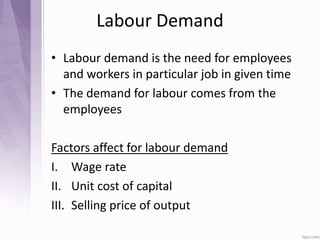
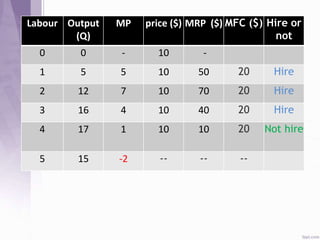
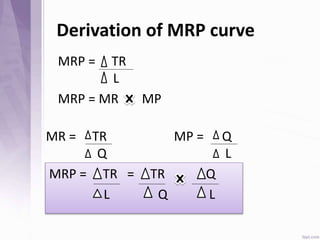
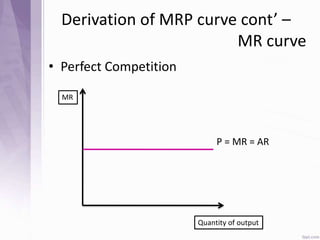
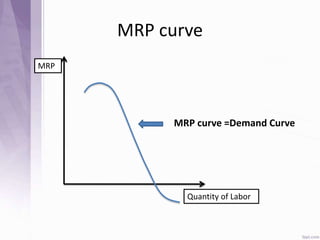
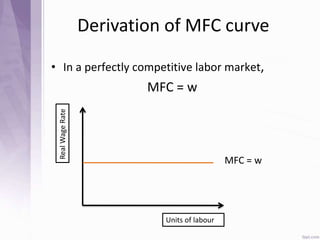
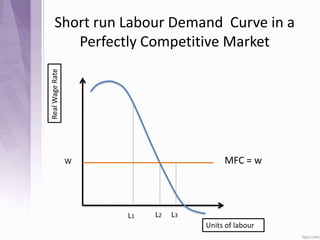
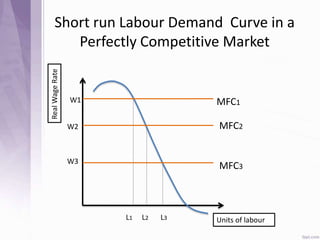
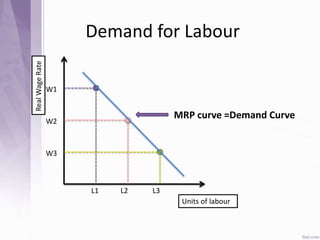
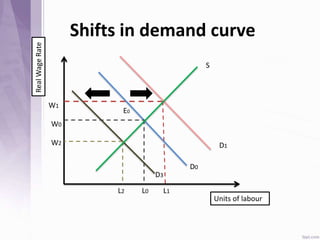
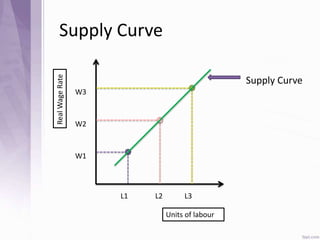
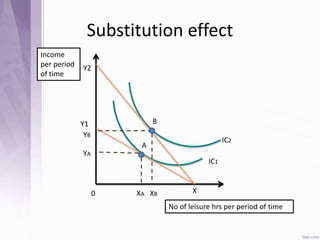
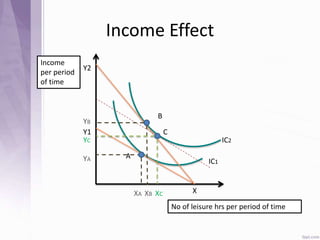
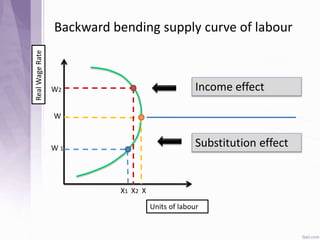
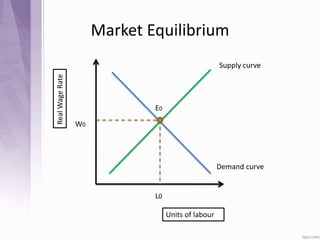
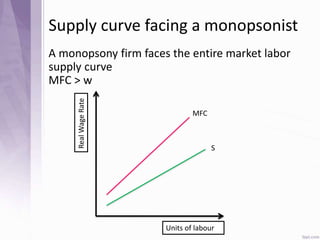
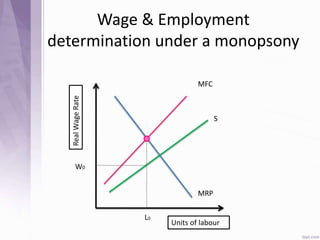
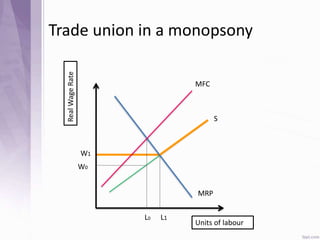
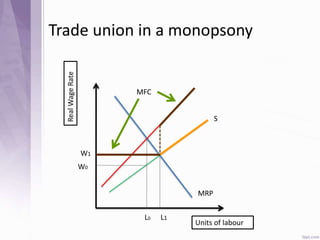
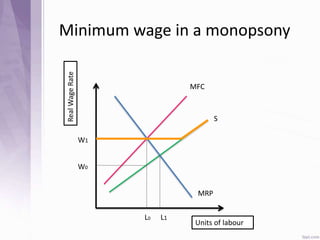
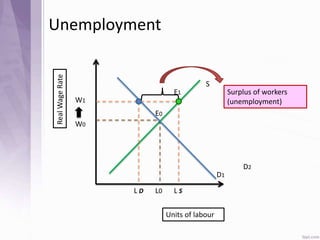
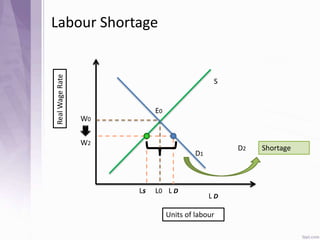
This document provides an introduction to labour economics. It discusses key concepts such as labour demand and supply, and how they interact in the labour market to determine equilibrium wage and quantity. Labour demand comes from firms and is affected by the wage rate, capital costs and output prices. Firms will maximize profits by hiring workers up to the point where marginal revenue product equals marginal factor cost. Labour supply depends on wages as well as income and substitution effects. The interaction of labour demand and supply curves results in the equilibrium wage and employment level in the market. Monopsony and factors like unions, minimum wages can impact the wage-employment relationship. Unemployment may occur if demand shifts leftward resulting in a surplus of workers.