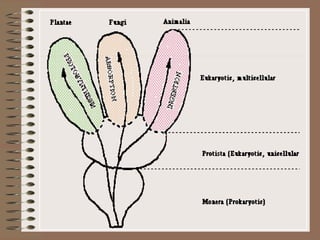
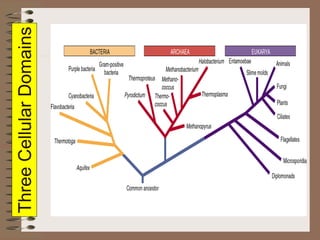
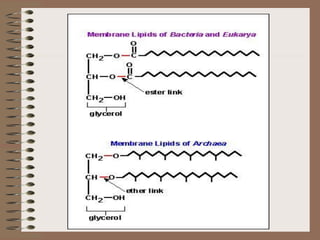
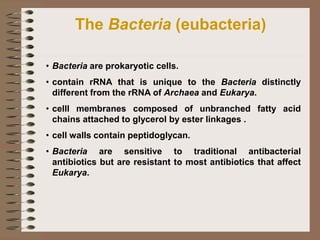
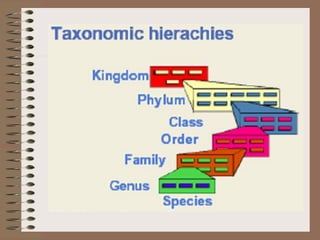
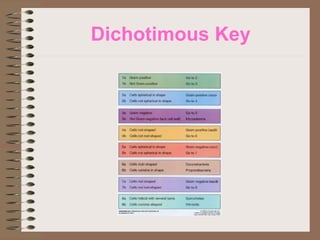
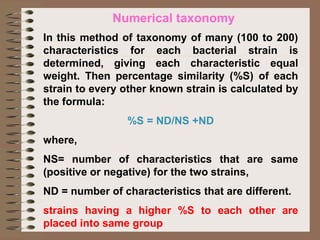
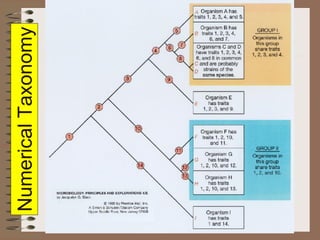
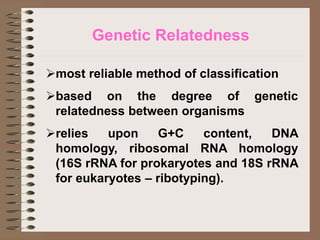
Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms based on evolutionary relationships. It includes identification, nomenclature, and classification. Bacteria were originally classified as part of the plant and animal kingdoms but are now placed in their own domains. Carl Woese proposed classifying all life into three domains based on rRNA sequences: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Each domain has distinct cellular features. Bergey's Manual is the standard reference for bacterial taxonomy and classification, which has evolved from phenotypic to phylogenetic approaches based on genetic analysis.