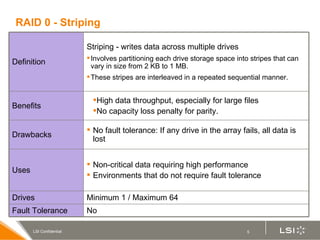
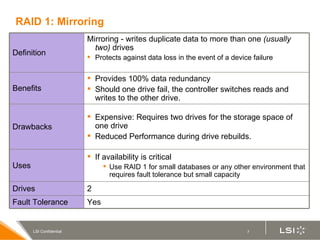
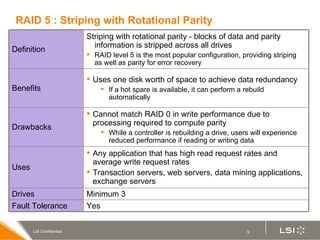
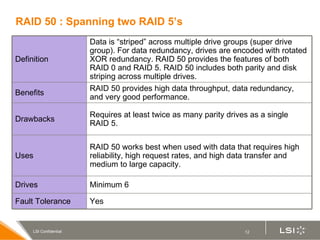
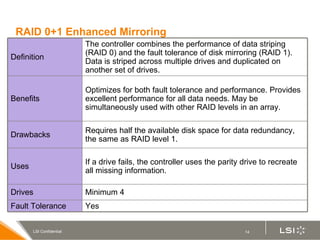
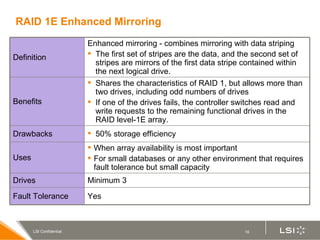
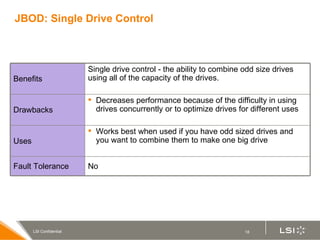
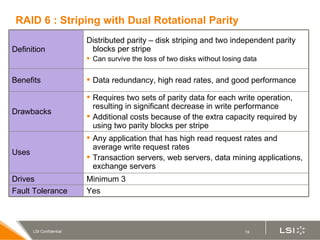
RAID (redundant array of independent disks) manages multiple disk drives as one unit for improved performance and fault tolerance. The document discusses various RAID levels and their characteristics, including advantages and disadvantages for different applications. RAID 0 provides no fault tolerance but high performance, while RAID 1 offers full data mirroring for fault tolerance. RAID 5 uses parity for redundancy with good performance. Higher RAID levels like RAID 10 and RAID 50 provide both redundancy and performance through combinations of striping and mirroring.