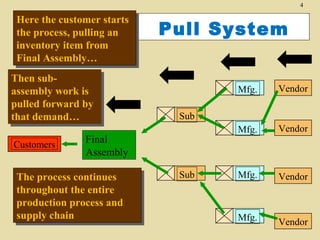
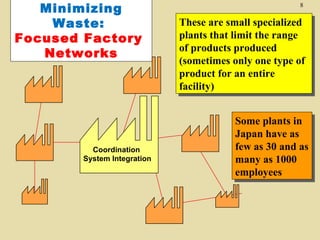
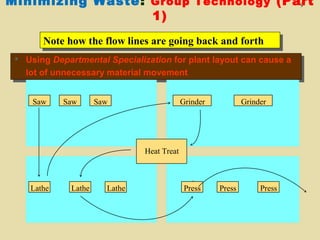
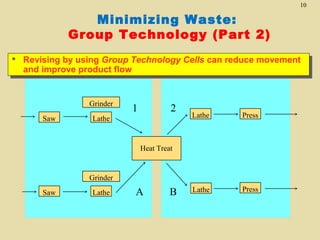
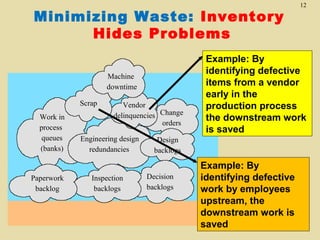
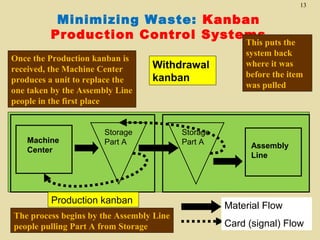
The document discusses lean production and the Toyota Production System. It defines lean production as using minimal inventories of raw materials, work in process, and finished goods while eliminating waste. The Toyota Production System is based on eliminating waste and respecting people. The seven types of waste are identified as overproduction, waiting time, transportation, processing, inventory, motion, and defects. Key aspects of lean implementation include value stream mapping, pull systems using kanban, continuous improvement, and respect for employees.




























/10=1050)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch12-jitleansystems-131122013821-phpapp01/85/Ch12-jit-lean-systems-35-320.jpg)
