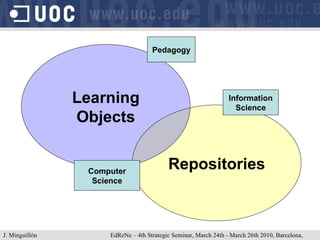
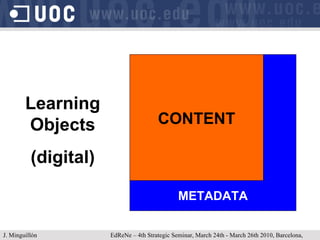
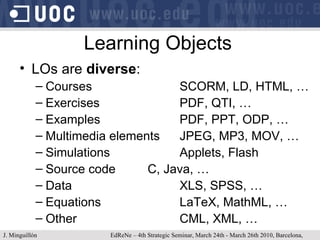
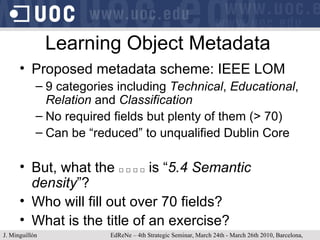
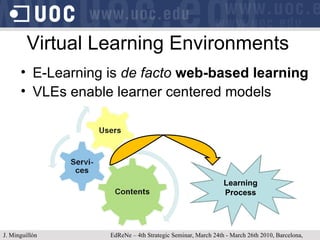
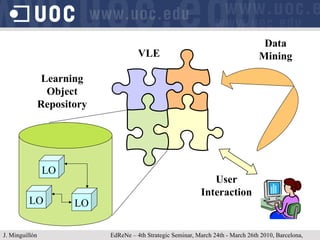
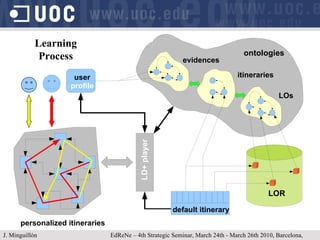
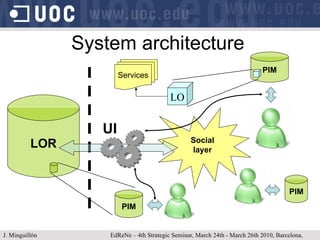
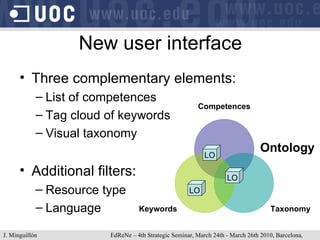
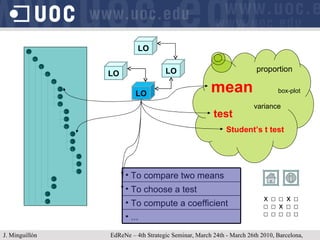
The document discusses learning object repositories from a learner-centered perspective. It addresses issues like describing learning objects with metadata, designing repositories to support learning and reuse of resources, and improving learner experience with repositories. The ideal learning object repository is envisioned as one that helps learners browse and organize resources, allows social interaction around resources, and gathers usage data to enhance the learning process. Improving existing repositories like DSpace to support these learner-centered goals is also discussed.





















![Thank you! Contact information: Julià Minguillón [email_address] CC-BY-NC-SA http://www.slideshare.net/jminguillona J. Minguillón EdReNe – 4th Strategic Seminar, March 24th - March 26th 2010, Barcelona, Spain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edrene2010minguillon-100323055632-phpapp01/85/Learning-Object-Repositories-a-learner-centered-perspective-32-320.jpg)