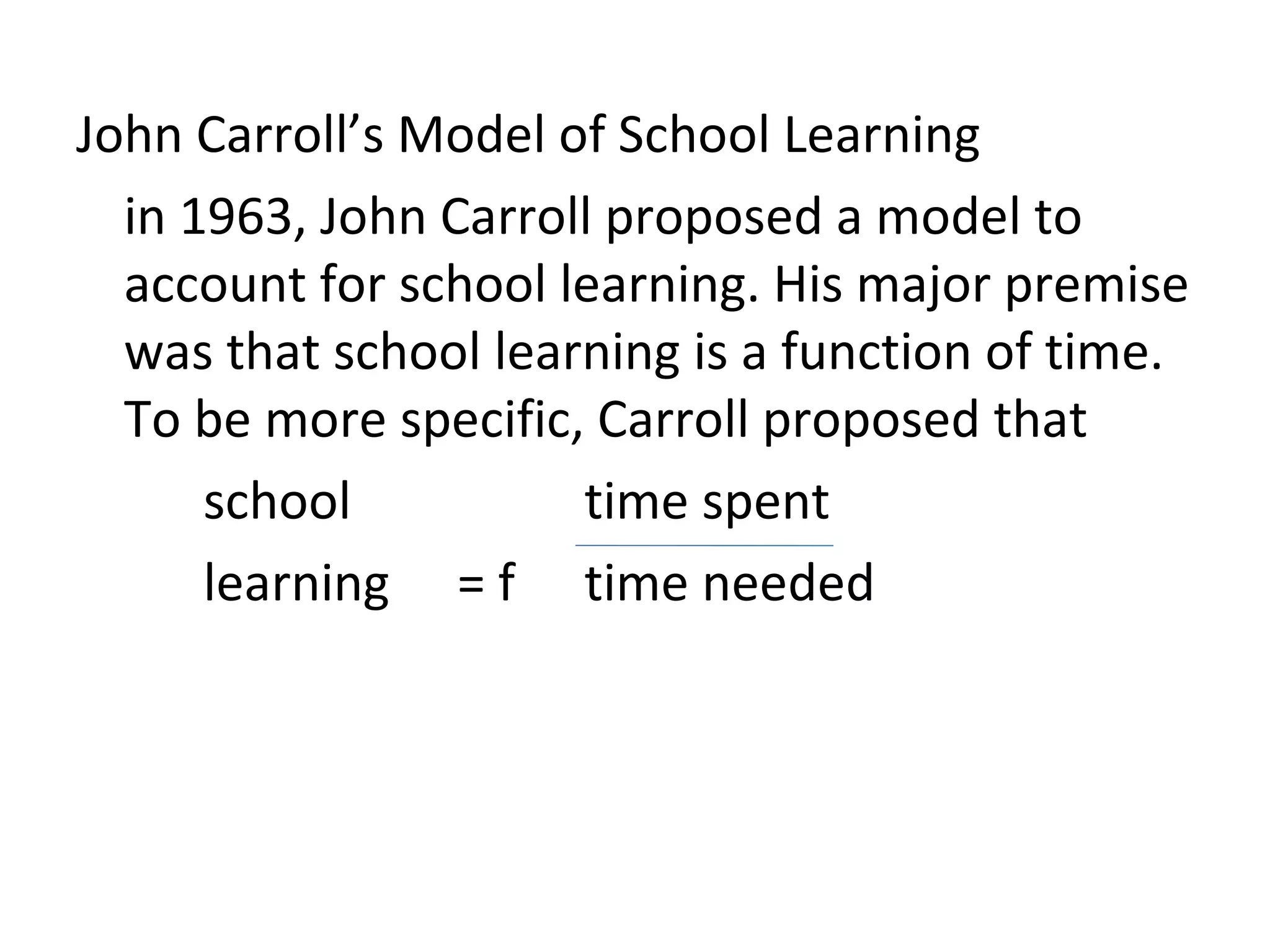
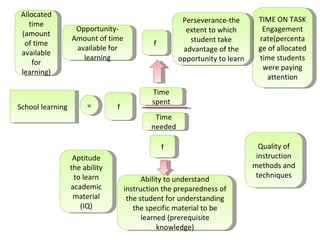
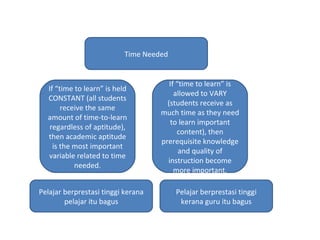
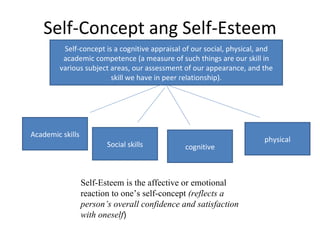
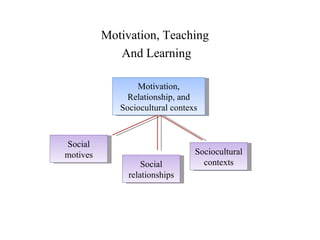
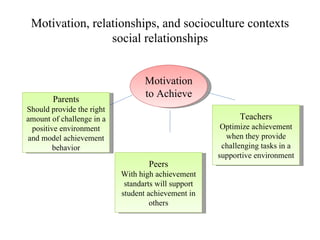
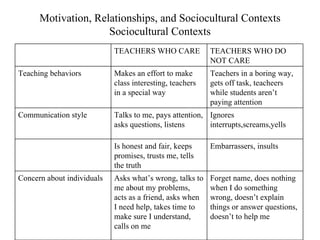
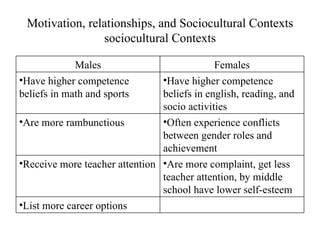
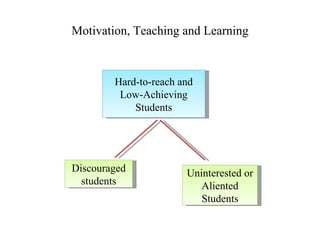
John Carroll proposed a model of school learning where the amount learned is a function of time spent learning, including the time needed, time allocated, perseverance, and engagement; academic aptitude and quality of instruction also impact the time needed to learn; and academic learning time measures the quality and quantity of time students spend successfully learning important content.