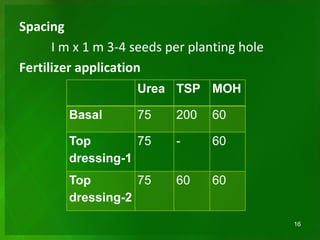
The document provides a comprehensive guide on cucumber agriculture, detailing its morphology, recommended varieties, soil and climatic requirements, field establishment, harvesting, storage, and pest management. It highlights the cucumber's origin, major growing areas in Sri Lanka, and the importance of proper irrigation and weed control. Additionally, it discusses the challenges posed by pests and diseases and offers references for further reading.