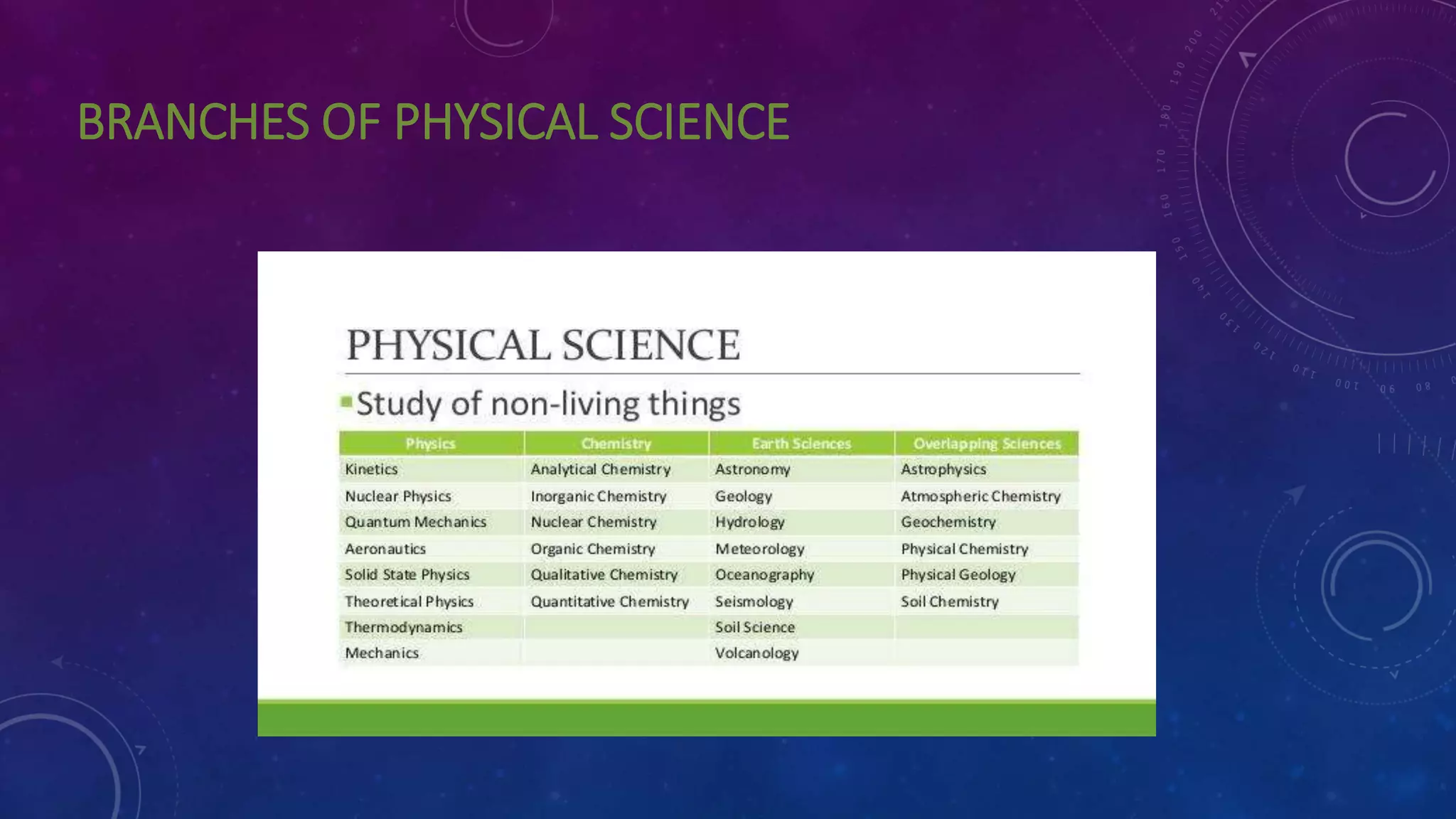
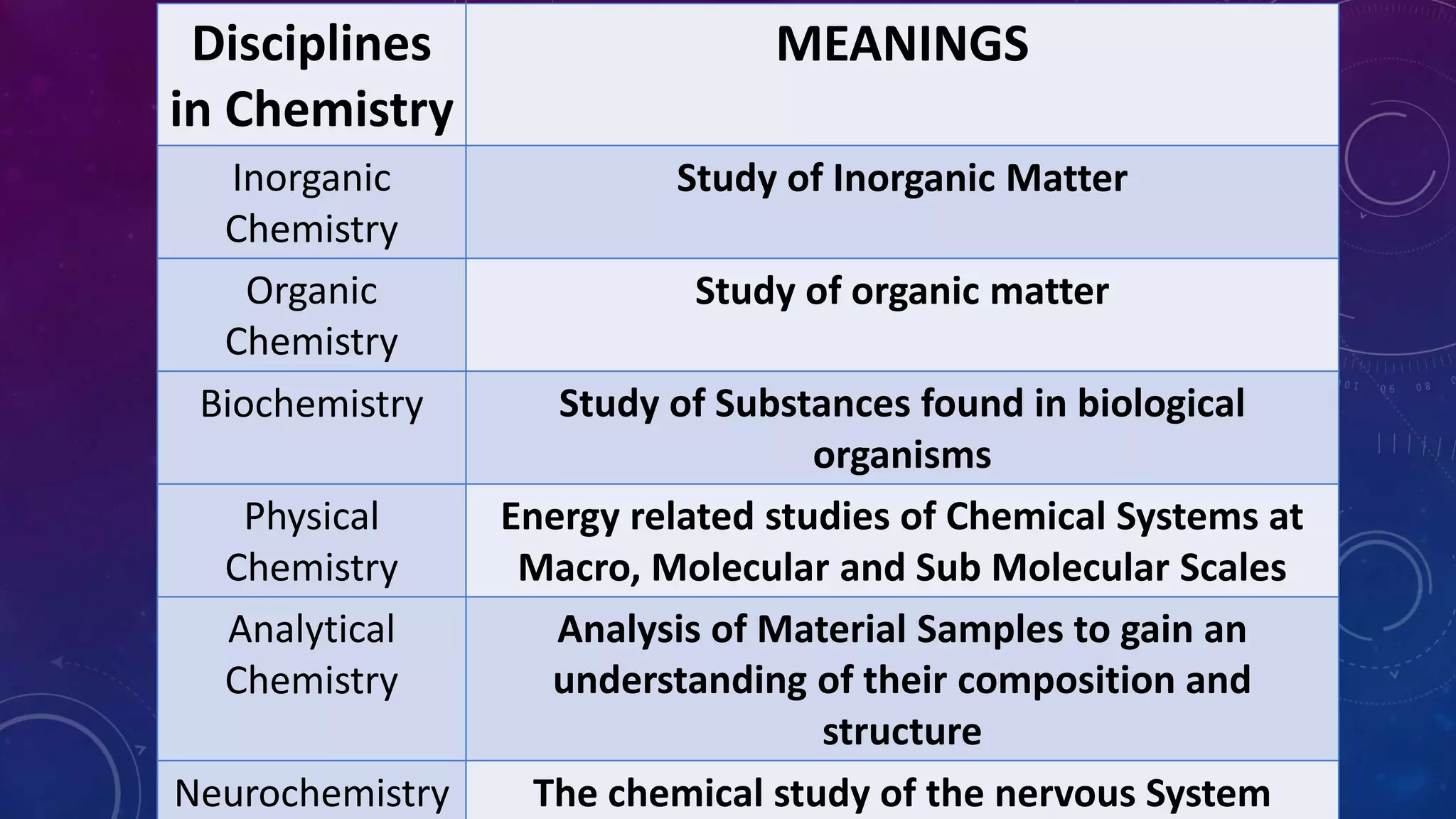
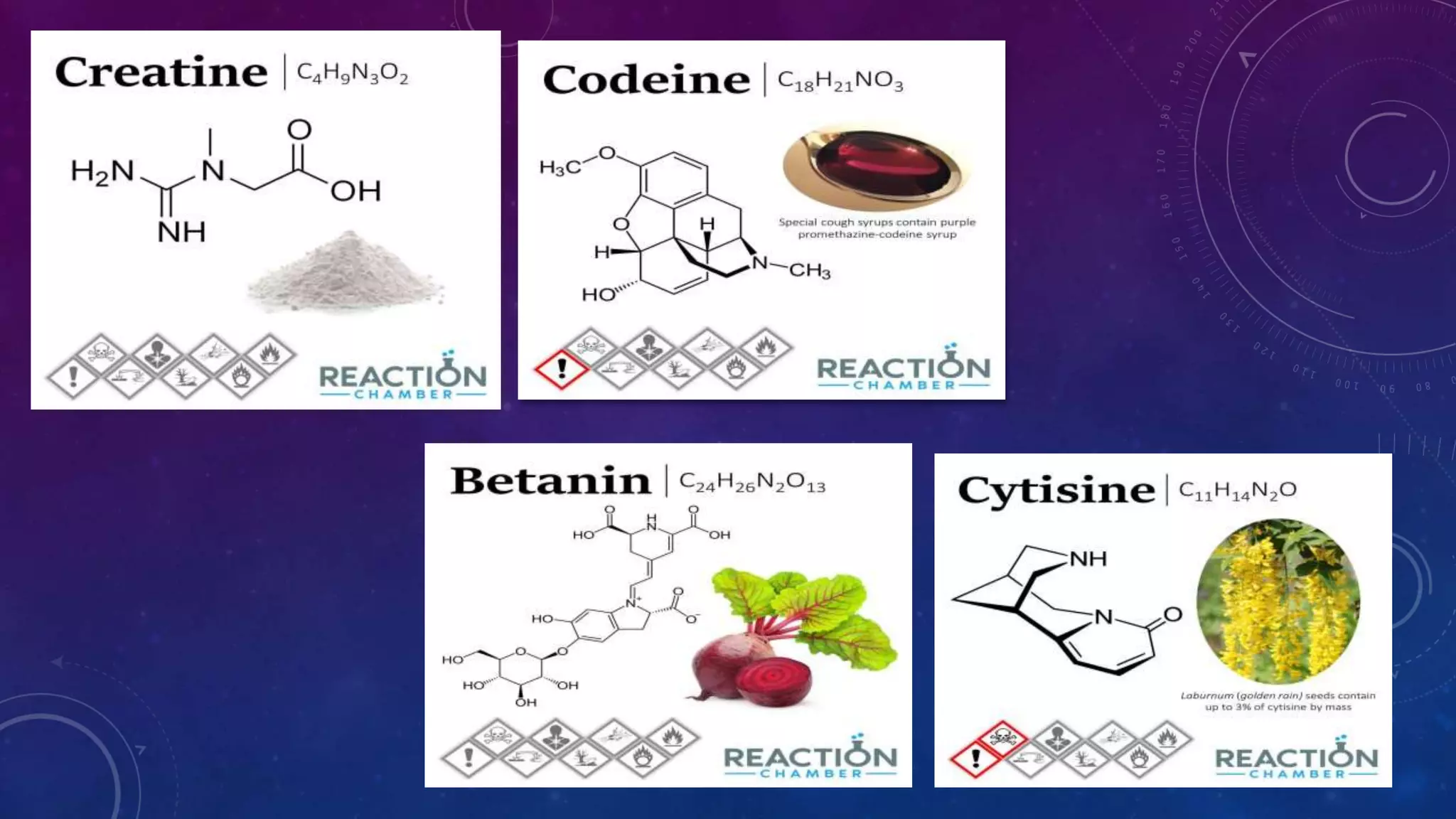
The document discusses the importance and scope of teaching physical science, emphasizing how it helps understand the natural world through observation and experimentation. It outlines the aims of teaching physical science and highlights the essential values—intellectual, utilitarian, vocational, moral, and cultural—associated with acquiring scientific knowledge. Overall, it argues for the significance of science education in fostering critical thinking and addressing contemporary societal needs.