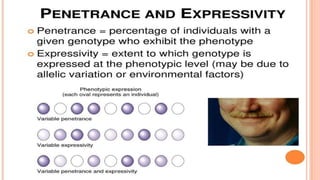
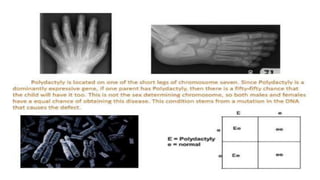
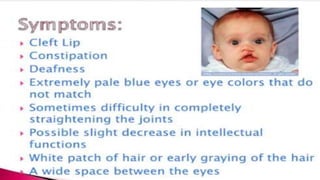
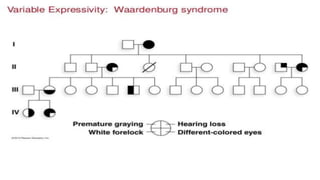
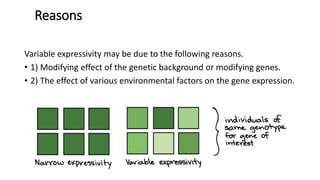
The document discusses expressivity, describing it as the degree to which trait expression varies among individuals with the same genotype. It contrasts penetrance, which measures the frequency of phenotype generation, with expressivity's focus on qualitative or quantitative variation. Examples include uniform and variable expressivity, with the latter illustrated by conditions like Waardenburg syndrome and neurofibromatosis, highlighting how genetic and environmental factors influence phenotypic outcomes.