The document discusses computer forensics techniques including:
1) Basic investigation techniques like WHOIS searches, DNS lookups, and analyzing web server logs.
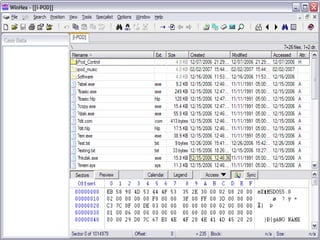
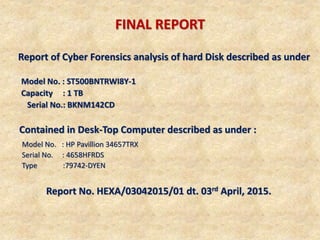
2) Analyzing digital evidence from sources like hard drives, network cards, routers, and removable storage devices.
3) The computer forensics process of acquiring, authenticating, analyzing, and documenting digital evidence while avoiding modifying the original source.