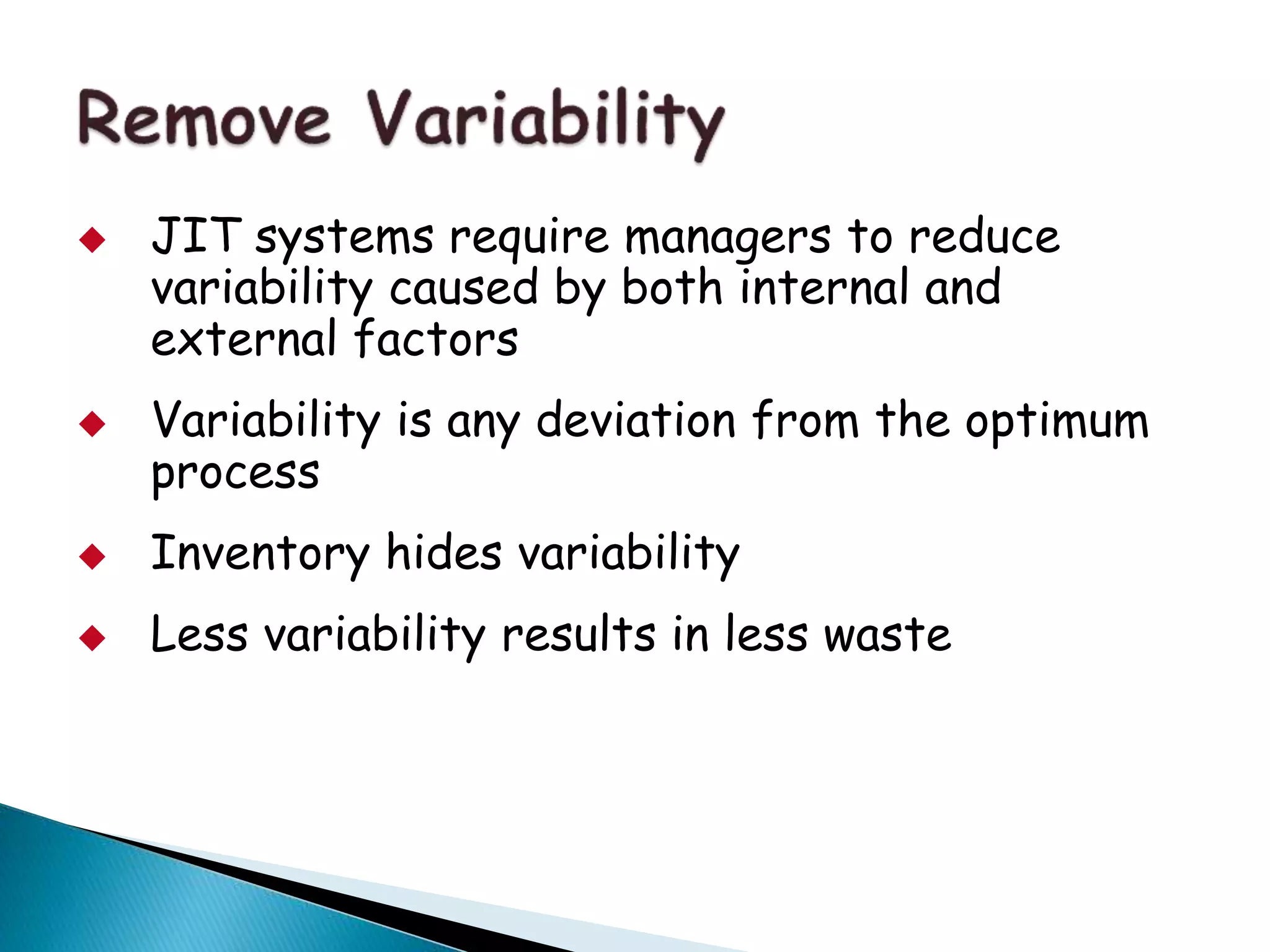
This document discusses lean production and just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing. It describes lean as minimizing waste and inventory to produce only what is needed when it is needed. Key aspects of lean covered include the 5S methodology, eliminating sources of variability, using kanban cards to pull materials through production, and the goals of JIT partnerships between suppliers and purchasers. The Toyota Production System is cited as originating many lean principles including continuous improvement, standard work practices, and respect for people.