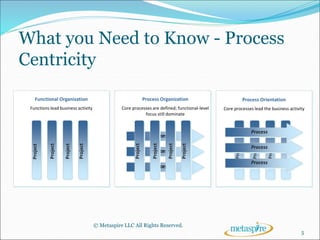
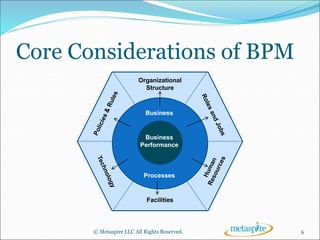
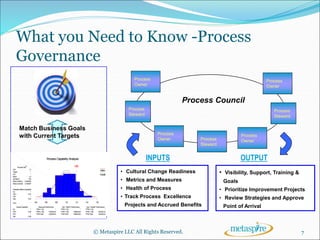
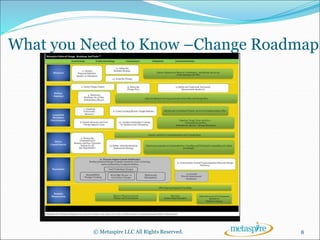
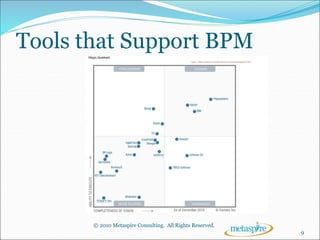
This document outlines the key topics to be covered in a course on business process management (BPM). It will introduce BPM and discuss its core components, what is needed to implement a successful BPM program, and the tools that support BPM. The course will define BPM, explain the importance of process-centricity in organizations, and cover considerations like organizational structure, business processes, and business performance that are at the core of BPM. It will also address the need for process governance and change management in BPM.


![Introduction
Business process management (BPM) is a management approach focused on
aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. It is a
holistic management approach [1] that promotes business effectiveness and
efficiency while striving for innovation, flexibility, and integration with technology.
Business process management attempts to improve processes continuously. It
could therefore be described as a "process optimization process." It is argued that
BPM enables organizations to be more efficient, more effective and more capable
of change than a functionally focused, traditional hierarchical management
approach. – Wiki
Business process management provides governance of a business's process
environment to improve agility and operational performance. – Gartner Group
BPM: the discipline that improves measurable business performance for
stakeholders, through ongoing optimization and synchronization of enterprise-
wide process capabilities. – The BPM Group
© Metaspire LLC All Rights Reserved.
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bpmteaser-200618201530/85/Bpm-teaser-3-320.jpg)