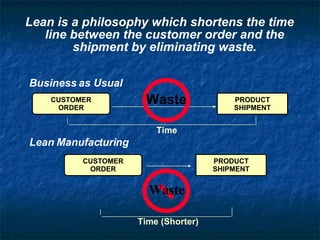
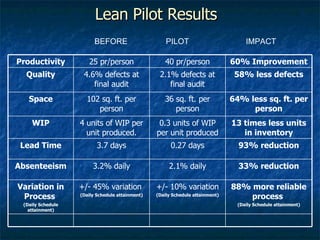
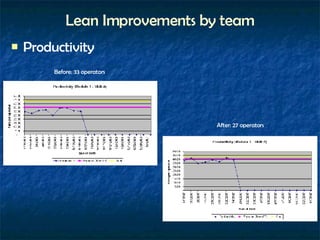
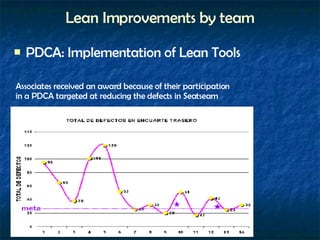
Lean manufacturing aims to eliminate waste and continually improve the flow of value to customers. It involves implementing tools like kanban, 5S, standardized work, and value stream mapping to shorten the timeline between a customer order and product shipment. Successful lean transformation requires leadership commitment, frequent communication, ongoing training, and establishing metrics to measure progress. Pilot projects demonstrate improvements in key areas like productivity, lead times, quality and space utilization through a lean approach.