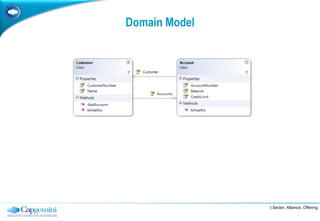
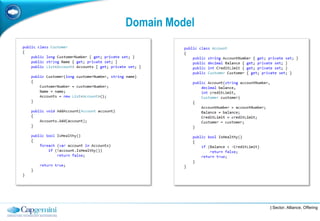
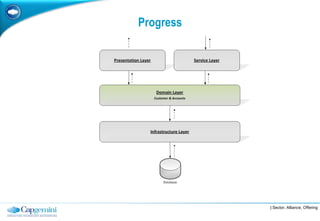
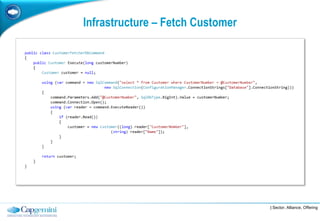
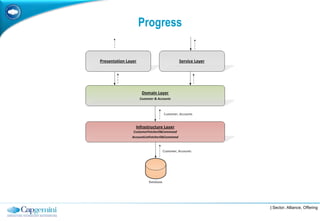
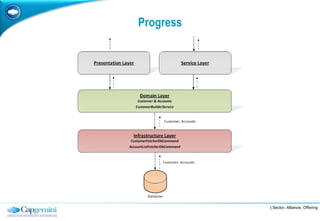
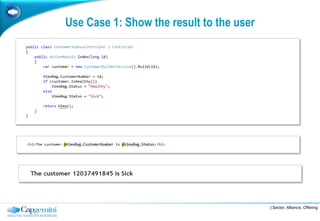
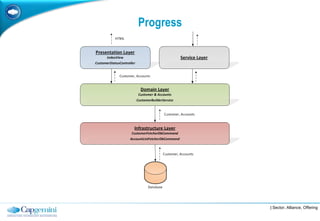
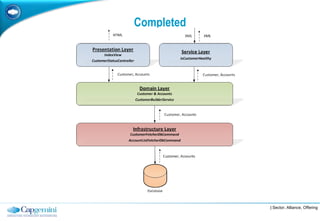
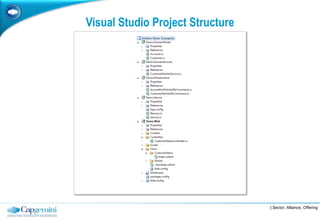
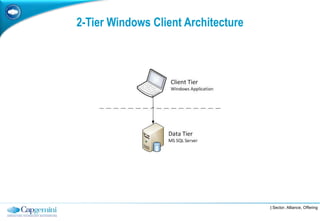
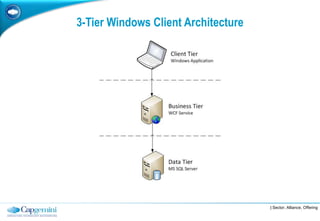
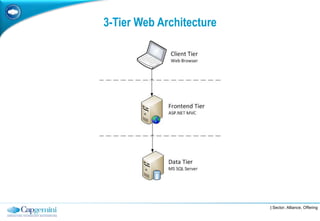
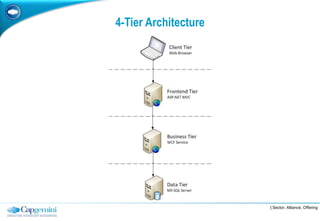
The document discusses layered architecture in application development, focusing on the logical and physical layers. It describes key components such as the presentation layer, service layer, domain layer, and infrastructure layer, along with their responsibilities. The document also emphasizes the benefits of using multiple layers and tiers for better maintainability, scalability, and security.