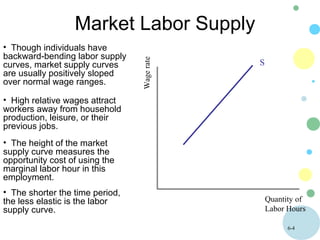
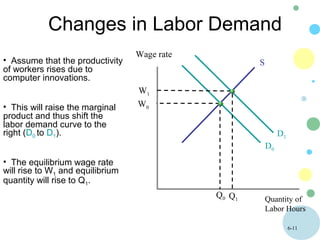
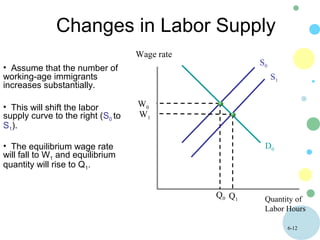
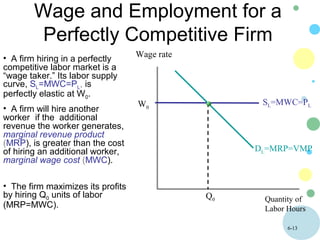
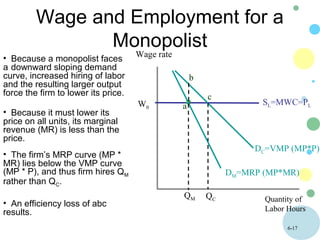
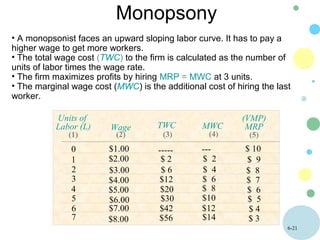
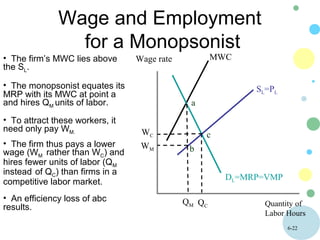
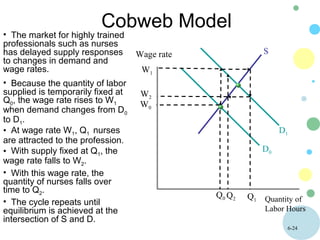
This document discusses theories of wage determination in labor markets including perfectly competitive labor markets, monopsony, and delayed supply responses. In a perfectly competitive labor market, the equilibrium wage and employment are determined by the intersection of supply and demand. A monopsony is a labor market with a single employer, which pays workers less than a competitive wage and hires fewer workers, resulting in inefficiency. Delayed supply responses in some professions can lead to cyclical "cobweb" adjustments as supply lags behind changing demand.