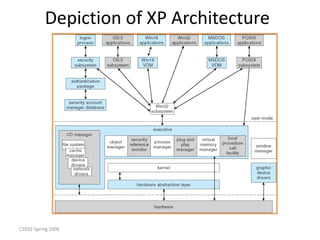
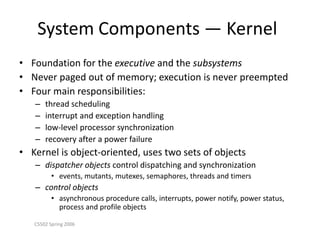
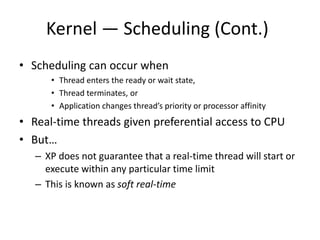
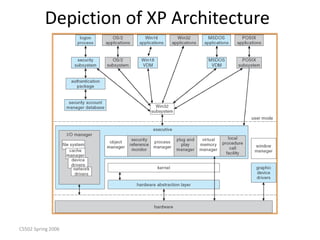
Windows XP is a 32-bit, preemptive multitasking operating system that was the most widely used OS at the time. It has a layered architecture with a microkernel at its core providing basic services, and various user-mode subsystems that emulate other operating systems. Its design focuses on extensibility, portability, reliability, compatibility, and performance. It uses a file system called NTFS that supports advanced features like security and recovery through transaction logging.