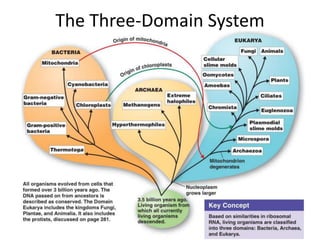
The document describes the three-domain system of classifying life. It divides life into Archaea, Eubacteria, and Eukarya. Archaea and Eubacteria are prokaryotes without nuclei or organelles, while Eukarya are more complex eukaryotic organisms with nuclei and organelles. Eukarya are further divided into four kingdoms - Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Protista include unicellular organisms like protozoa and algae. Fungi are multicellular decomposers with cell walls made of chitin. Plantae are multicellular and autotrophic organisms that perform photosynthesis. Animalia are