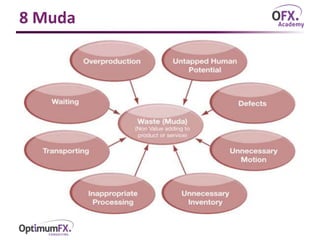
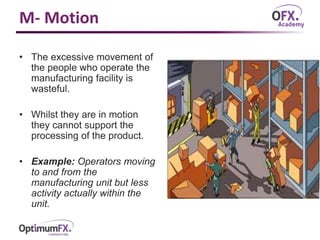
The document outlines the 8 types of waste (muda) in production processes: transport, inventory, motion, people, waiting, overproduction, overprocessing, and defects. Each waste is defined and an example is given to illustrate how it does not add value to the customer and is therefore wasteful. The 8 wastes framework aims to identify and eliminate non-value adding activities in operations.