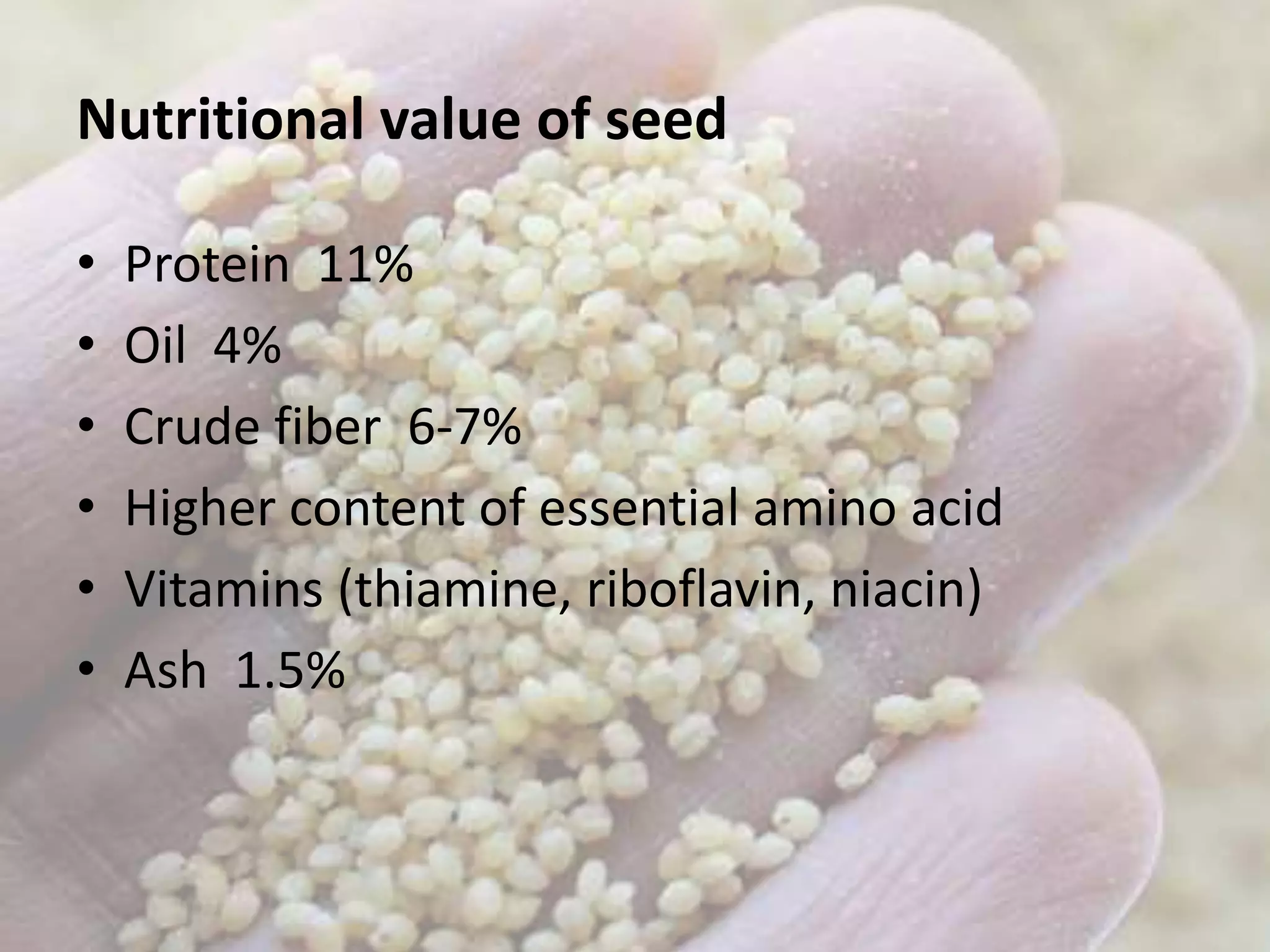
Thana haal (Setaria italica) is one of the oldest cultivated crops, primarily grown in countries such as China, India, and Indonesia, yielding around 800-900 kg/ha, with potential exceeding three tons per hectare. This C4 warm-season annual plant is used for food, animal feed, and in erosion control, and has nutritional benefits including high protein and vitamin content. Its cultivation requires specific ecological conditions and practices, including proper irrigation and pest management.