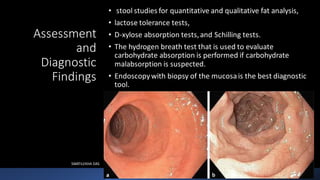
Malabsorption occurs when the digestive system is unable to absorb one or more nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Interruptions anywhere along the digestive tract can cause decreased absorption. Diseases of the small intestine are a common cause of malabsorption. Diagnostic tests include stool studies, lactose tolerance tests, D-xylose absorption tests, Schilling tests, and hydrogen breath tests to evaluate specific nutrient absorption. Biopsies of the small intestine can identify damage, infections, or tumors. Treatment focuses on supplementing lost nutrients and managing any underlying diseases through diet, medication, surgery, or antibiotics. Nurses educate patients and monitor for fluid and electrolyte imbalances, assessing

![Medical Management
• Intervention is aimed at avoiding dietary substances that aggravate
malabsorption and at supplementing nutrients that have been lost.
• Common supplements are water-soluble vitamins (eg, B12, folic acid), fat-
soluble vitamins (ie, A, D, and K), and minerals (eg, calcium, iron).
• Primary disease states may be managed surgically or nonsurgically.
• Dietary therapy is aimed at reducing gluten intake in patients with celiac sprue.
Folic acid supplements are prescribed for patients with tropical sprue.
• Antibiotics (eg, tetracycline [Tetracyn], ampicillin [Polycillin]) are sometimes
needed in the treatment of tropical sprue and bacterial overgrowth syndromes.
• Antidiarrheal agents may be used to decrease intestinal spasms. Parenteral
fluids may be necessary to treat dehydration.
SWATILEKHA DAS
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/malabsorptionsyndrome-210217203100/85/Malabsorption-syndrome-6-320.jpg)