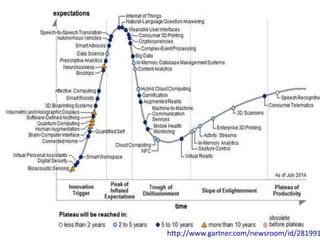
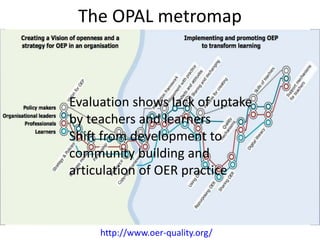
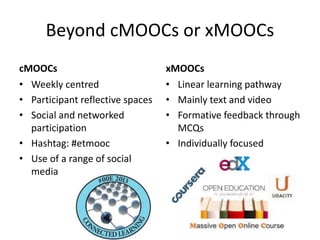
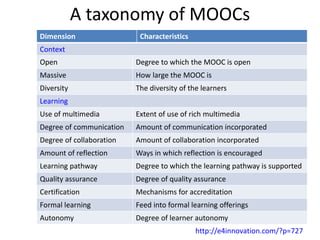
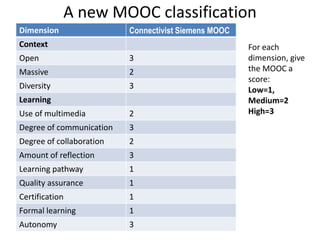
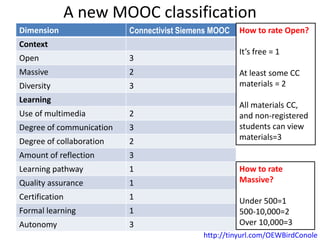
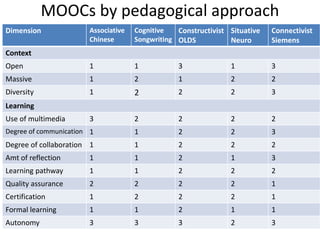
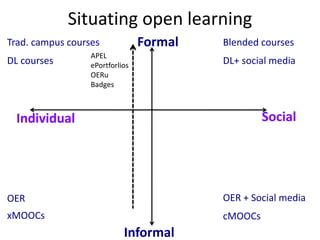
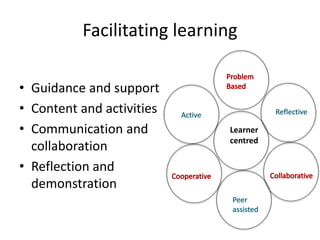
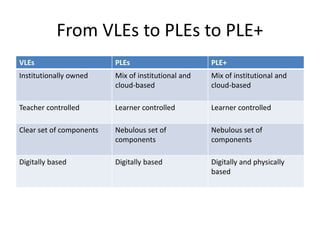
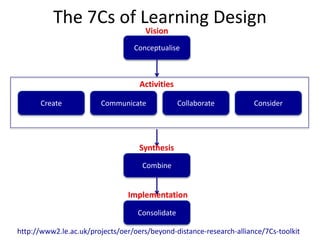
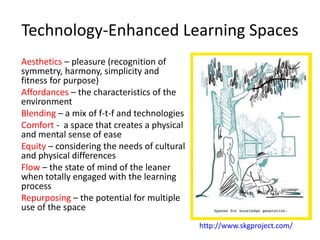
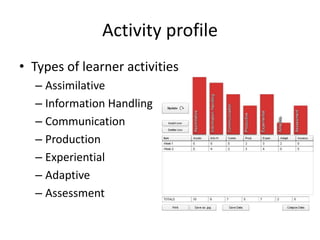
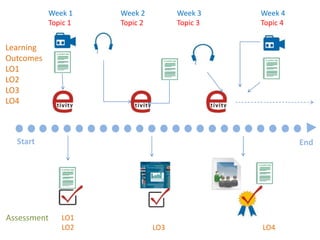
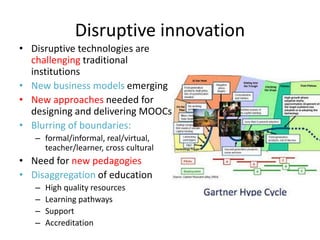
This document summarizes Gráinne Conole's presentation on disruptive learning innovations. The presentation discusses (1) disruptive technologies like MOOCs and their impact on education, (2) emerging learning innovations like the flipped classroom and mobile learning, (3) the shift from VLEs to more learner-controlled PLEs and PLE+, and (4) the need for new pedagogical approaches and learning designs to facilitate learning in changing environments.