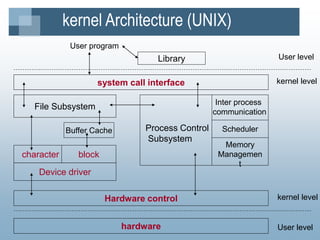
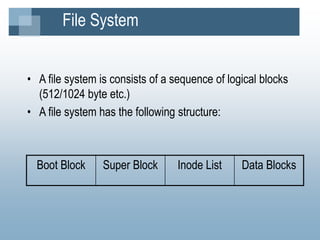
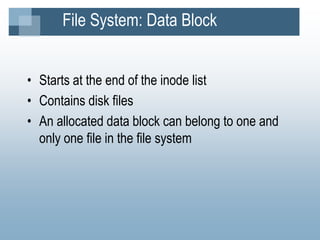
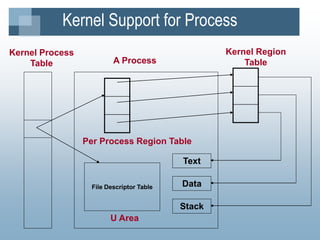
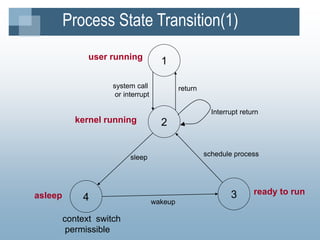
The kernel manages processes, memory, and I/O. It has two levels - user level and kernel level. Processes interact with the kernel through system calls. A process contains text, data, stack, and a U area. The kernel uses process tables, region tables, and context switches to manage multiple simultaneous processes. The file system contains boot blocks, super blocks, inode lists, and data blocks to organize files on disk. Processes can create new processes using the fork system call.