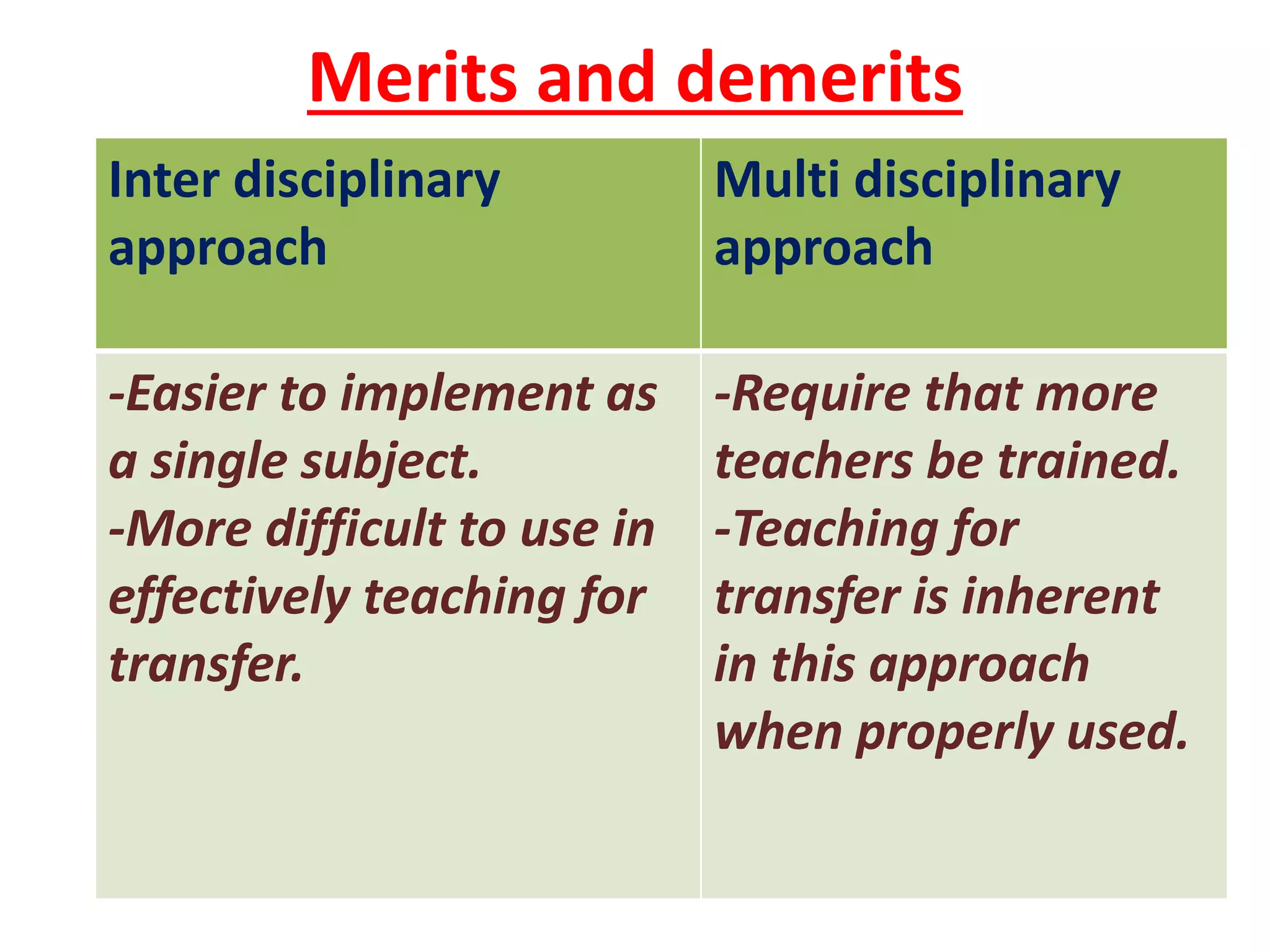
This document discusses two approaches to environmental education: infusion and problem solving. Infusion involves integrating environmental concepts into existing school subjects without changing the core content. Problem solving is a student-centered approach where students investigate and solve an environmental issue. It involves defining a problem, analyzing it, gathering information, developing solutions, and evaluating outcomes. Both approaches aim to transfer knowledge and skills to students to promote behavioral changes around environmental issues.