Embed presentation
Download to read offline


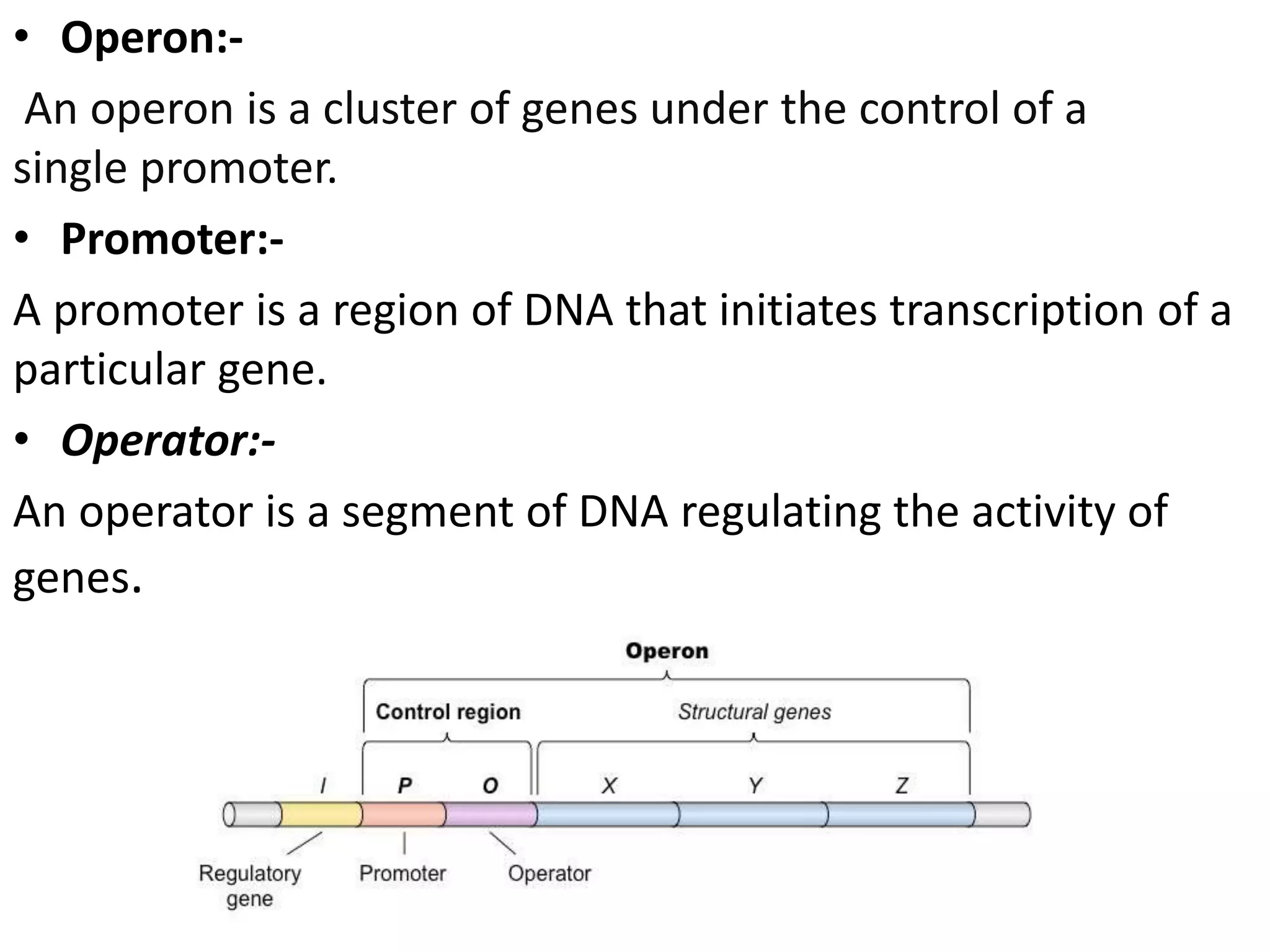

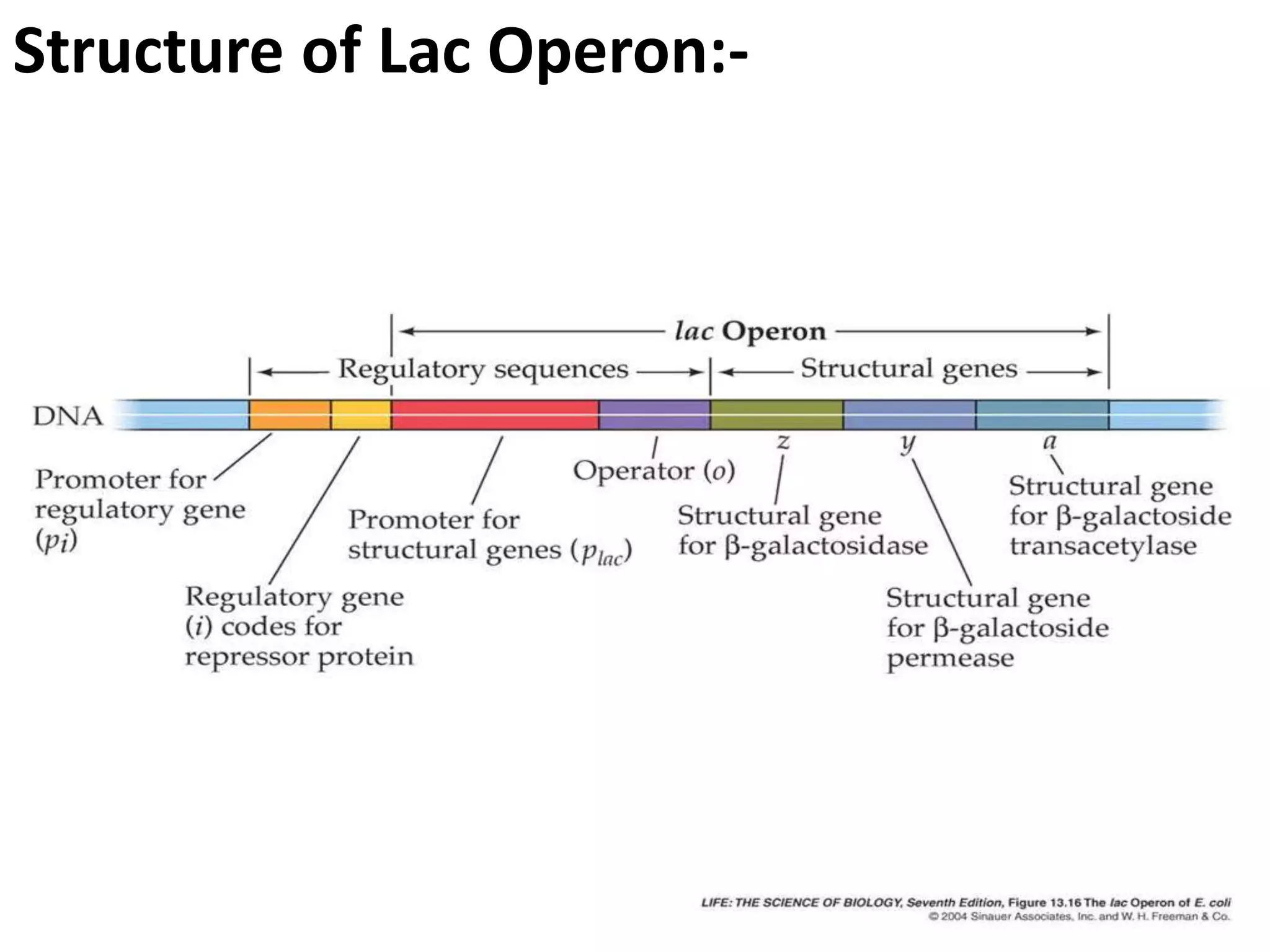

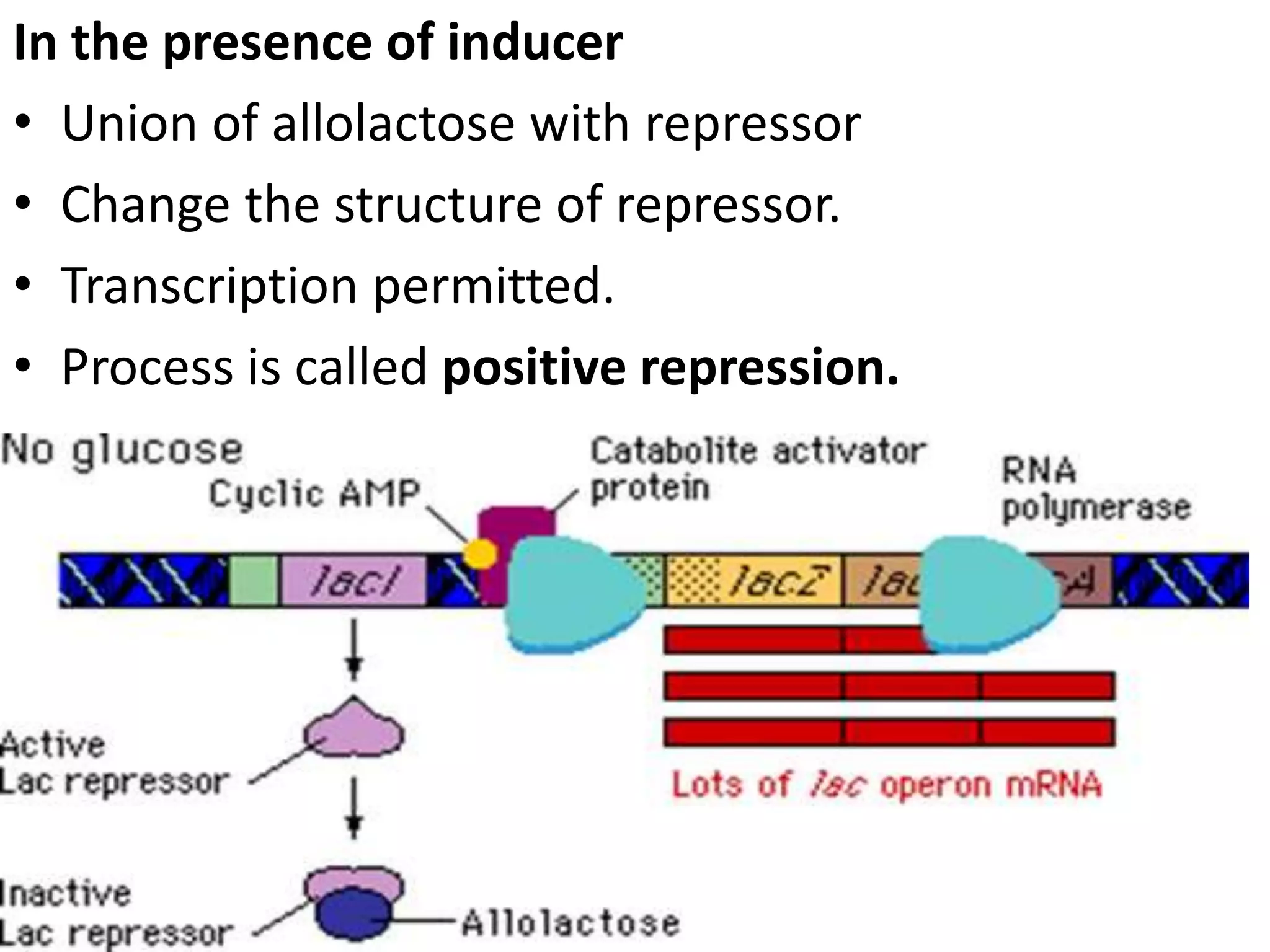




The lac operon controls genes involved in lactose transport and metabolism in E. coli. It contains three genes - lacZ, lacY, and lacA - that are regulated by a single promoter. The lac repressor protein binds to the operator region between the promoter and genes, inhibiting transcription in the absence of the inducer allolactose. When allolactose is present, it binds to the repressor and causes a configuration change that allows transcription of the genes and expression of beta-galactosidase, beta-galactoside permease, and beta-galactoside transacetylase. This classic model of operon regulation was discovered by François Jacob and Jacques Monod in their work










