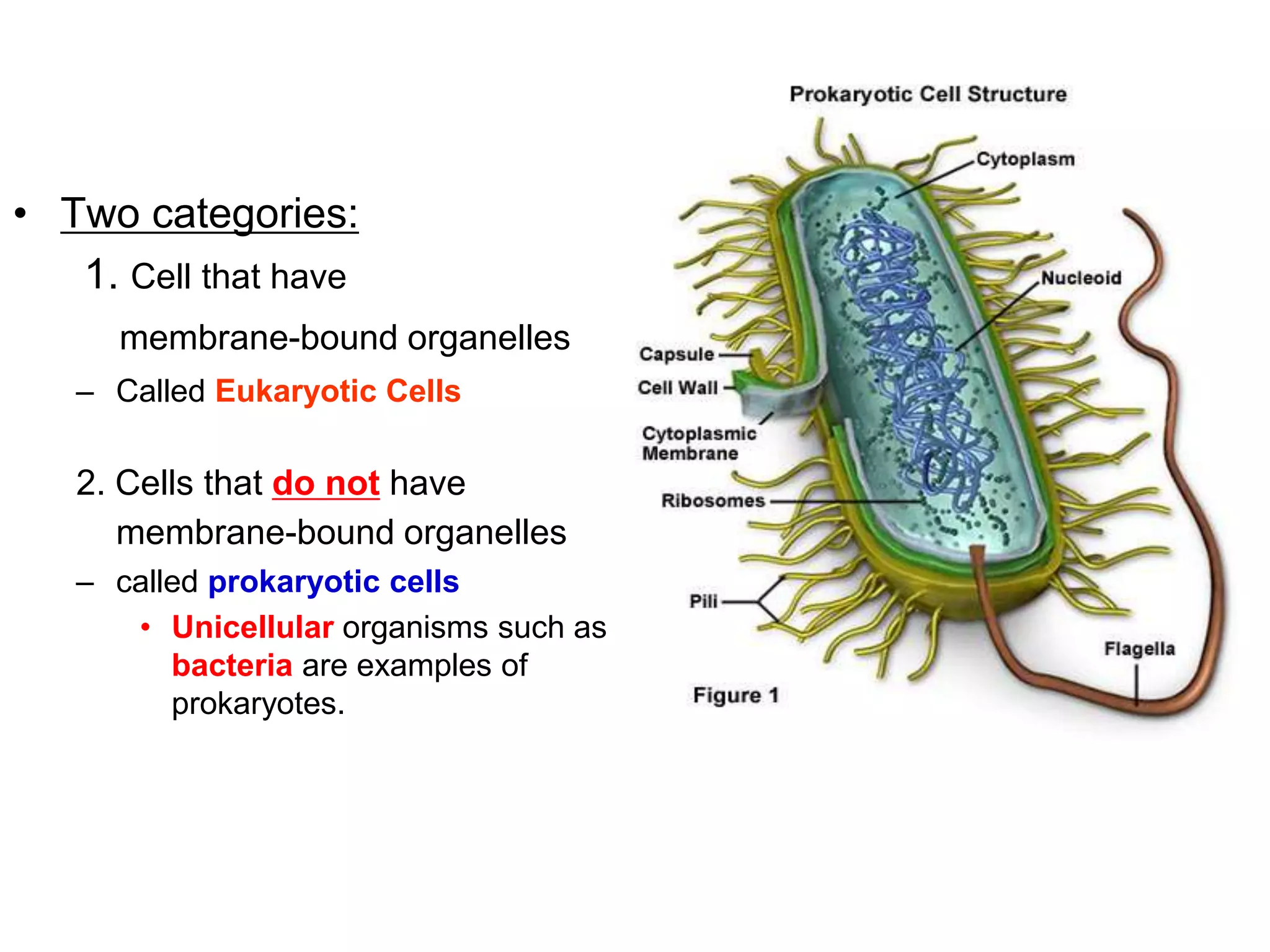
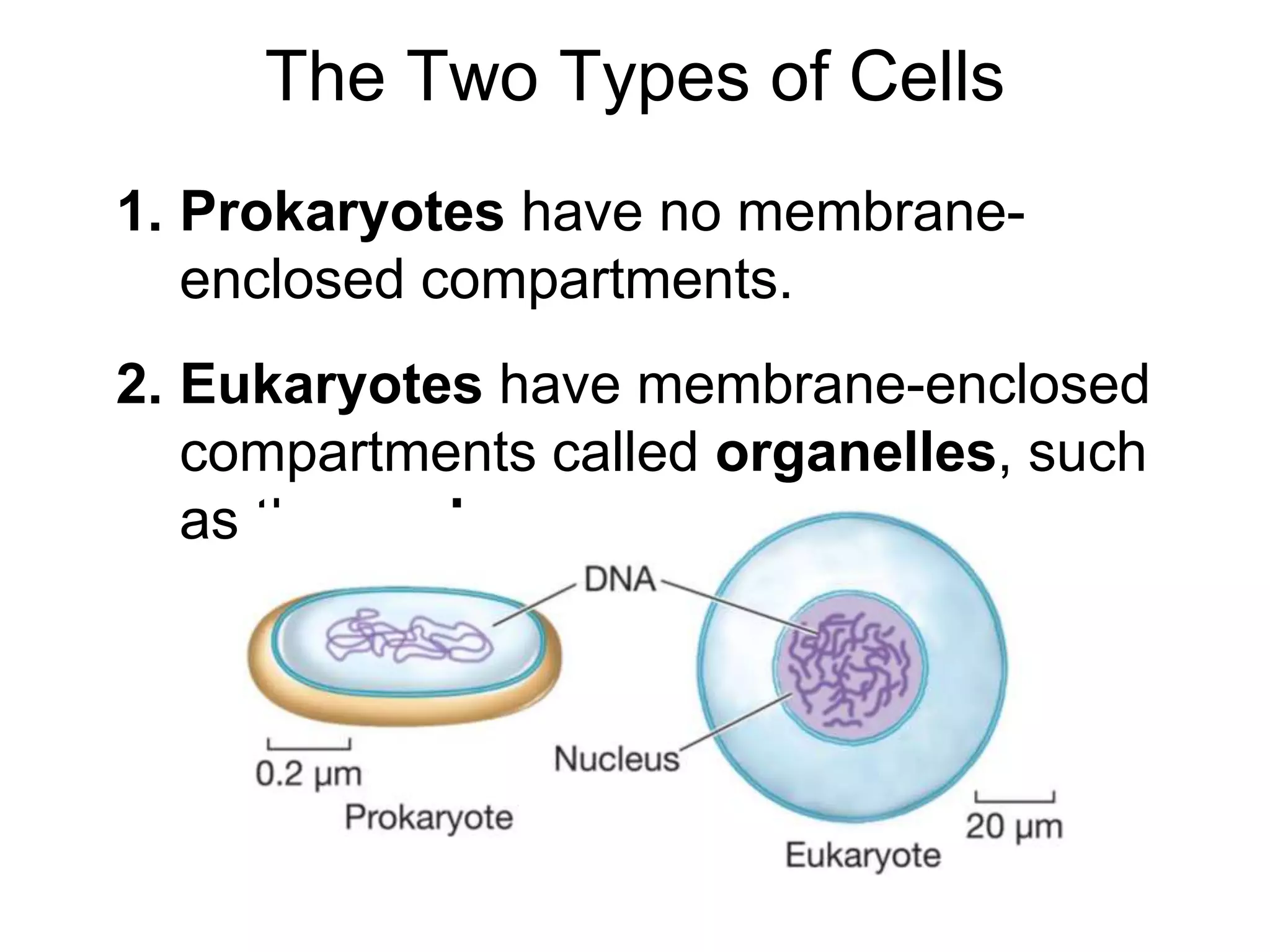
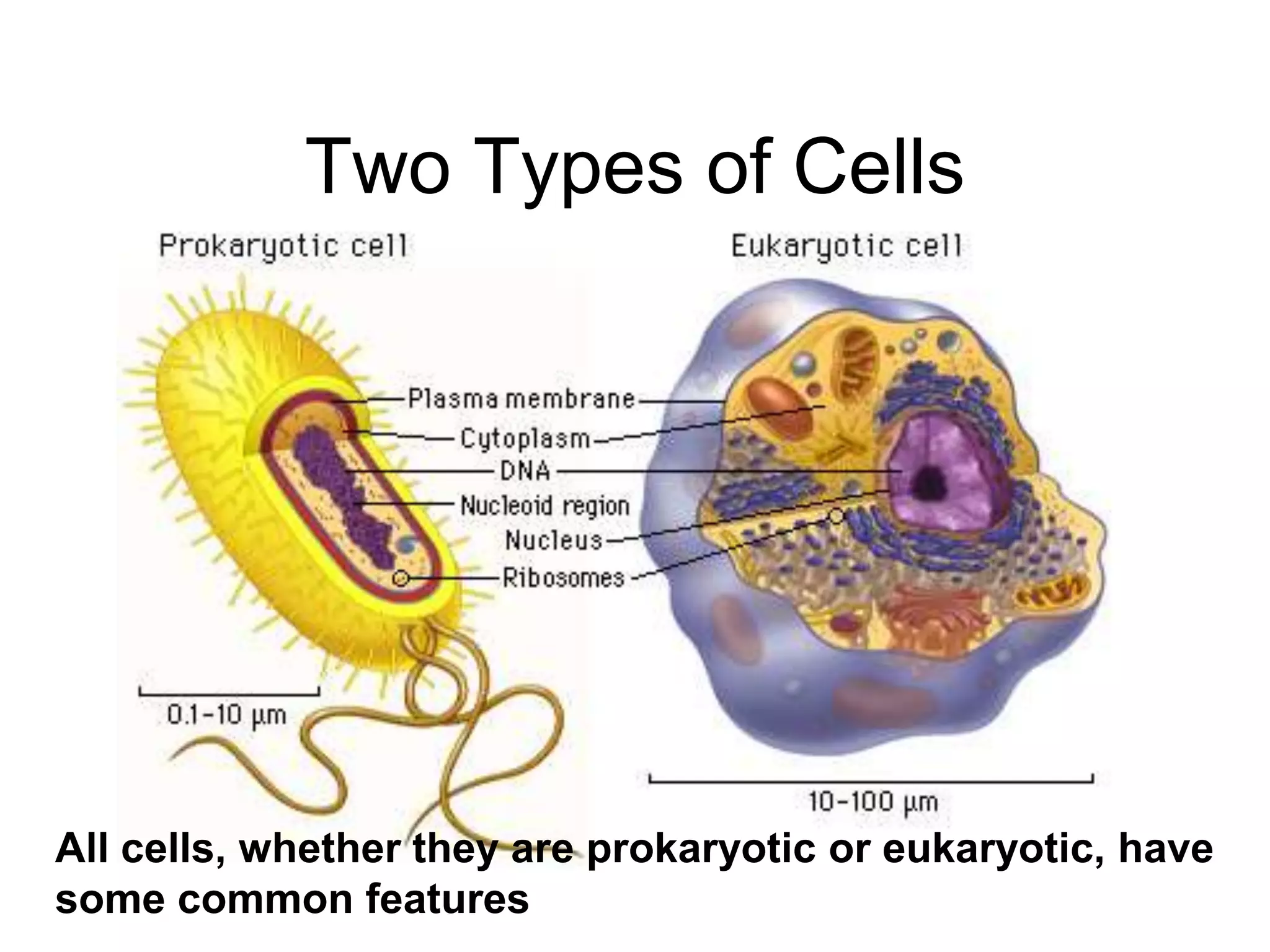
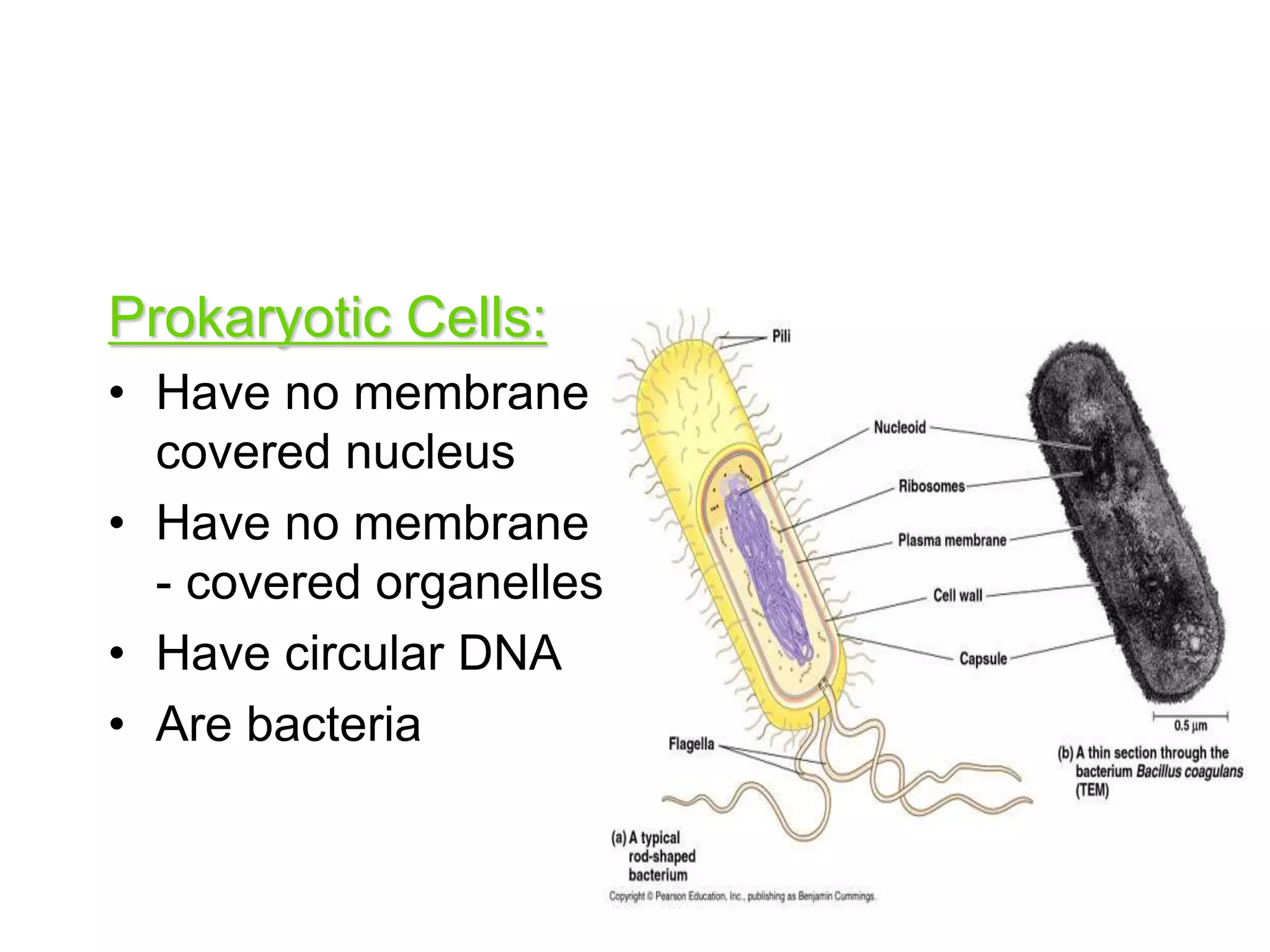
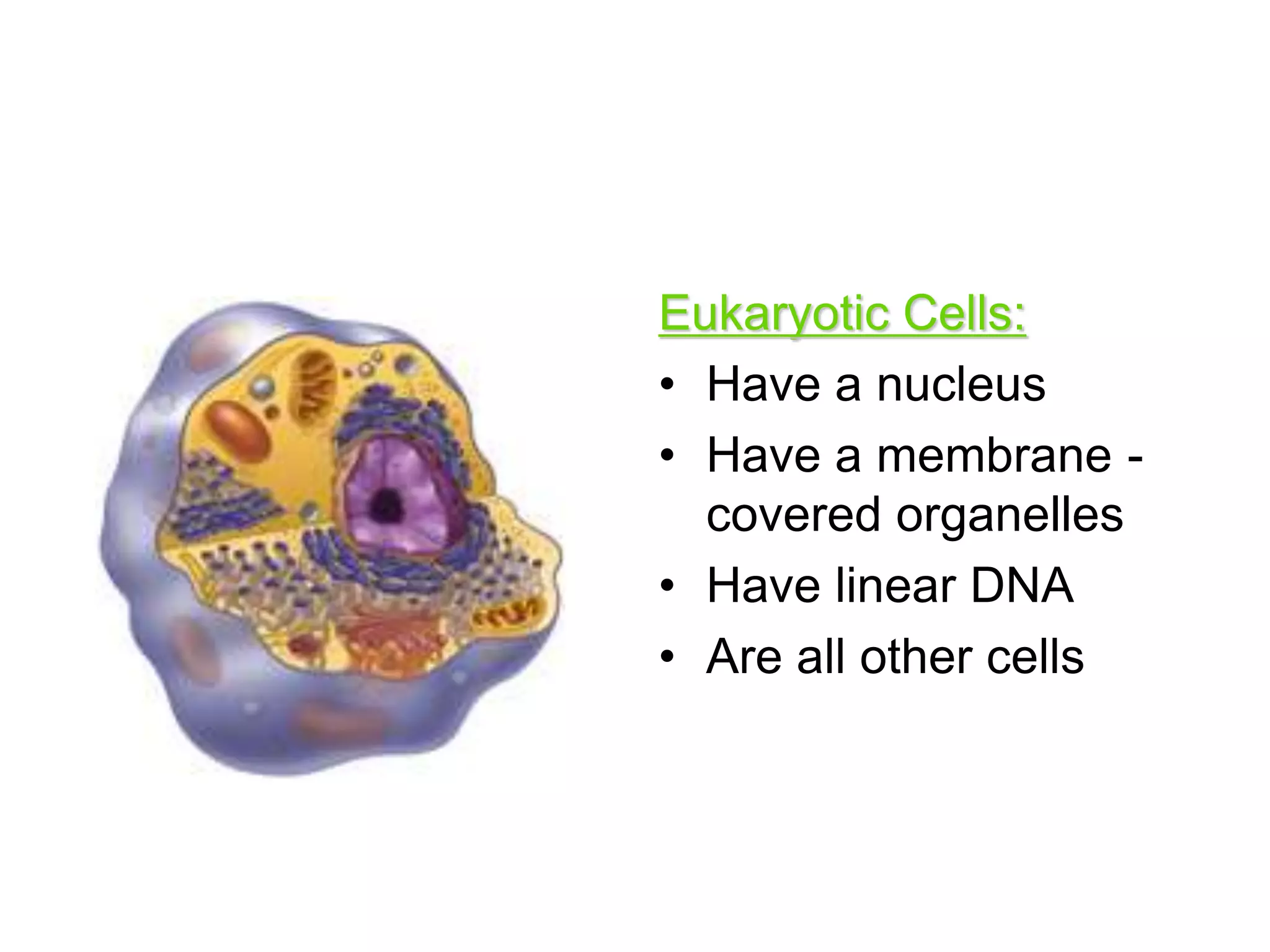
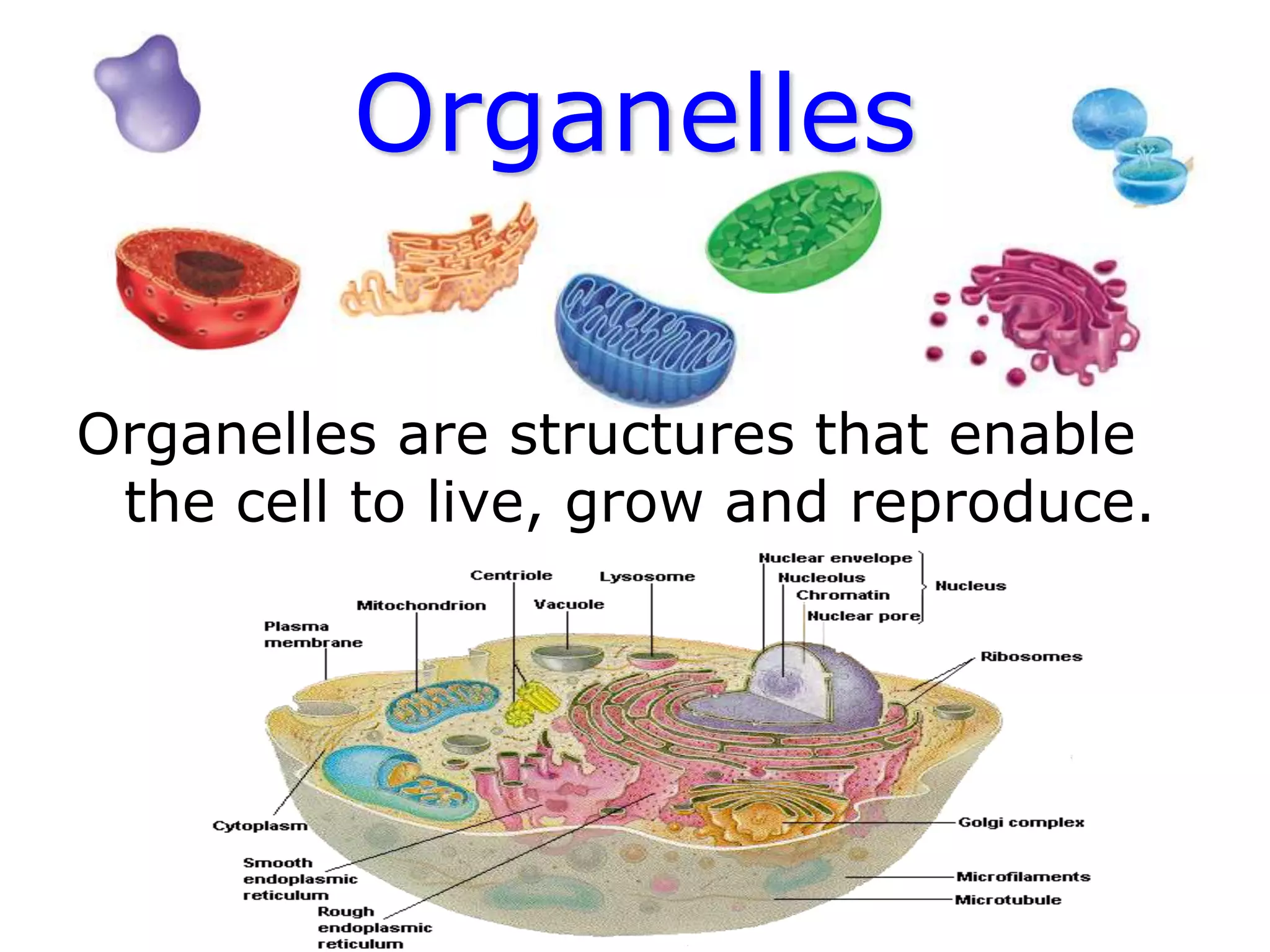
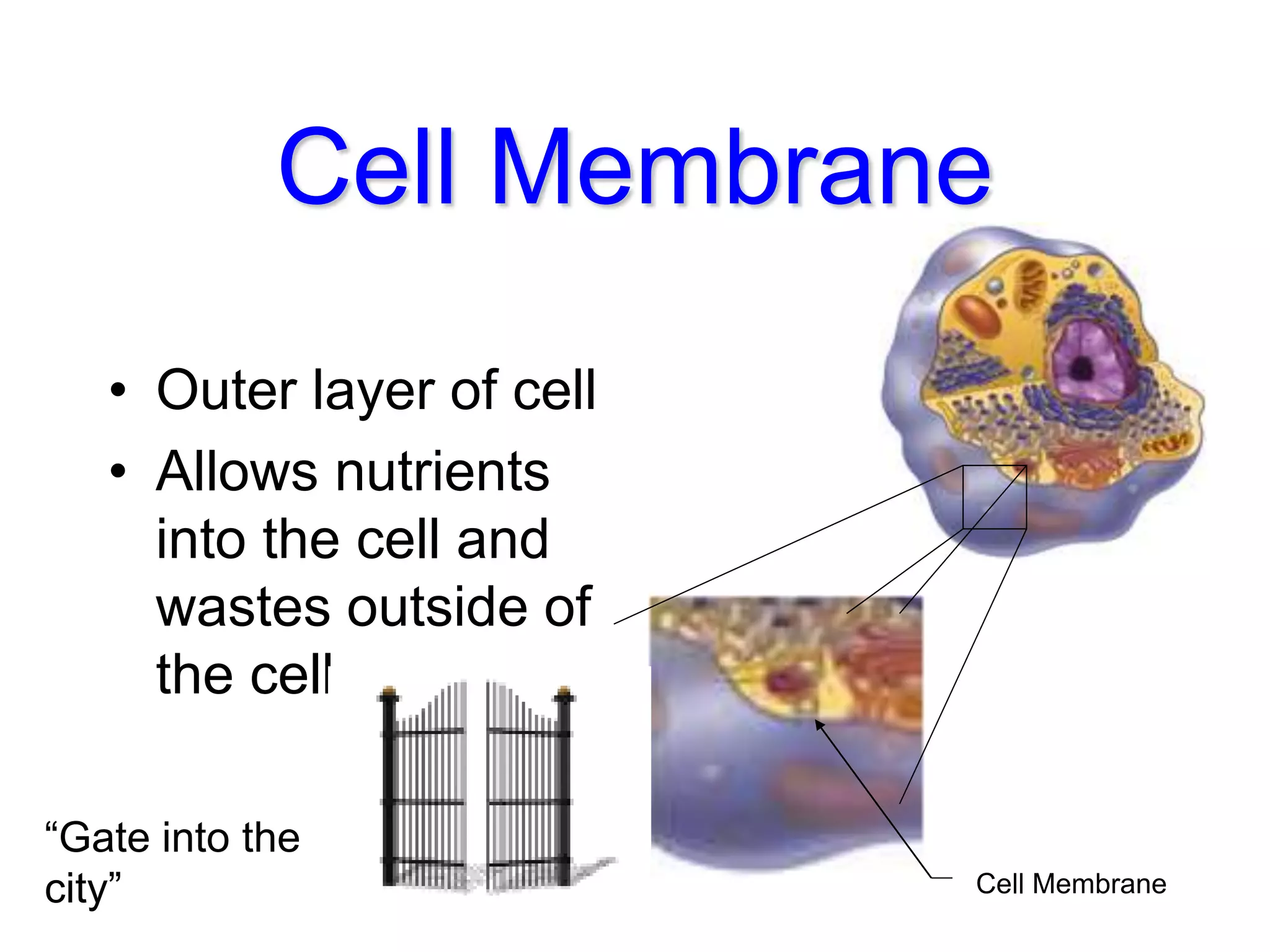
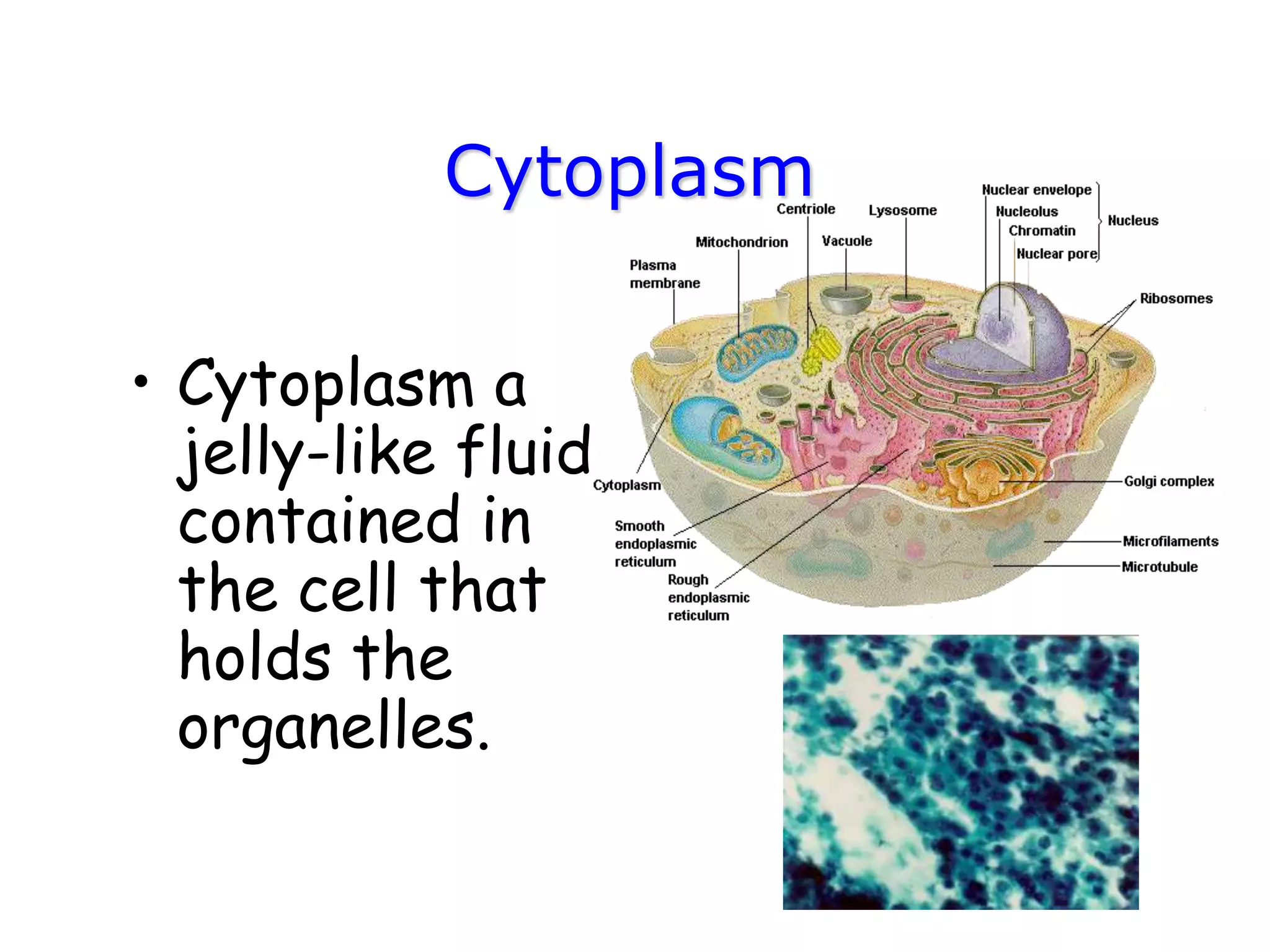
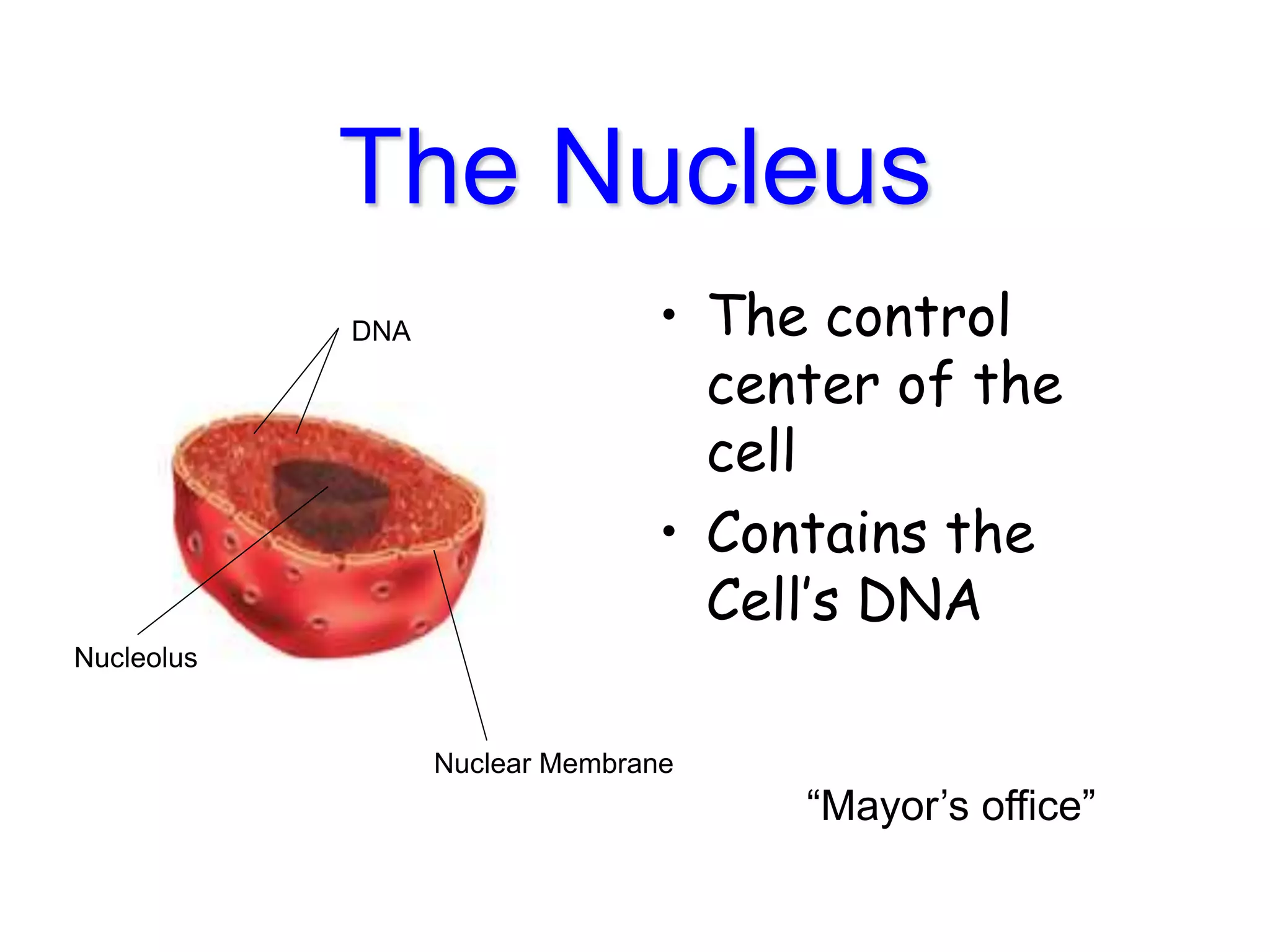
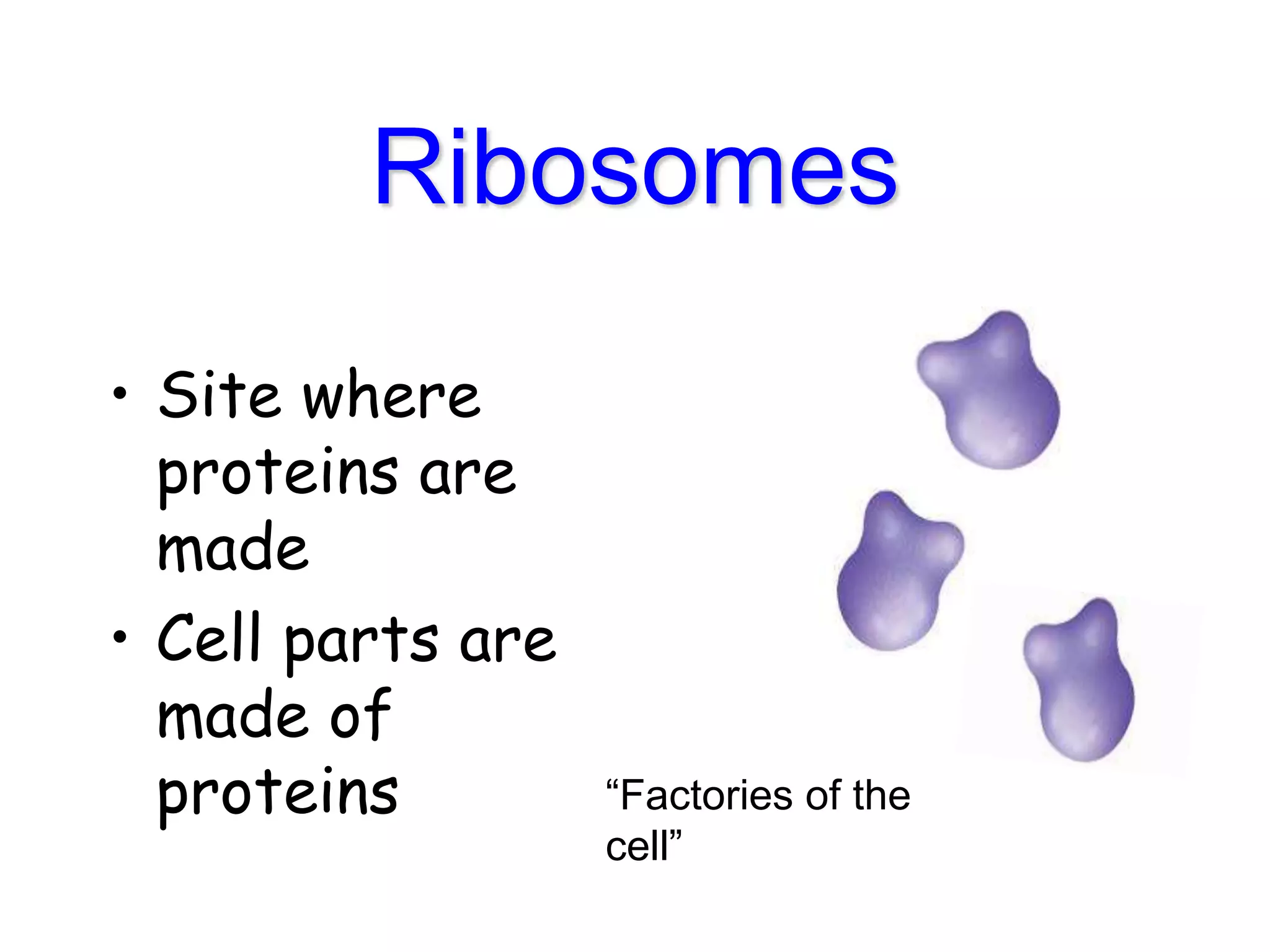
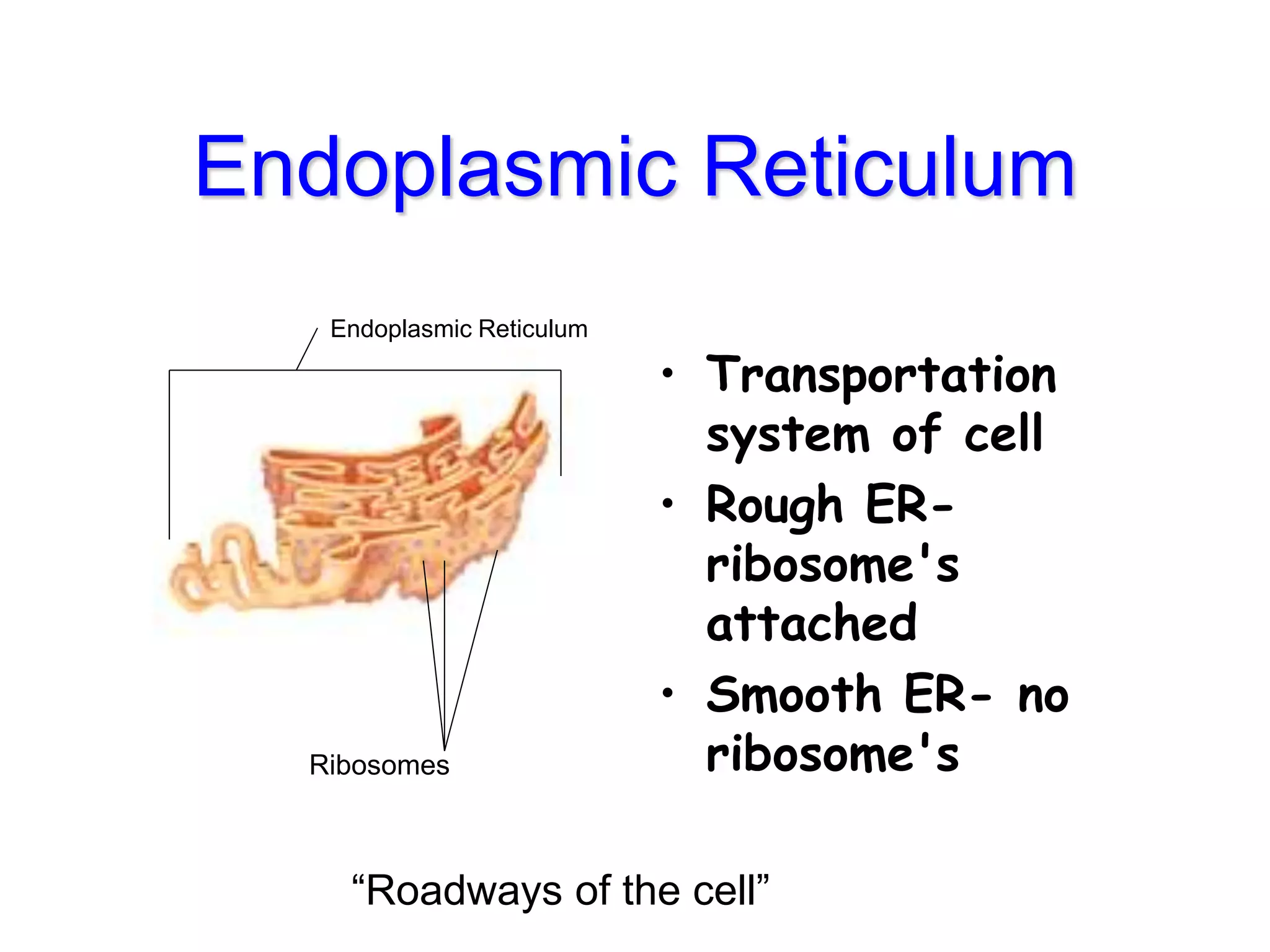
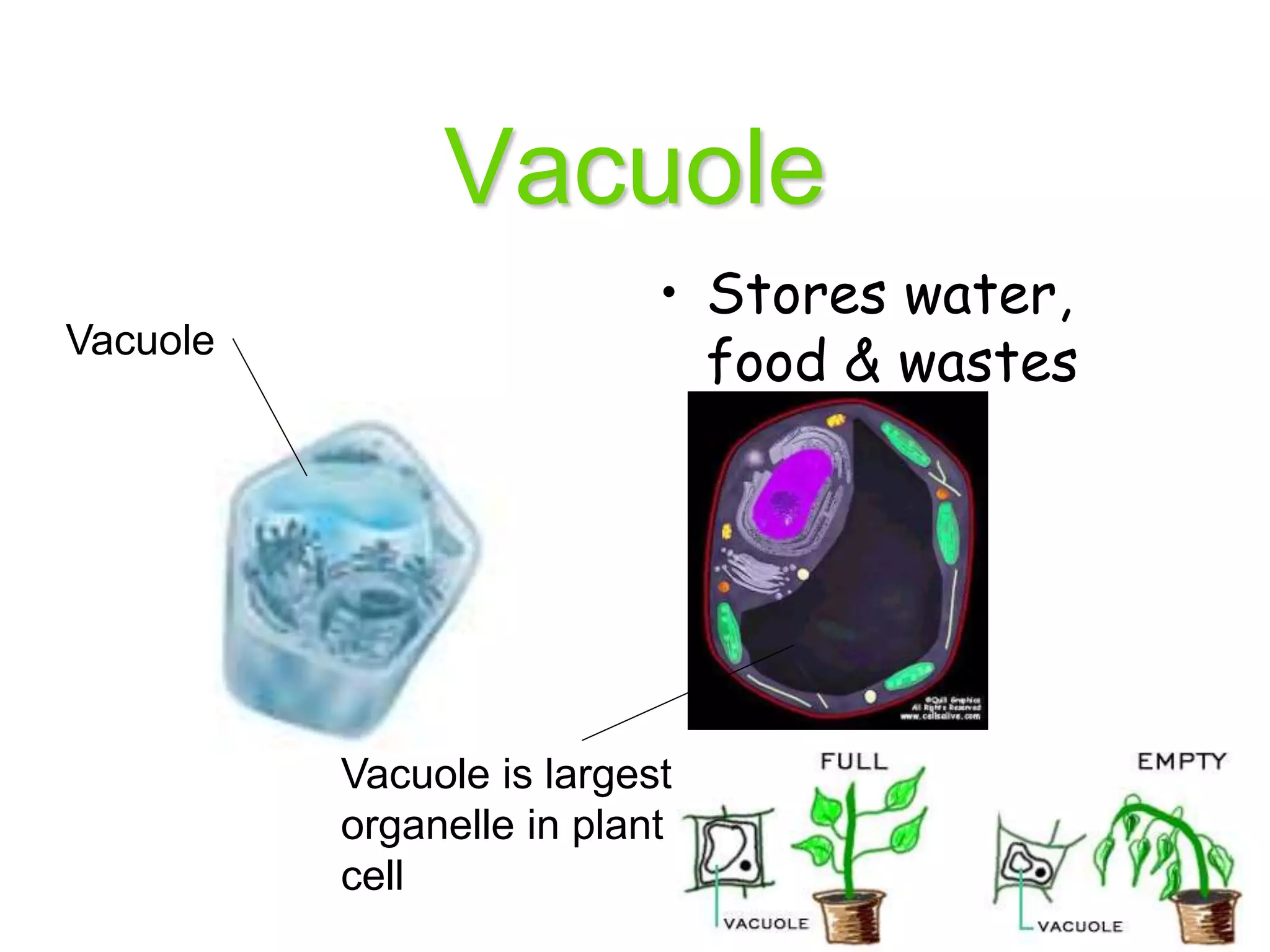
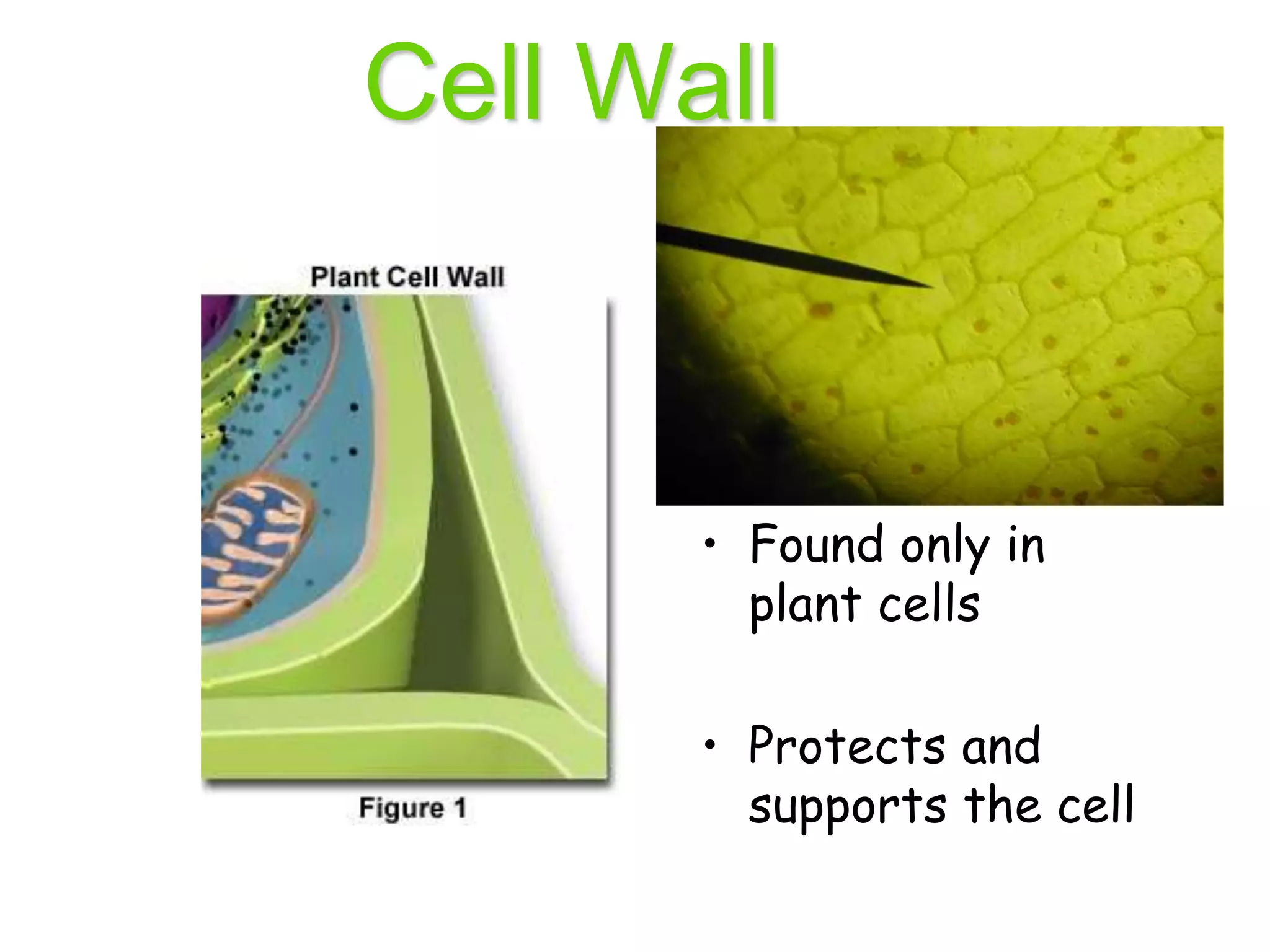
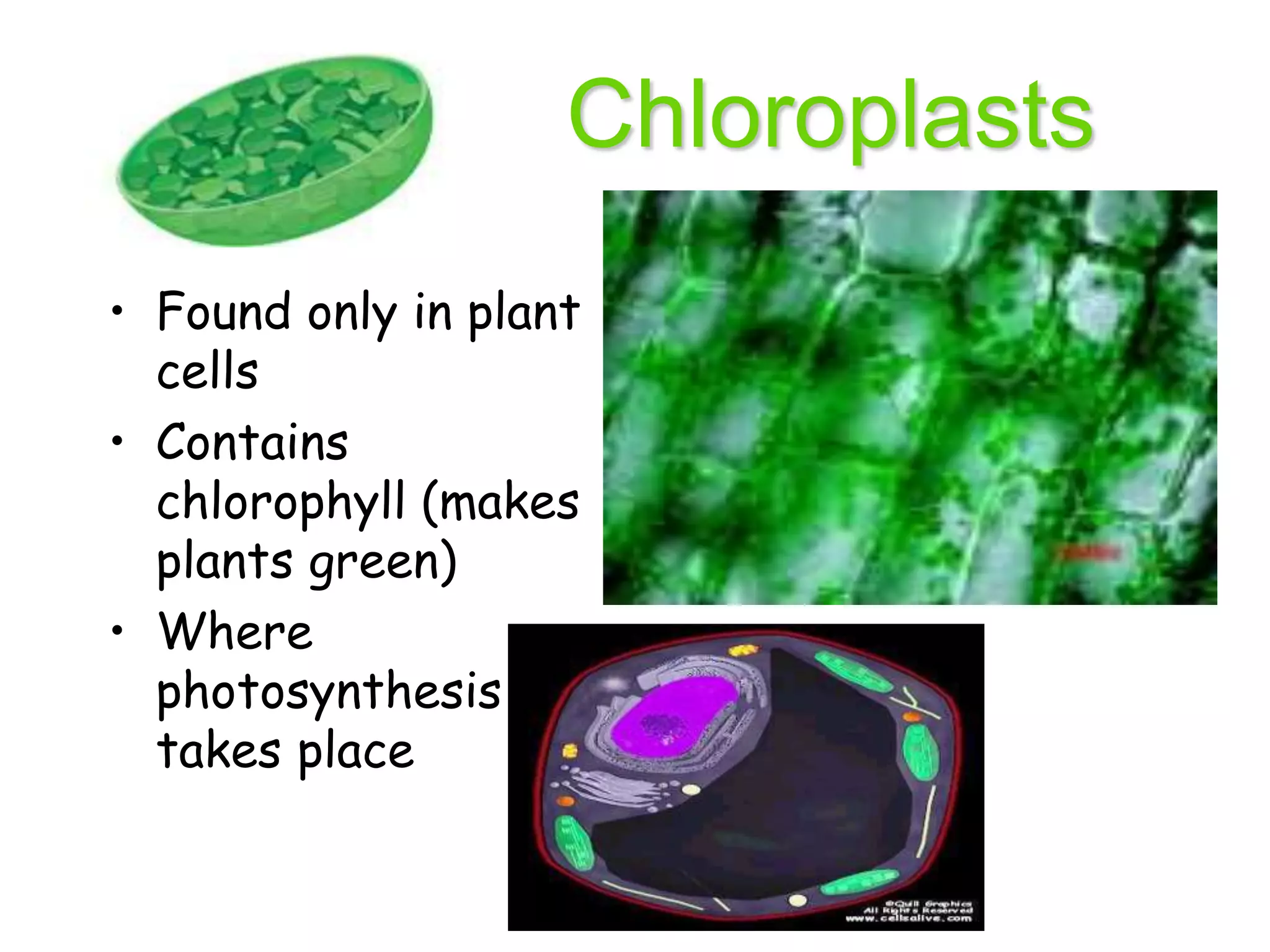
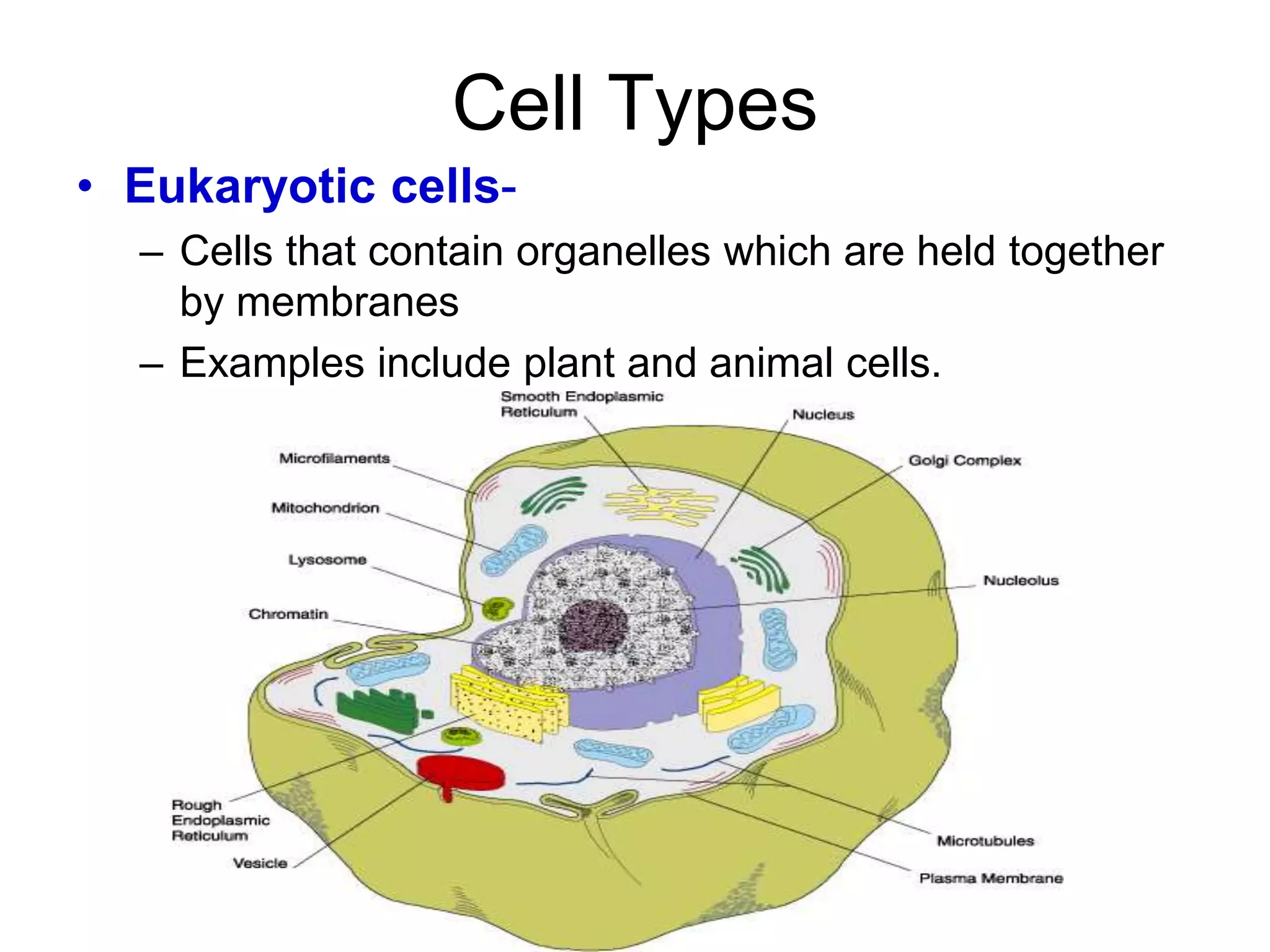
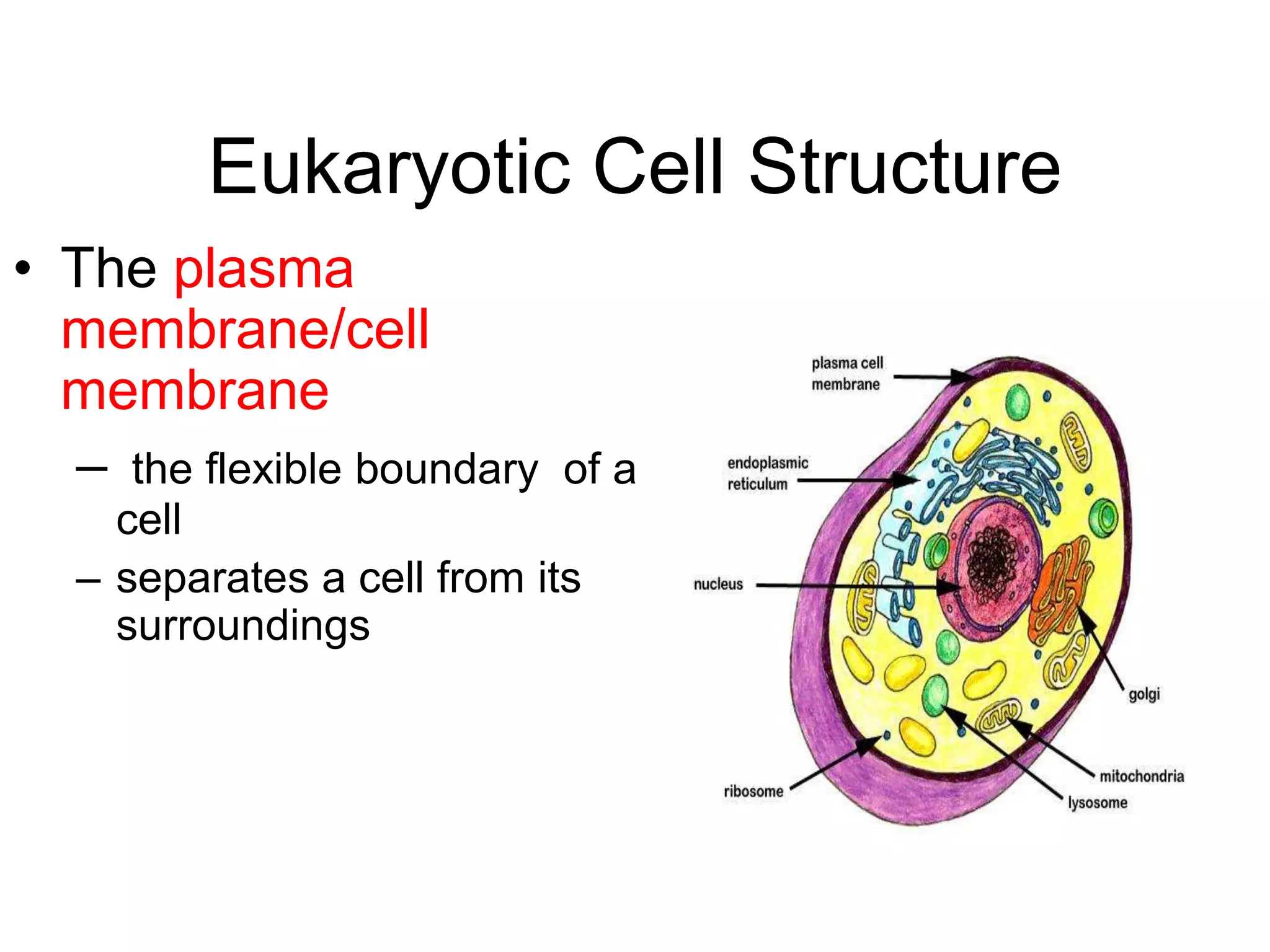
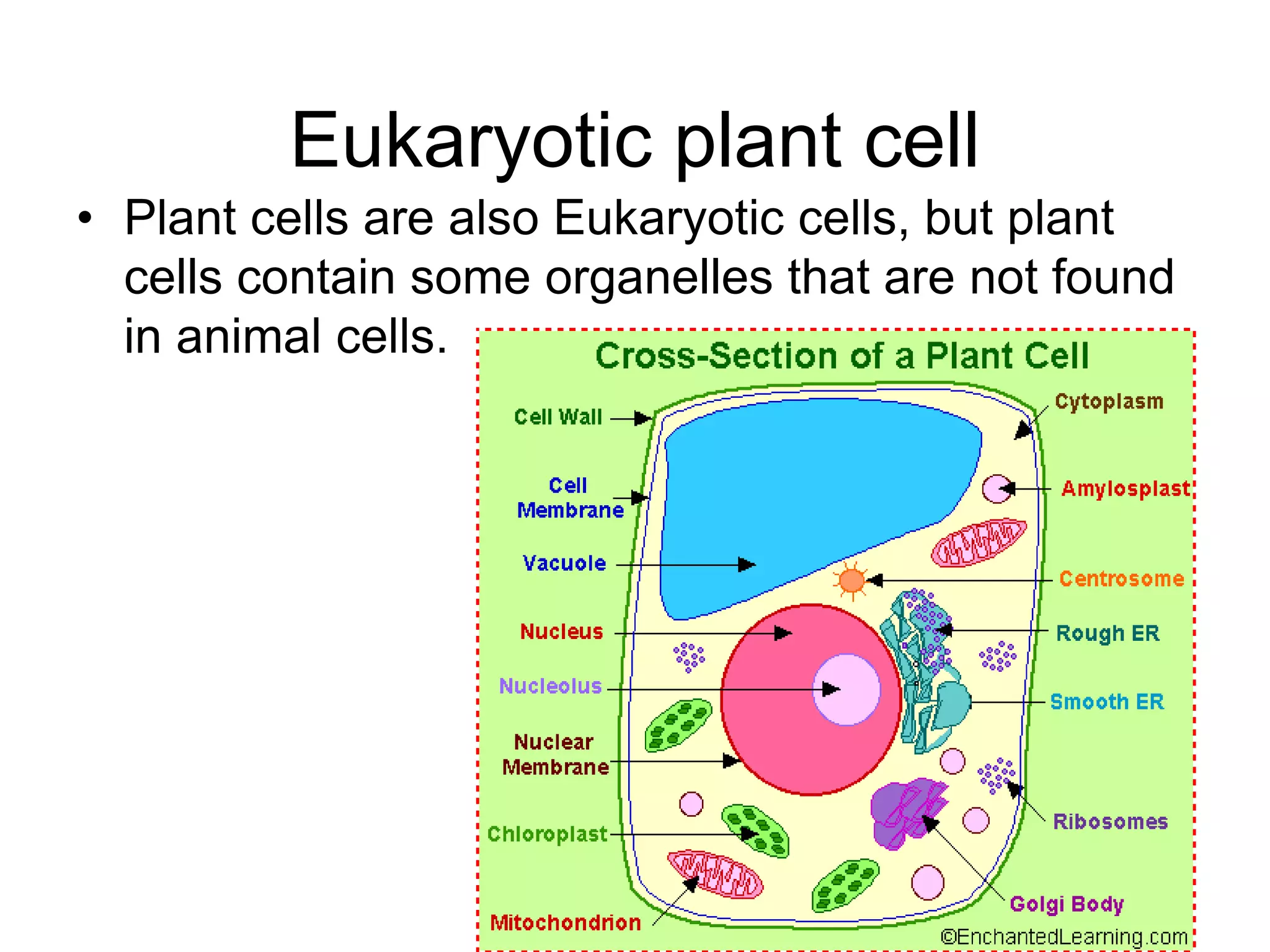
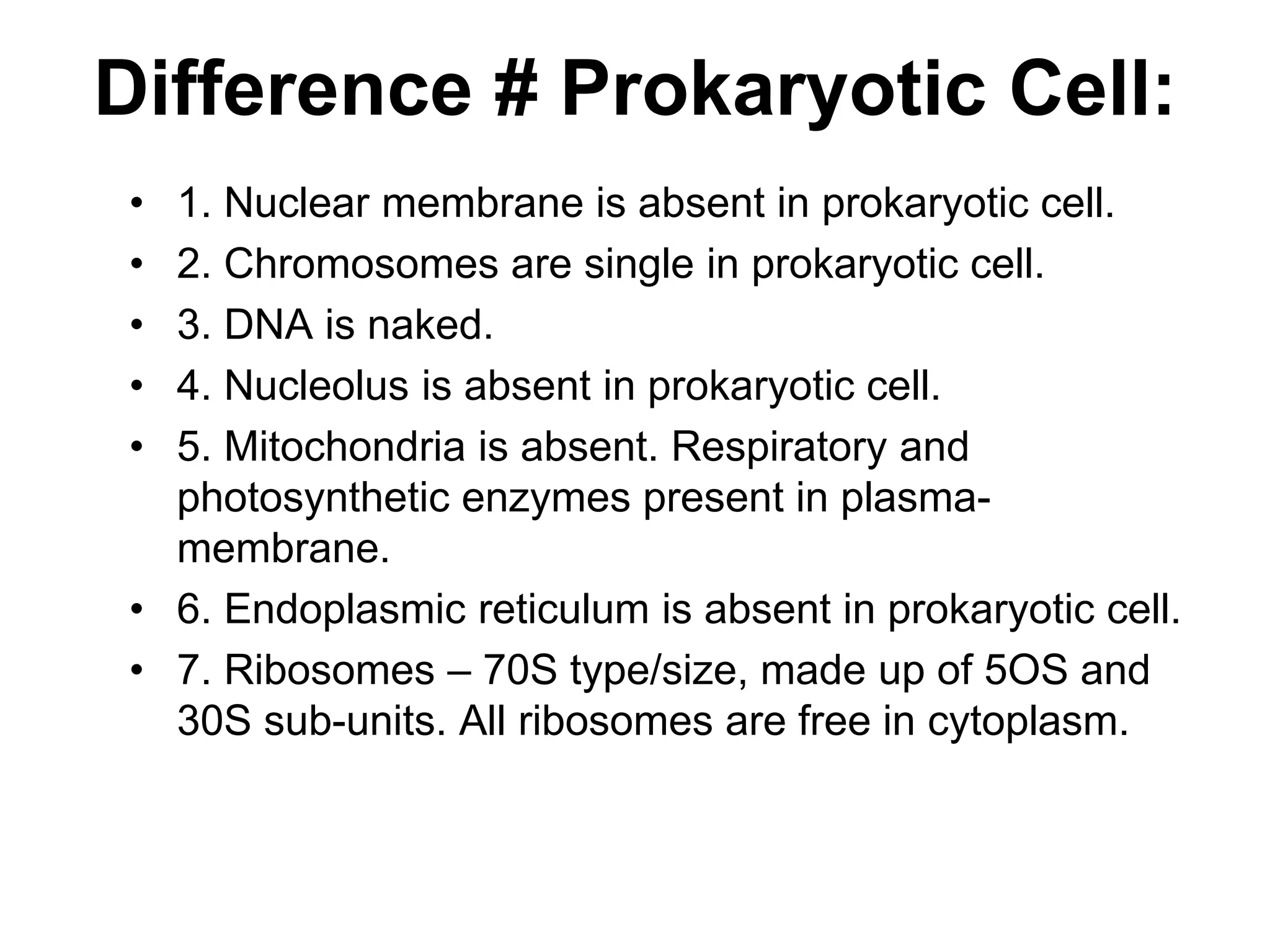
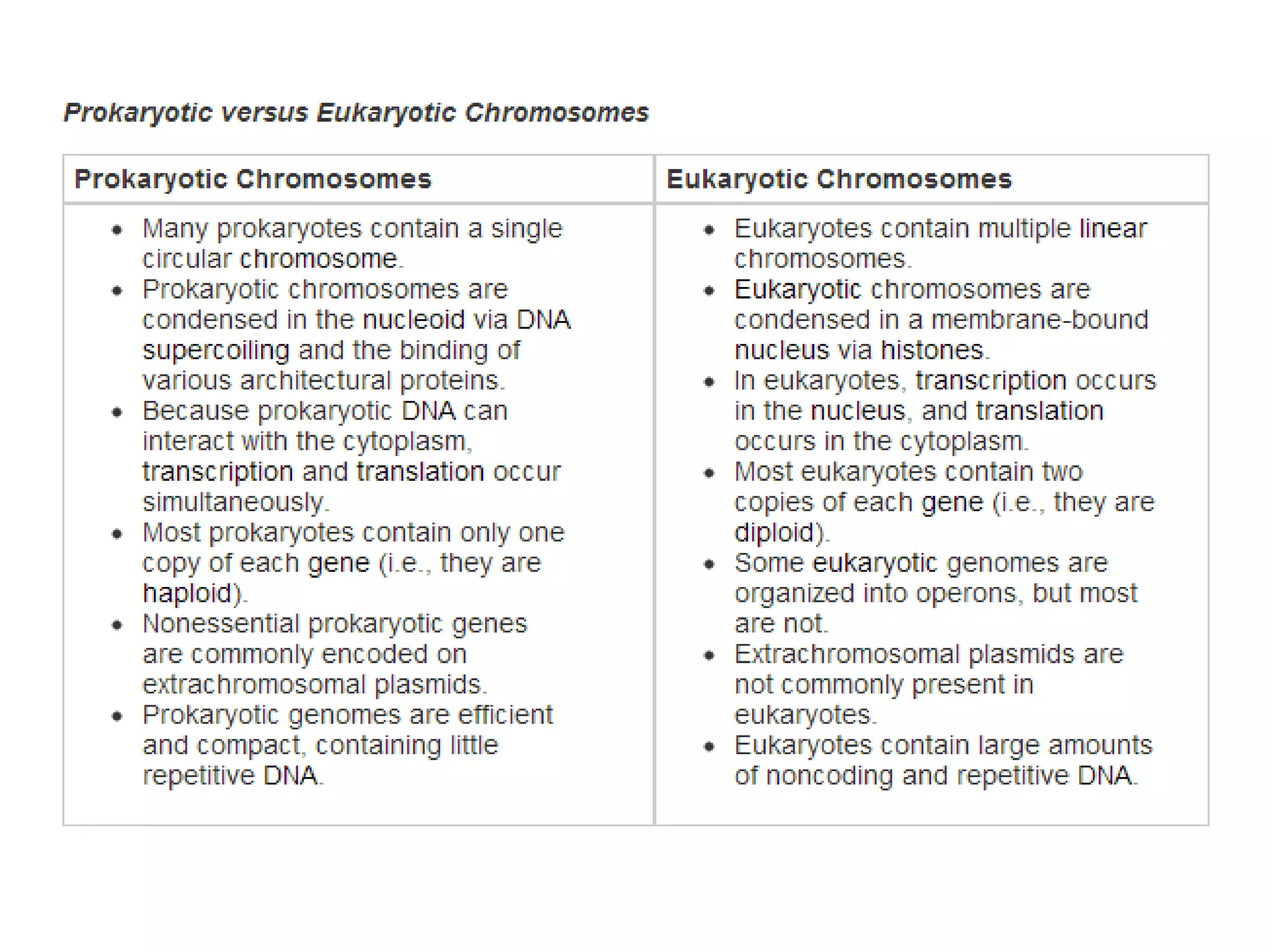
This document discusses the cell theory and provides information about prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It states that all organisms are made of cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and all cells come from existing cells. It then describes the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, noting that prokaryotes lack membrane-bound organelles while eukaryotes have organelles like the nucleus. The document also provides details on the structures and functions of organelles in plant and animal cells like the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts and more.