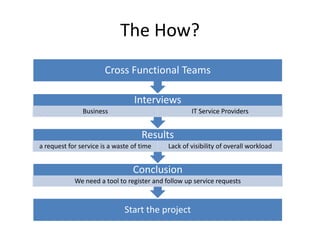
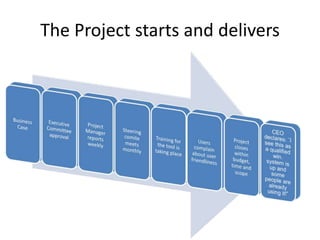
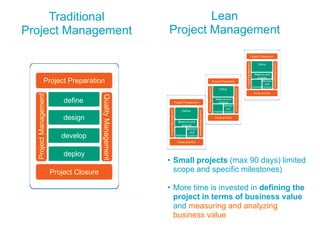
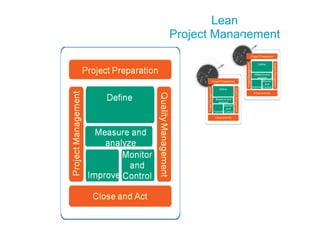
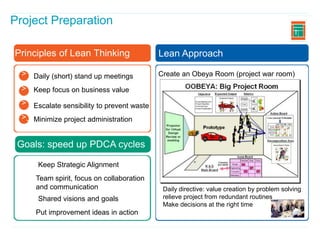
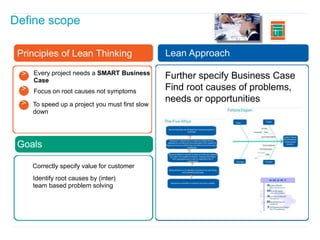
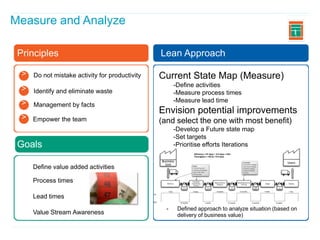
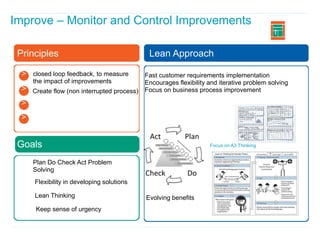
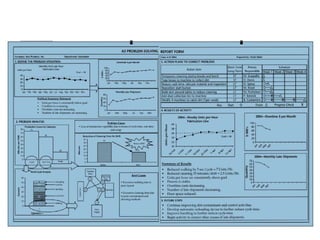
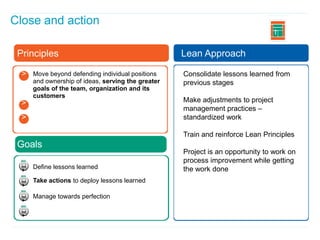
This document discusses how applying lean principles can improve project management. It defines lean project management as emphasizing iterative discovery, problem solving, value delivery, and eliminating waste. This leads to improved quality, reduced timelines and costs. Key lean project management principles include focusing on customer value, eliminating waste, empowering cross-functional teams, and using visual management. Adopting lean requires changes like defining projects based on business value, measuring current processes, setting targets for improvements, and learning lessons to update practices. The benefits are faster value delivery, improved cash flow, increased agility, and higher success rates.