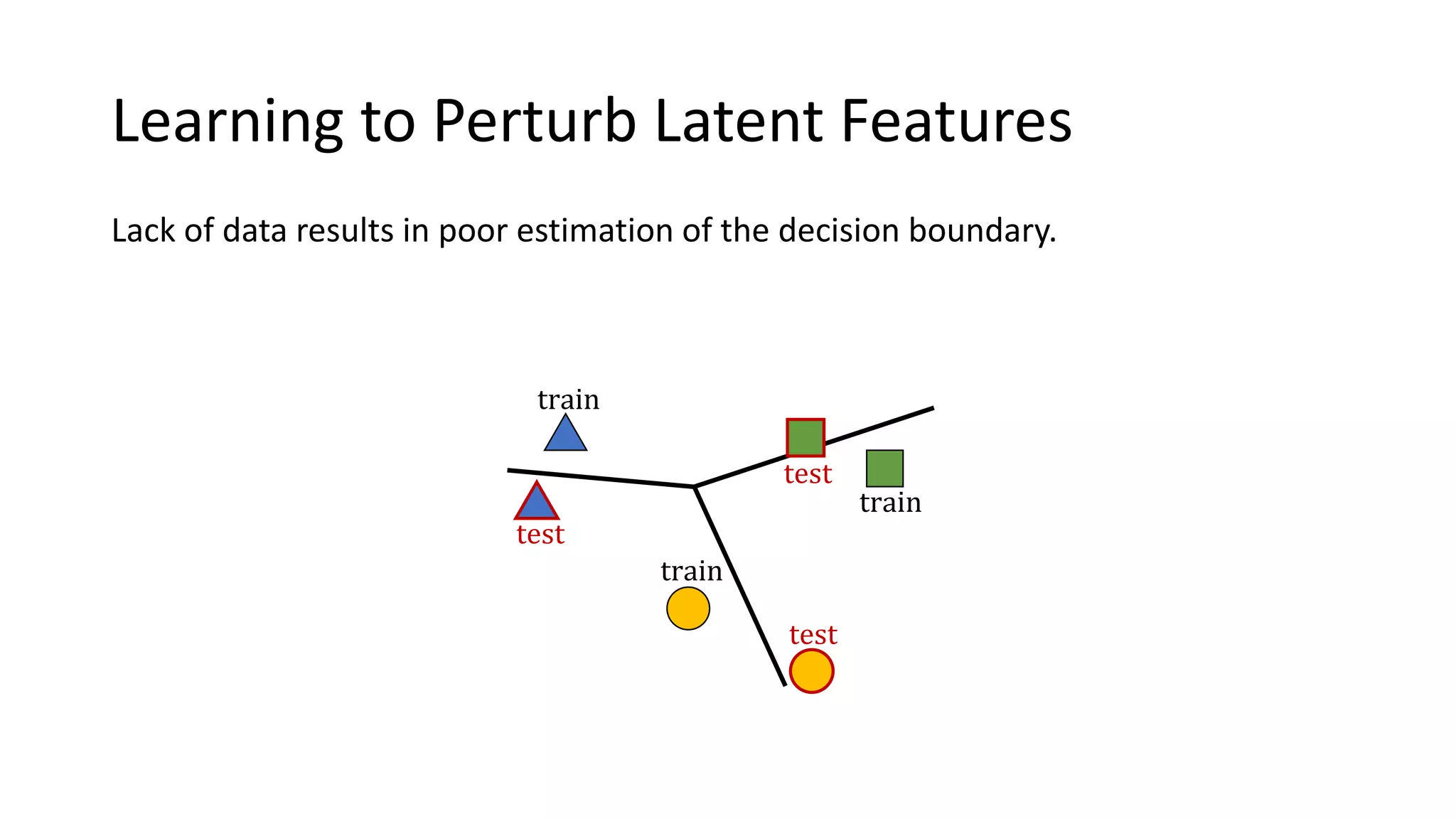
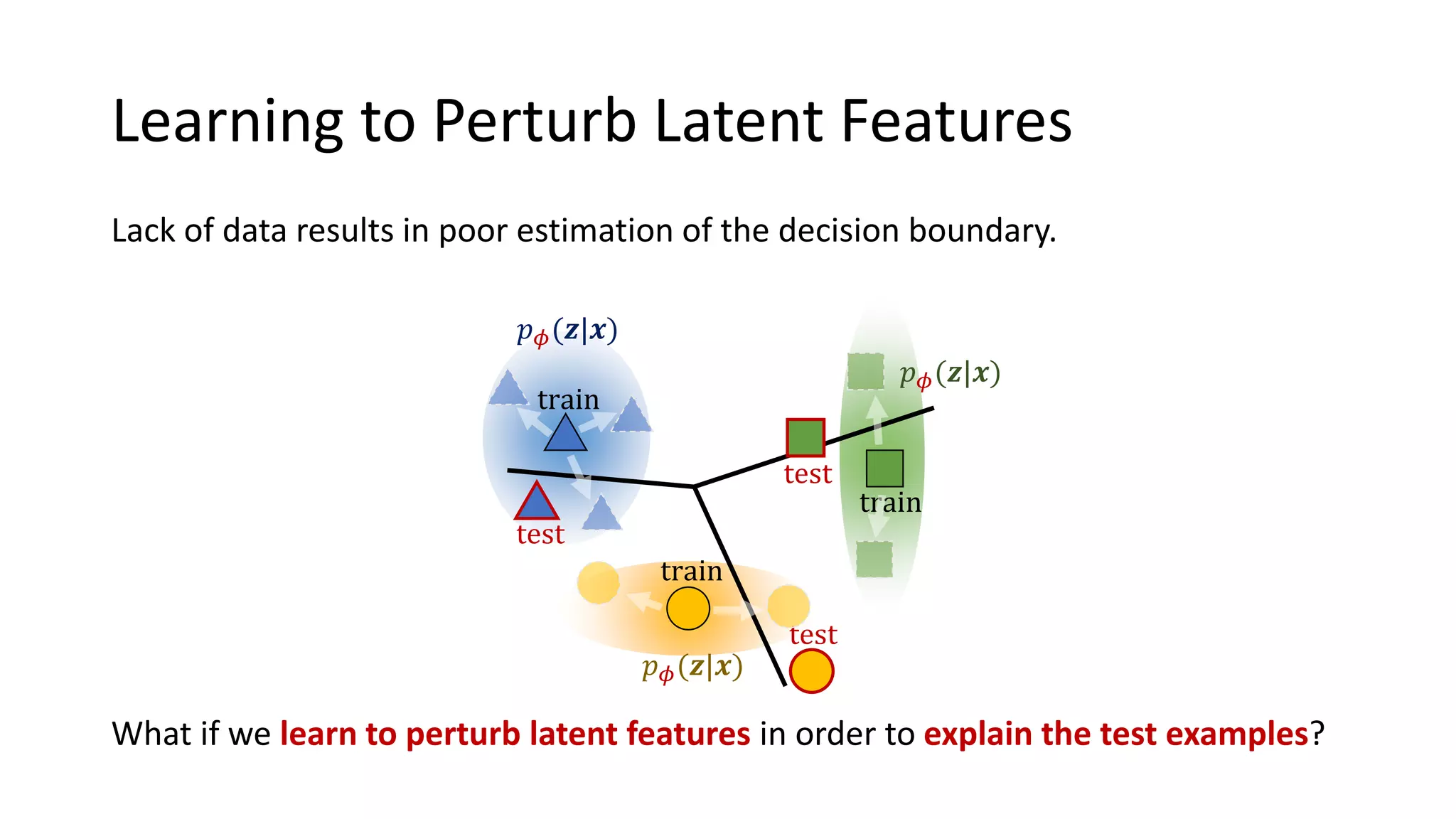
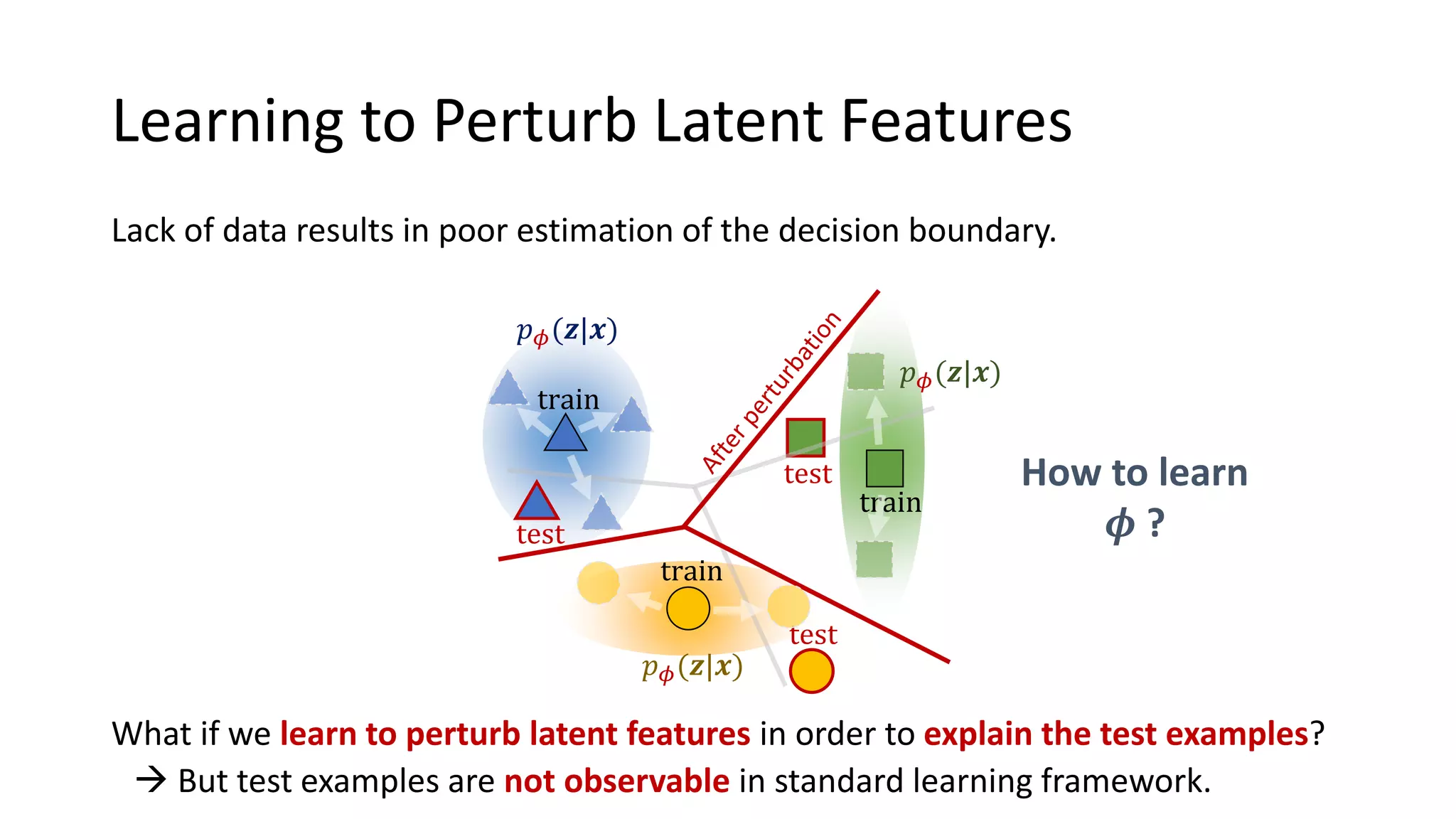
![Meta-Learning for few-shot classification
Meta Learning: Learn a model that can generalize over a task distribution!
Few-shot Classification
Knowledge
Transfer !
Meta-training
Meta-test
Test
Test
Training Test
Training
Training
: meta-knowledge
𝑝 𝜙(𝒛|𝒙)
[Ravi and Larochelle. 17] Optimization as a Model for Few-shot Learning, ICLR 2017](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metadropoutlearningtoperturbfeaturesforgeneralization-200529022020/75/Meta-Dropout-Learning-to-Perturb-Latent-Features-for-Generalization-8-2048.jpg)
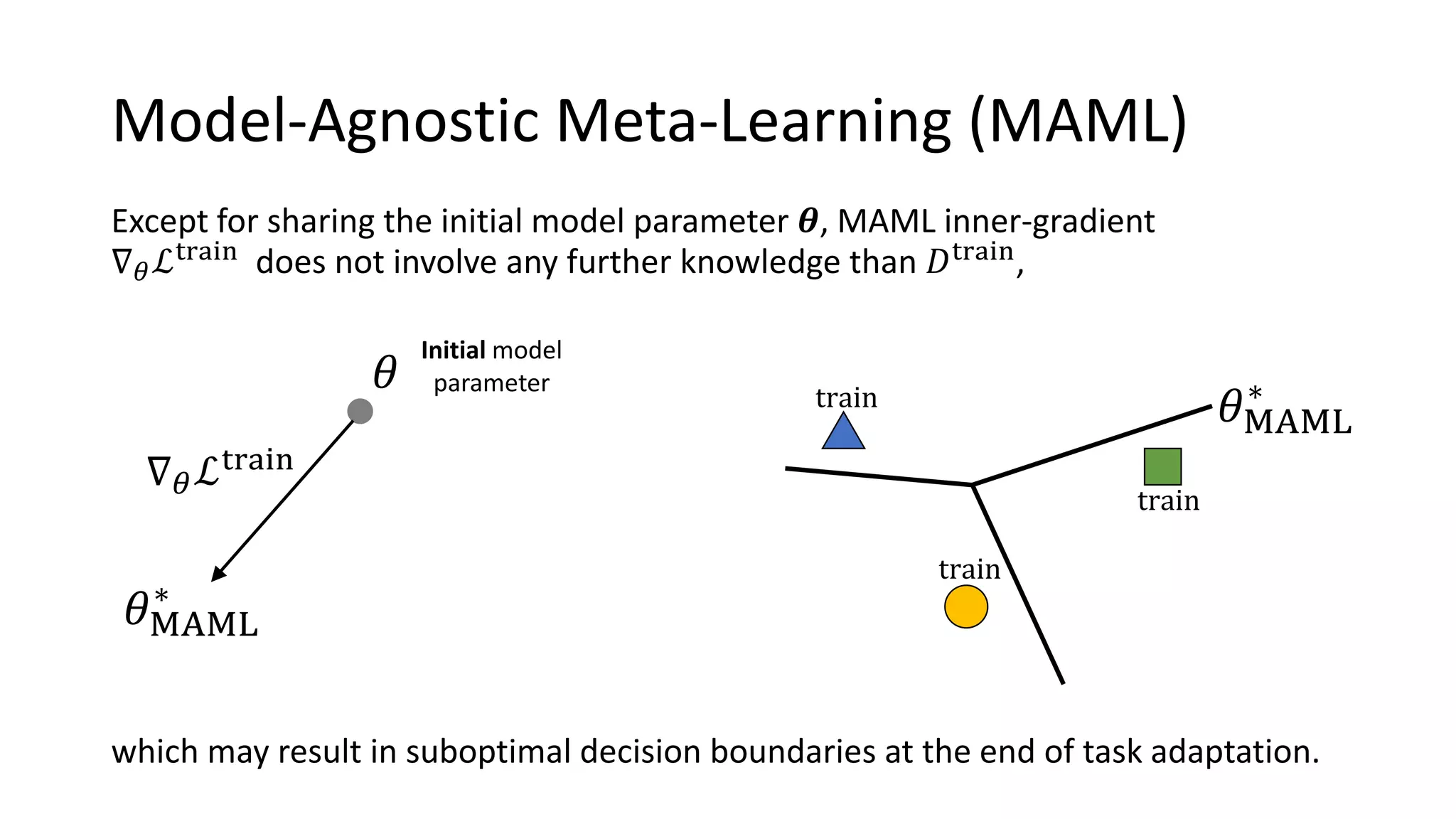
![Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML)
Model Agnostic Meta Learning (MAML) aims to find a good initial model
parameter that can rapidly adapt to any tasks only with a few gradient steps.
[Finn et al. 17] Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks, ICML 2017
Task-specific
parameter
Task-specific
parameter
Task-specific
parameter
Initial model
parameter
∇ℒ1
∇ℒ2
∇ℒ3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metadropoutlearningtoperturbfeaturesforgeneralization-200529022020/75/Meta-Dropout-Learning-to-Perturb-Latent-Features-for-Generalization-9-2048.jpg)
![Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML)
[Finn et al. 17] Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks, ICML 2017
Initial model
parameter
Task-specific
parameter
Task-specific
parameter
Task-specific
parameter
Task-specific parameter
for a novel task
∇ℒ∗
∇ℒ1
∇ℒ2
∇ℒ3
Model Agnostic Meta Learning (MAML) aims to find a good initial model
parameter that can rapidly adapt to any tasks only with a few gradient steps.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metadropoutlearningtoperturbfeaturesforgeneralization-200529022020/75/Meta-Dropout-Learning-to-Perturb-Latent-Features-for-Generalization-10-2048.jpg)