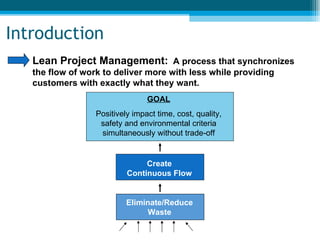
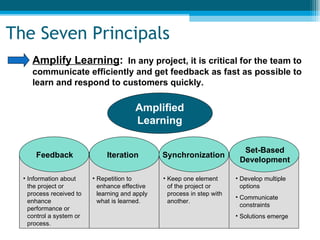
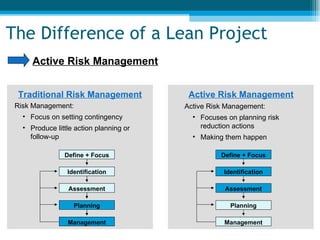
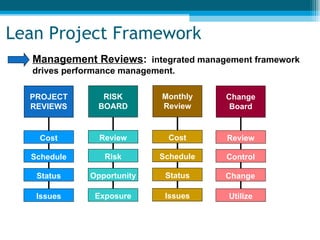
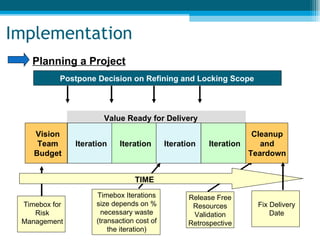
The document summarizes key aspects of lean project management. It discusses the seven principles of lean project management which include identifying and eliminating waste, amplifying learning, making decisions at the right time, fast delivery, empowering the team, building integrity, and seeing the whole. It also explains that lean project management focuses on synchronizing workflow to deliver more with less while providing customers exactly what they want. Implementation involves defining and focusing the project, identifying and assessing risks and opportunities, planning risk reduction actions, and ongoing management reviews.