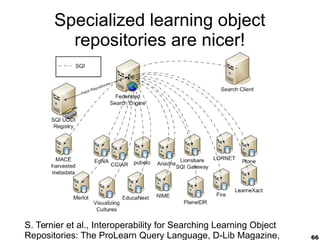
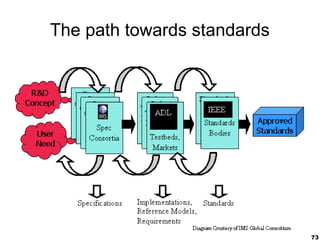
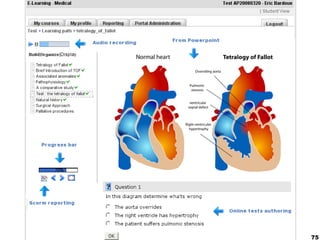
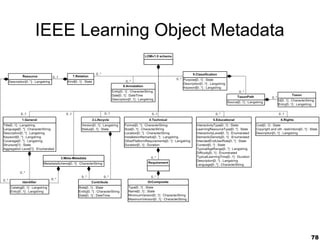
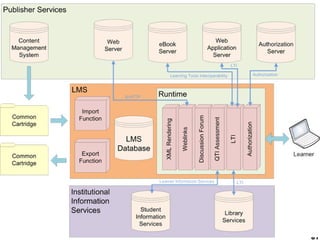
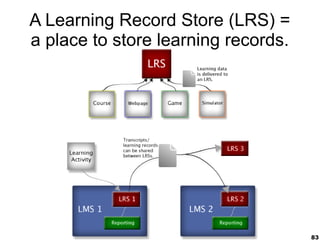
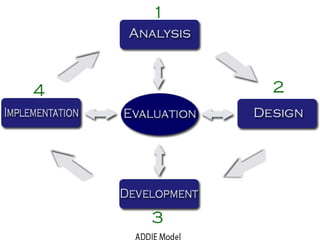
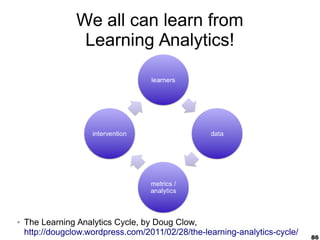
This document provides an overview of e-learning and open educational resources (OER) for libraries. It discusses how e-learning and OER can be useful for libraries and how libraries can help their organizations with e-learning and OER needs. It also covers challenges with textbooks costs, evolving models of e-learning, the role of standards in interoperability, and recommendations for libraries to promote openness through infrastructure, repositories, and integrating library resources with virtual learning environments.