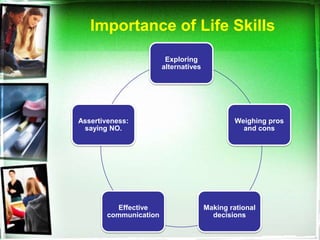
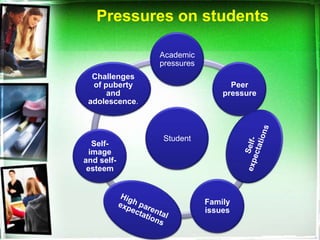
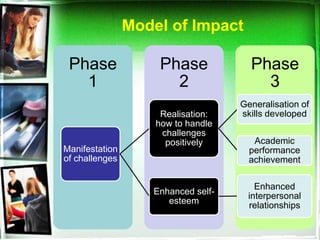
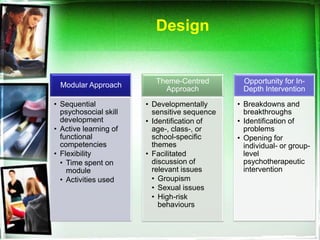
The document outlines a life skills training program aimed at equipping youth with essential life competencies such as self-awareness, empathy, decision-making, and effective communication. It emphasizes the importance of addressing academic pressures and challenges faced during adolescence, while promoting personal development and healthy coping mechanisms. The training adopts a flexible, modular approach to engage students actively, enhancing their academic performance and interpersonal relationships.