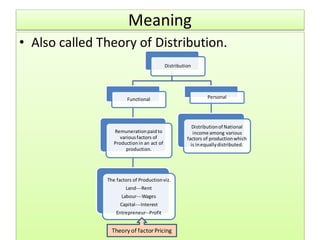
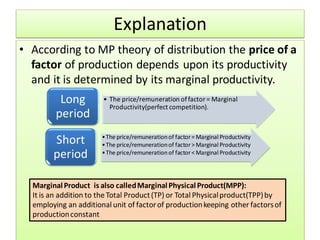
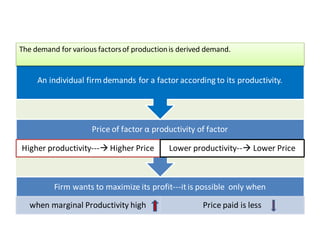
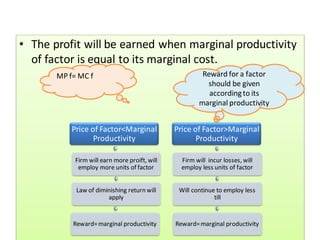
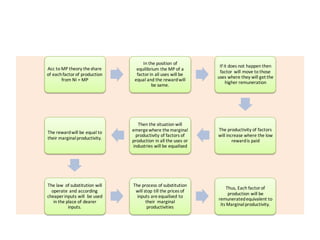
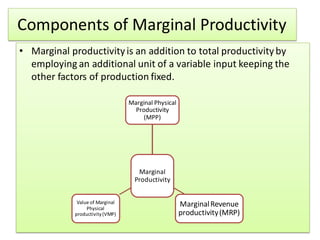
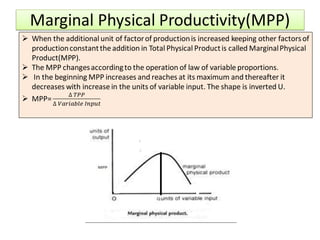
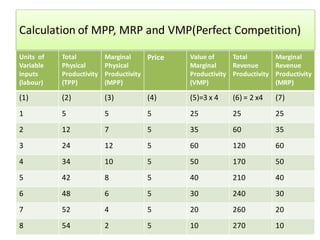
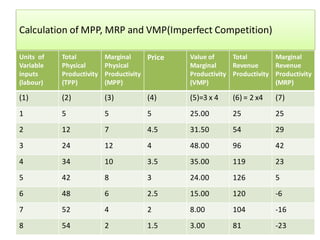
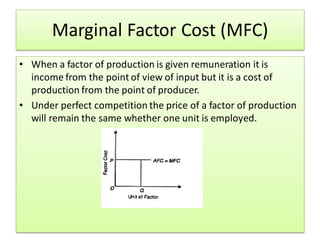
The document discusses factor pricing and the theory of distribution, focusing on how the remuneration for various production factors (land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship) is determined by their marginal productivity. It explains concepts such as marginal revenue productivity and the conditions for equilibrium among factors, while also highlighting the assumptions and criticisms of the theory. Overall, the material emphasizes the relationship between productivity and income distribution among factors of production.