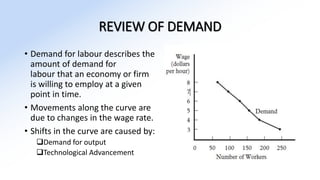
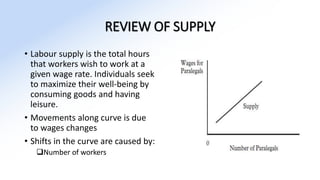
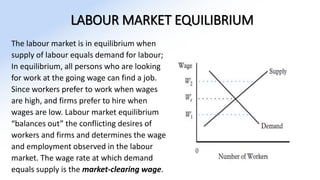
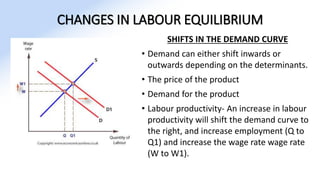
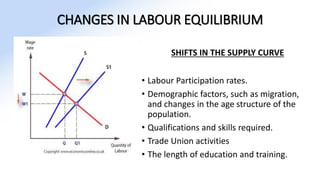
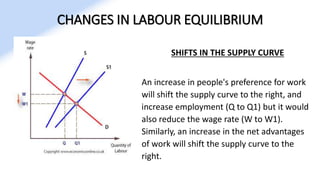
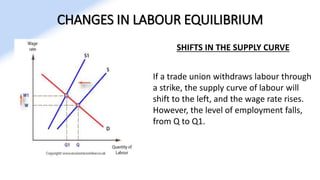
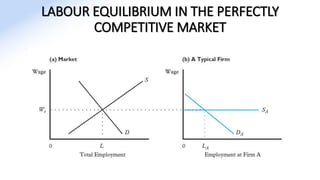
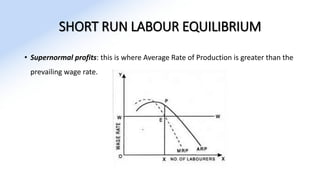
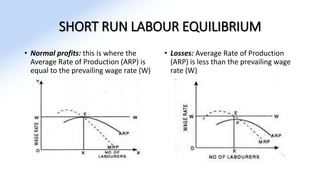
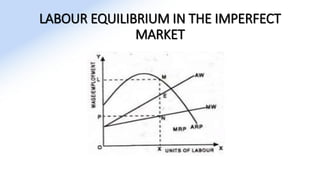
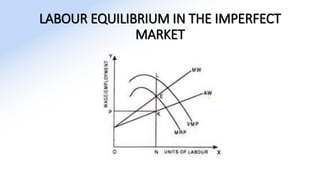
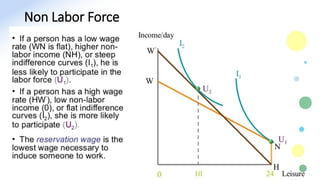
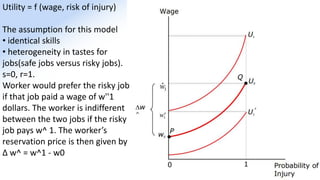
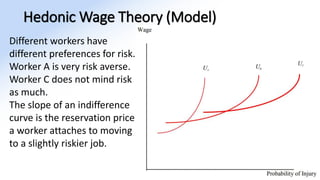
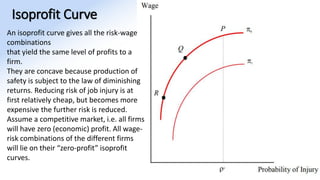
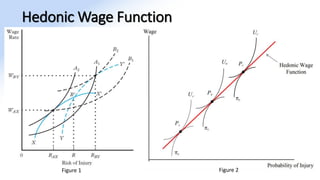
The document discusses various aspects of labor market equilibrium, including demand and supply dynamics, equalizing differentials, and occupational choices. It highlights the conditions under which the labor market reaches equilibrium and the effects of shifts in demand and supply curves due to factors like wages, productivity, and demographics. Additionally, it explores the roles of government and trade unions in addressing market inequalities and the implications of occupational attractiveness on labor supply and compensation.





















![REFERENCES
• Banerjee, Abhijit V. and Andrew F. Newman (1993). “Occupational Choice
and the Process of Development”, Journal of Political Economy, 101 (2):
274-298.
• Ehrenberg, R. G., (1988). Workers’ compensation, wages, and the risk of
injury [Electronic version]. In J. Burton (Ed.), New Perspectives on Workers’
Compensation (pp. 71-96). Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. Available at:
http://digitalcommons.ilr.cornell.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1680&co
ntext=articles
• Gwartney, J.W et al. (2017). Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice.
(16th Ed.). California: South-Western College.
• Lucas, R. (1978): “On the Size Distribution of Business Firms,” Bell Journal
of Economics, 9.
END OF PRESENTATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation3marketequilibriumequalizingdifferentialsandoccupationalchoice-181125072035/85/Market-Equilibrium-Equalizing-Differentials-and-Occupational-Choice-44-320.jpg)