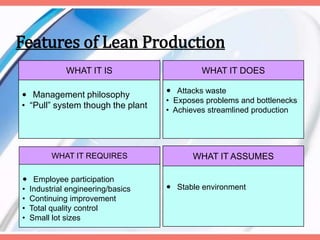
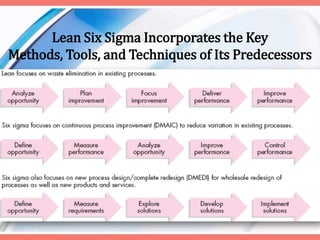
Lean production is an integrated approach aimed at high-volume production with minimal inventory and waste elimination. It emphasizes employee participation and continuous improvement, leveraging principles from the Toyota Production System. Key elements include waste reduction, quality control, and a respect for people through cooperative management and streamlined processes.