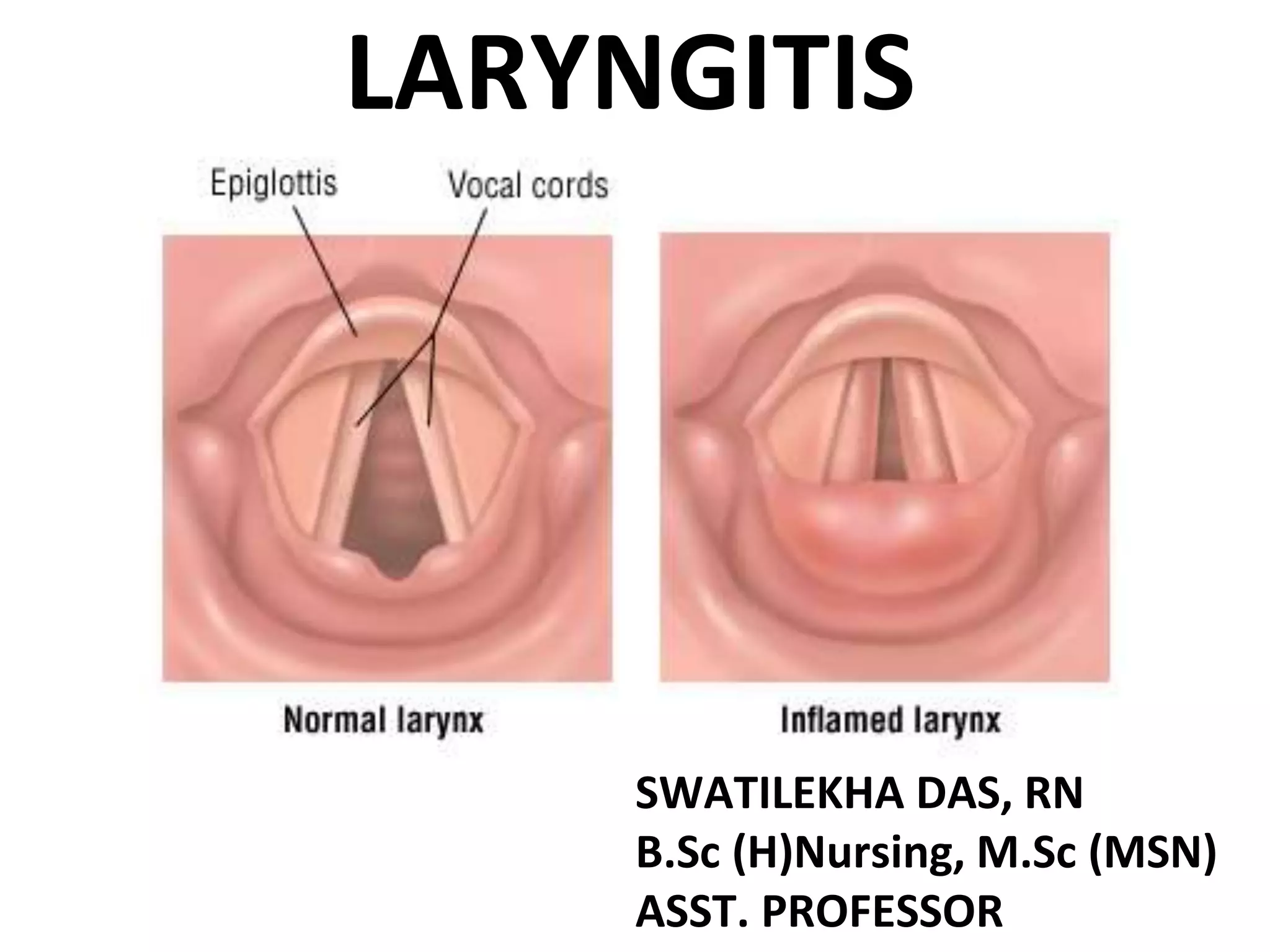
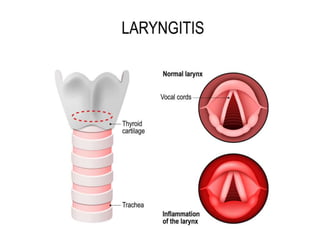
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx primarily caused by viral infections, voice abuse, or exposure to pollutants. Symptoms include hoarseness, cough, and possible dyspnea, with treatment focused on voice rest, avoiding irritants, and managing underlying infections or allergies. Most patients recover with conservative care, although severe cases may require additional medical interventions.