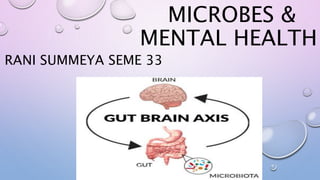
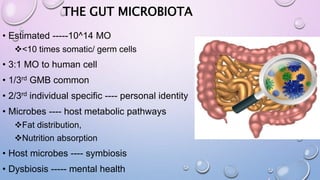
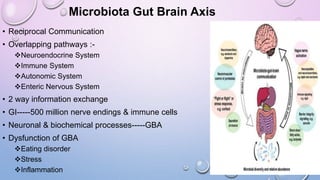
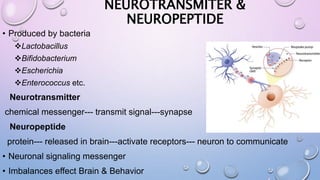
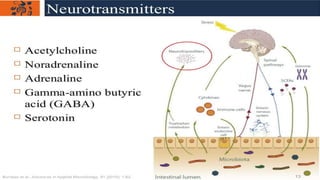
This document outlines the microbiota-gut-brain axis and its influence on mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. It discusses how gut microbes communicate with the brain through pathways like the vagus nerve, immune system, and neurotransmitters. Certain microbes can produce neurotransmitters like GABA and serotonin that impact brain functions related to mood. Imbalances in the gut microbiome through factors like stress, antibiotics, and diet have been linked to mental health issues by disrupting this axis. Future research aims to better understand these relationships and develop microbiome-targeted treatments and preventions.