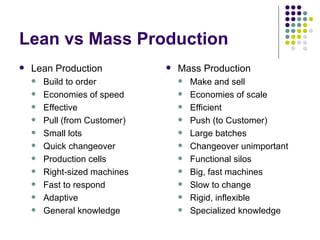
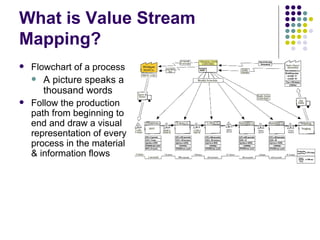
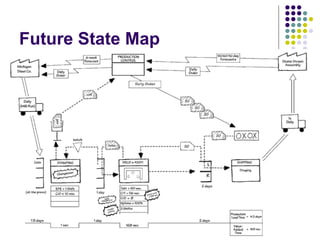
The document outlines the objectives and accomplishments of a lean manufacturing case study, focusing on improving customer service, reducing waste, and enhancing operational efficiency. Key concepts include eliminating non-value-added activities, employing lean tools such as the six s’s and value stream mapping, and integrating a culture of continuous improvement. Lessons learned highlight the positive impacts of these practices on team mindset, profitability, and customer satisfaction, while also identifying areas for further refinement.