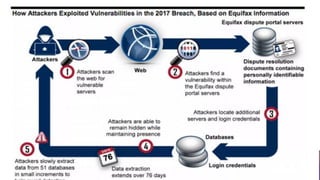
This document discusses cyber forensics and investigating large scale data breaches. It begins by defining cyber forensics as an electronic discovery technique used to determine and reveal technical criminal evidence, often involving extracting electronic data for legal purposes. It then discusses challenges in investigating corporate networks due to different operating systems, file systems, and administrative access used. When investigating large data breaches, security exploits and employee devices are common entry points, while pace of growth and lack of evidence erasure complicate progress. The Yahoo breach example turned tides by providing data to investigators that aided geopolitical understanding. Immediate actions include response and isolation, while tools like COFEE, SIFT, and ProDiscover aid forensic analysis at different levels.