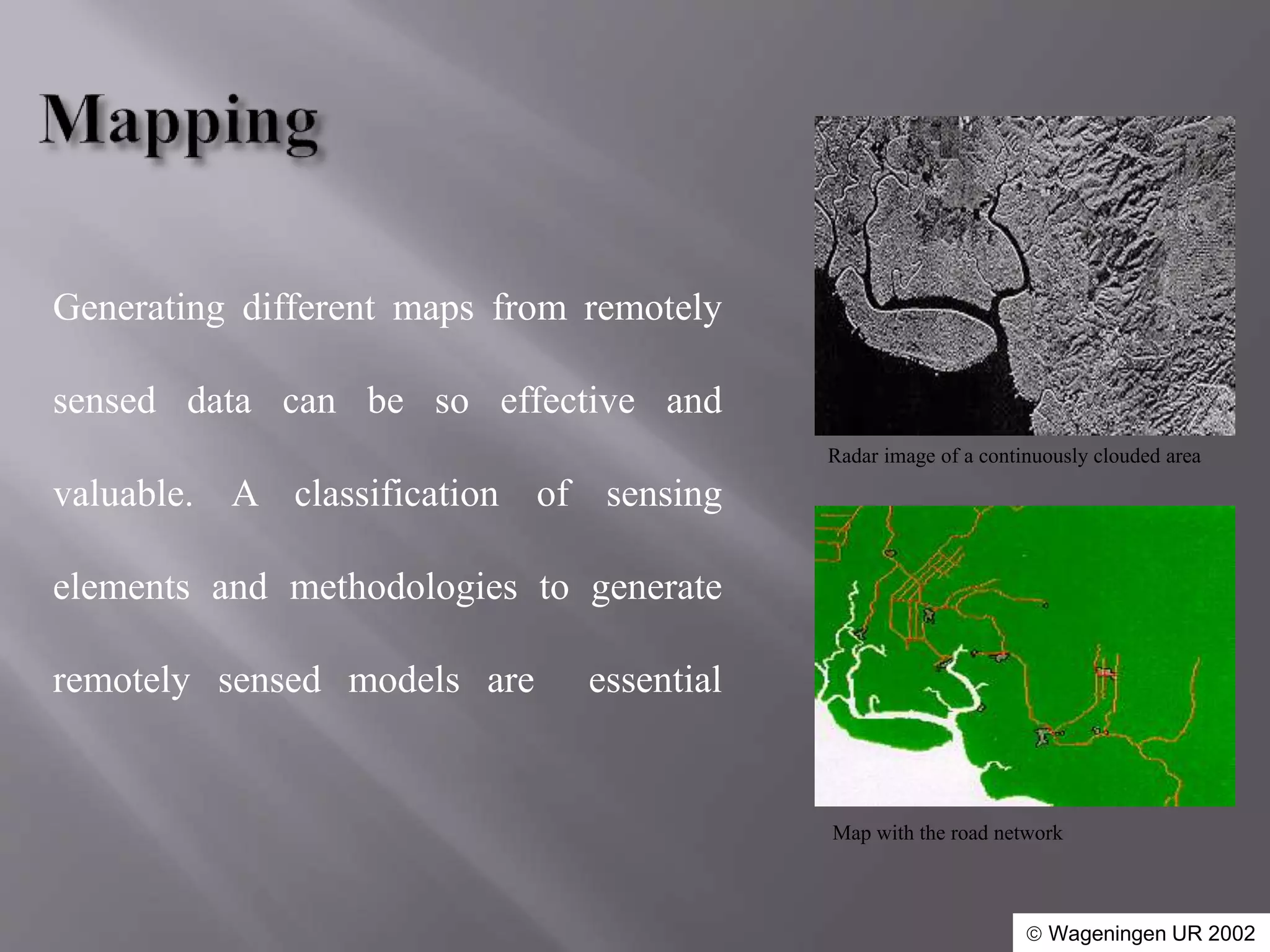
Remote sensing allows obtaining information about objects on Earth without direct physical contact. It has various applications in agriculture, forestry, urban planning, transportation, land use mapping, natural resource management, and coastal resource mapping. Remote sensing can be used to map and monitor soil conditions, crop growth, forest resources, urban expansion, roads, land use, water resources, habitats, and coastal changes over time. The data obtained through remote sensing provides valuable spatial information to support decision making and planning in various sectors.