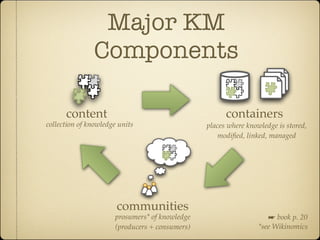
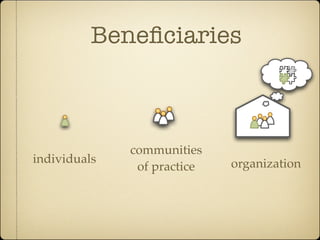
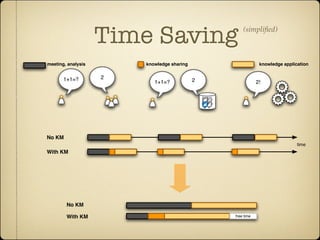
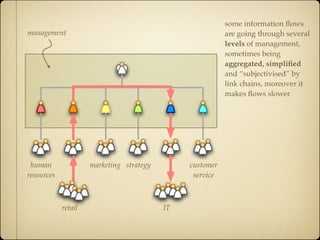
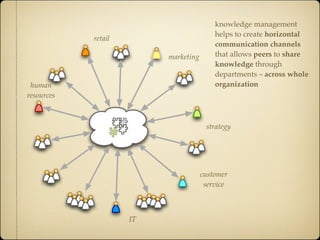
Knowledge management provides benefits for individuals, communities, and organizations. For individuals, it helps with job tasks, builds community bonds, and allows people to keep updated. For communities, it facilitates knowledge growth, transfer, and measuring value. For organizations, it helps drive strategy, solves problems quickly, diffuses best practices, increases innovation, improves embedded knowledge in products/services, and builds organizational memory.