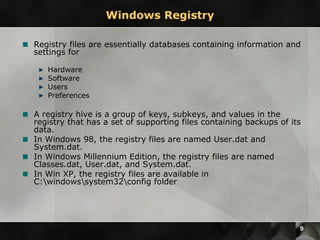
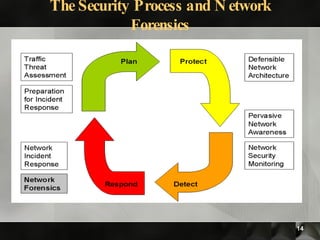
This document discusses various topics in digital and computer forensics. It introduces computer forensics and some key concepts like evidence of every action and absence of evidence can be evidence. It then discusses extracting information from Windows memory like login credentials, processes, and registry keys. Specific tools used for memory and registry analysis are also mentioned. Finally, it discusses network forensic processes like capturing traffic, analyzing logs and devices, and tools used for network traffic analysis.





![Extracting user assist keys from RAM Load the image in Encase and search for the keyword HRZR_EHACNGU {which is “UEME_RUNPATH”}. Keywords are HRZR_EHACNGU.*[\.]rkr HRZR_EHACNGU.*[\.]yax Decrypt the results using ROT13-decryptor.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kushwadhwaminingdigitalevidenceinwindows-100708150339-phpapp02/85/Kush-wadhwa-_mining_digital_evidence_in_windows-ClubHack2009-7-320.jpg)