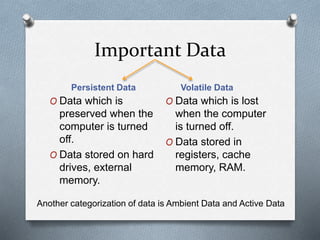
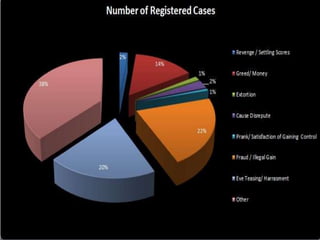
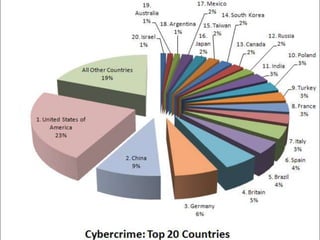
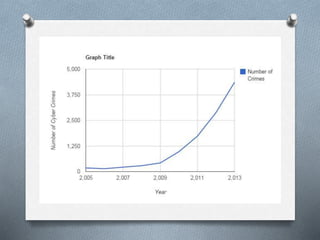
Computer forensics involves identifying, preserving, analyzing, and presenting digital evidence for legal matters, focusing on persistent and volatile data. It plays a critical role in addressing cyber crimes such as hacking, identity theft, and industrial espionage, ensuring the integrity of systems while aiding in criminal prosecution. The process encompasses acquisition, identification, evaluation, and presentation of evidence, utilizing various tools to enhance the accuracy of evidence retrieval.