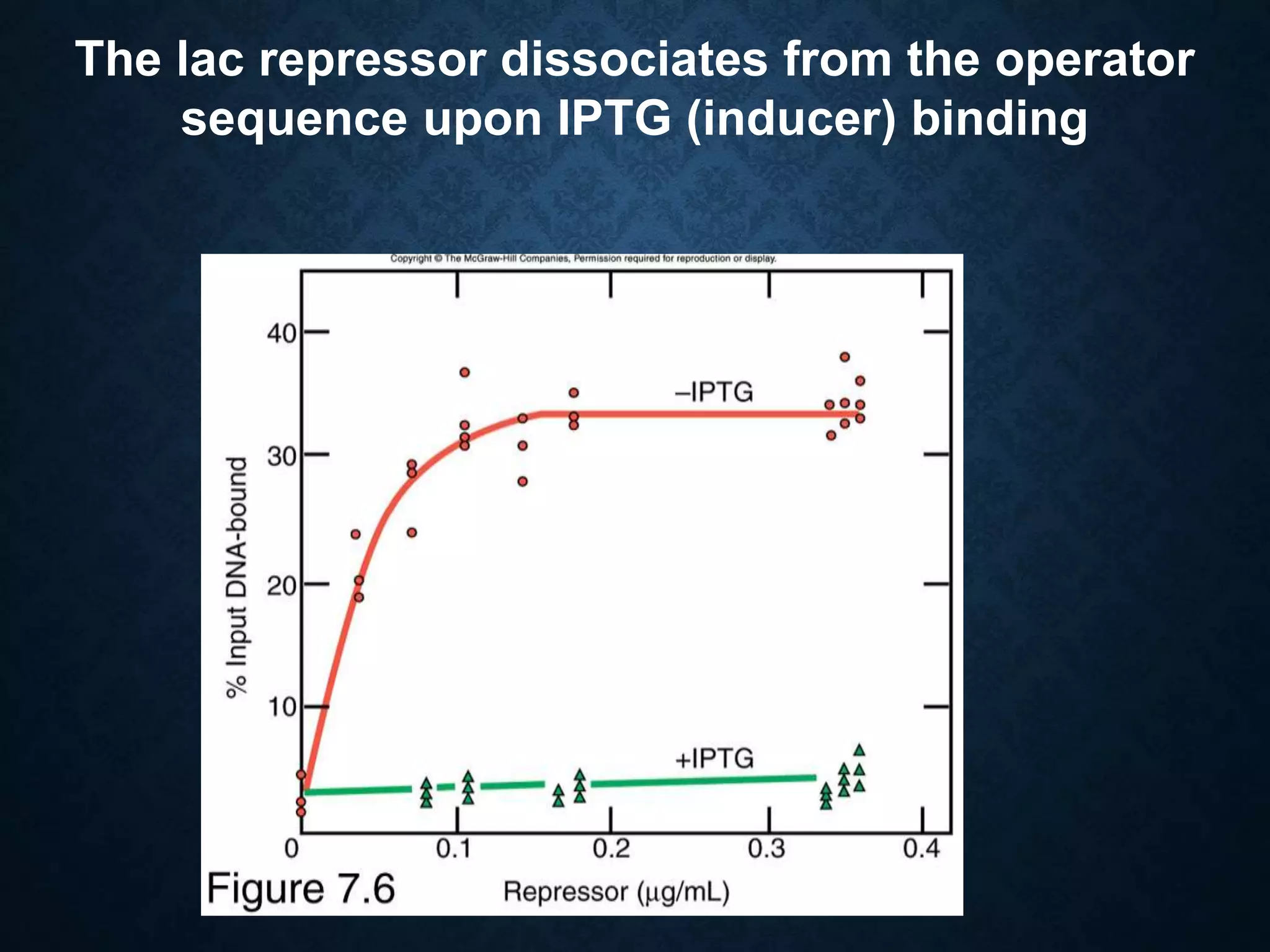
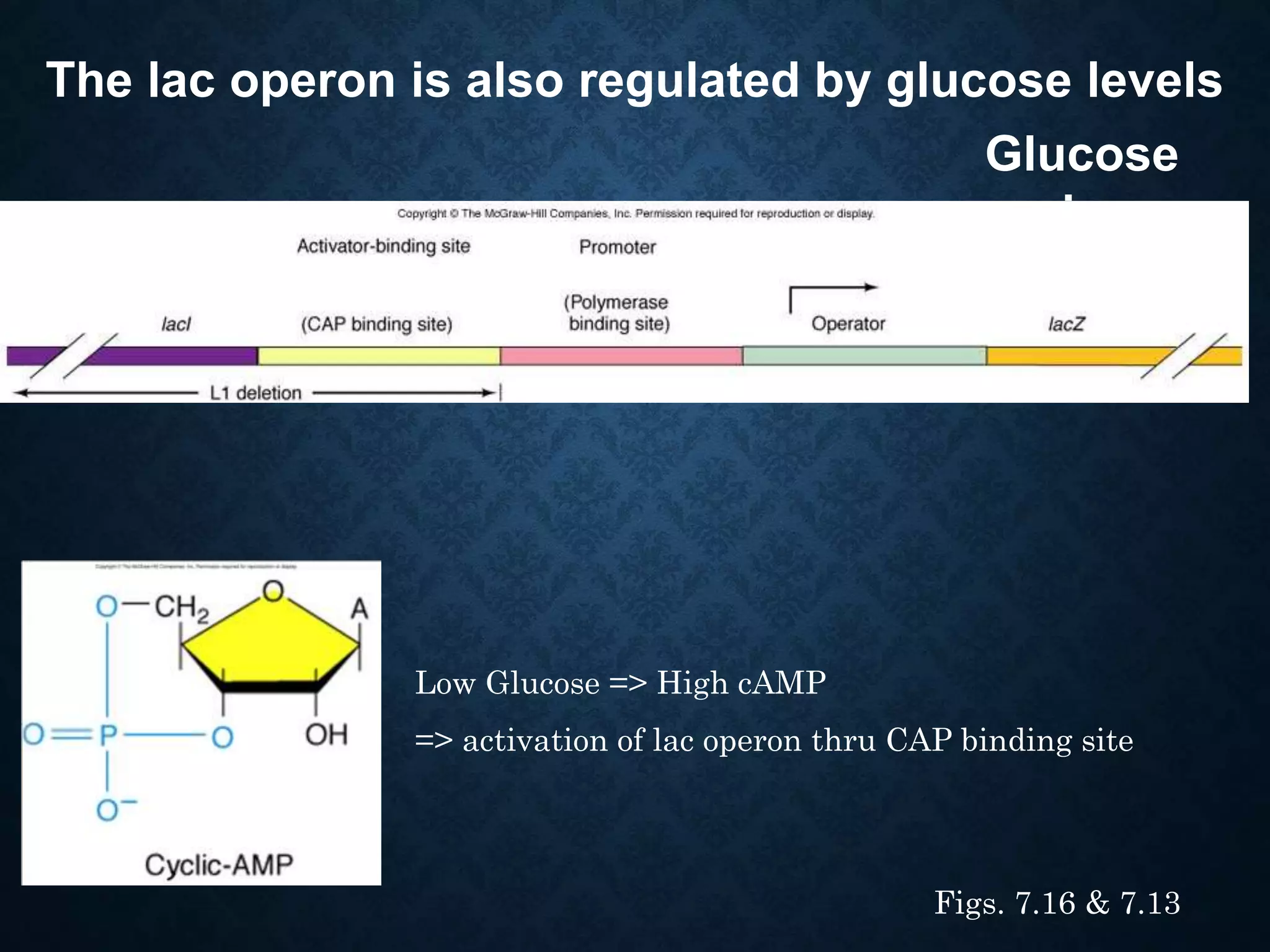
1. The lac operon regulates genes involved in lactose metabolism in E. coli and is controlled by both negative and positive regulation. It is negatively regulated by a repressor protein and positively regulated by the cAMP receptor protein binding to DNA when glucose levels are low.
2. The trp operon regulates genes for tryptophan biosynthesis in bacteria and is negatively regulated by tryptophan levels. High tryptophan levels activate the trp repressor protein, turning off transcription.
3. Catabolite repression is a form of positive regulation where high glucose levels reduce cAMP and cAMP receptor protein binding, decreasing transcription of other operons like the lac operon.