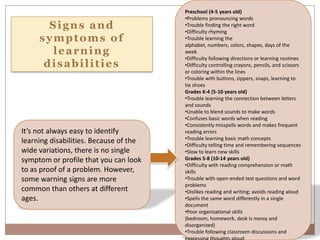
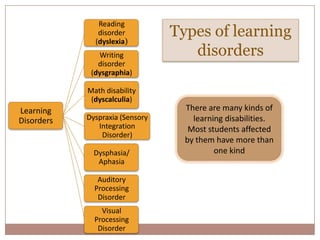
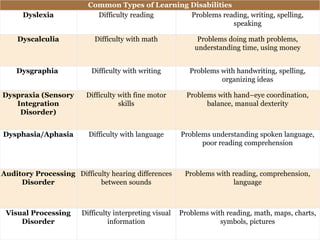
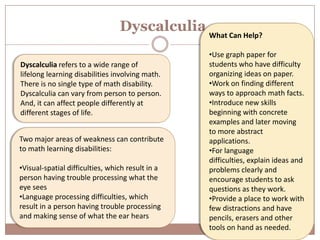
Learning disabilities are problems that affect the brain's ability to process or store information, making it difficult for students to learn as quickly as others. Common learning disabilities include dyslexia, affecting reading, writing and spelling; dyscalculia, affecting math skills; and dysgraphia, affecting writing abilities. Signs of learning disabilities vary by age but may include trouble with reading, writing, spelling, organizing ideas, math skills, and following instructions. While learning disabilities are lifelong, accommodations like structured learning, technology tools, and modifying assignments can help students succeed.