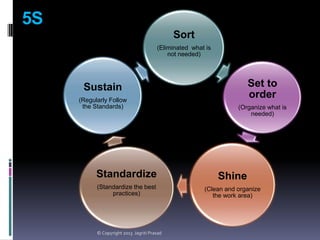
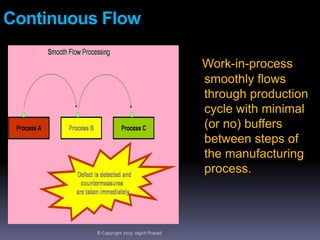
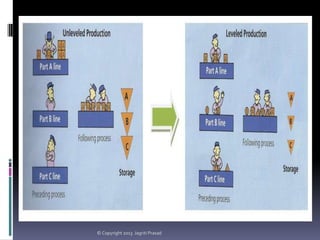
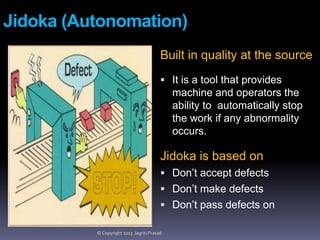
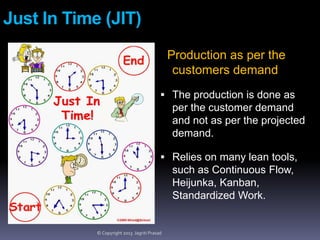
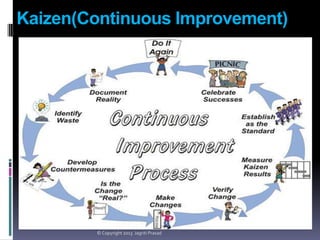
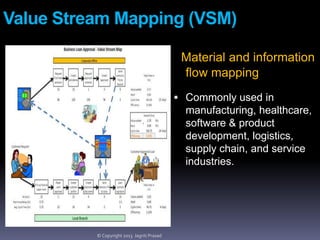
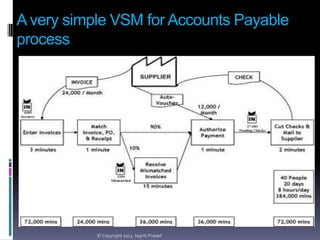
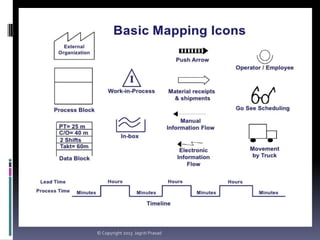
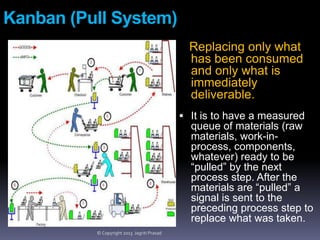
The document provides an overview of lean tools, focusing on their ability to identify and eliminate waste to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality in processes. Key tools discussed include 5S, continuous flow, heijunka, jidoka, just in time, kaizen, poka yoke, value stream mapping, key performance indicators, visual management, and kanban. A summary emphasizes the importance of maintaining clean work environments, automating processes, and tracking performance to achieve organizational goals.