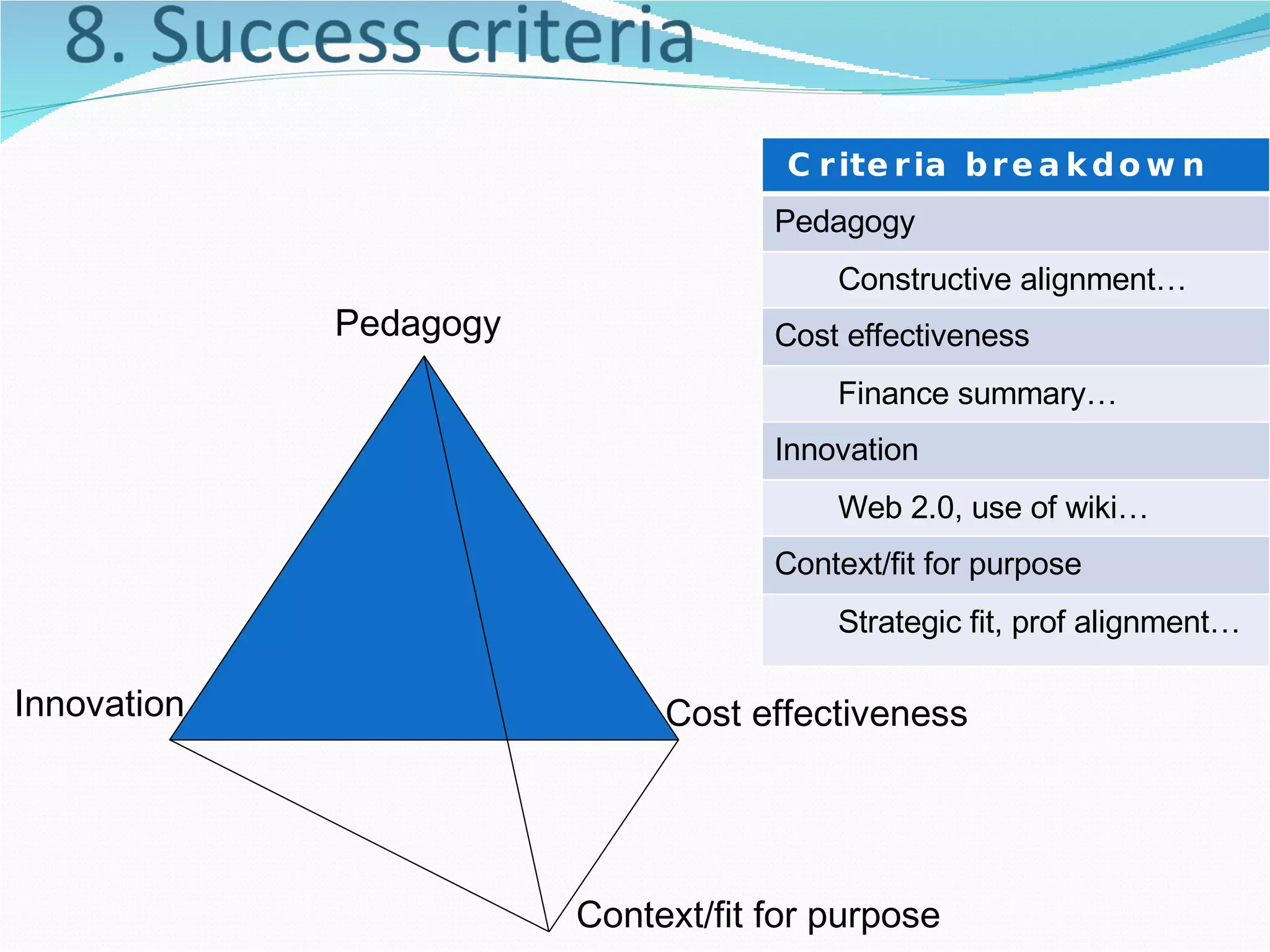
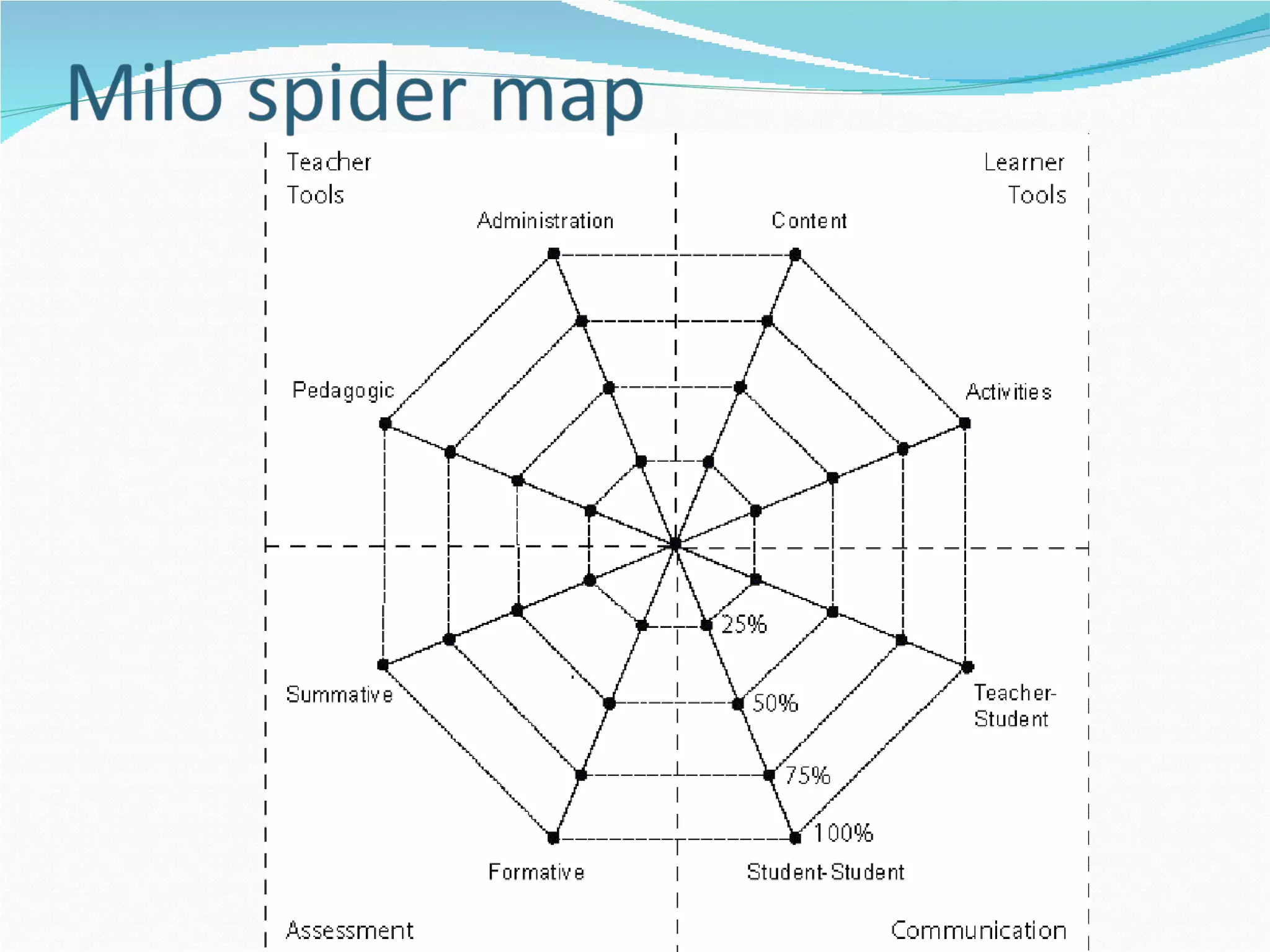
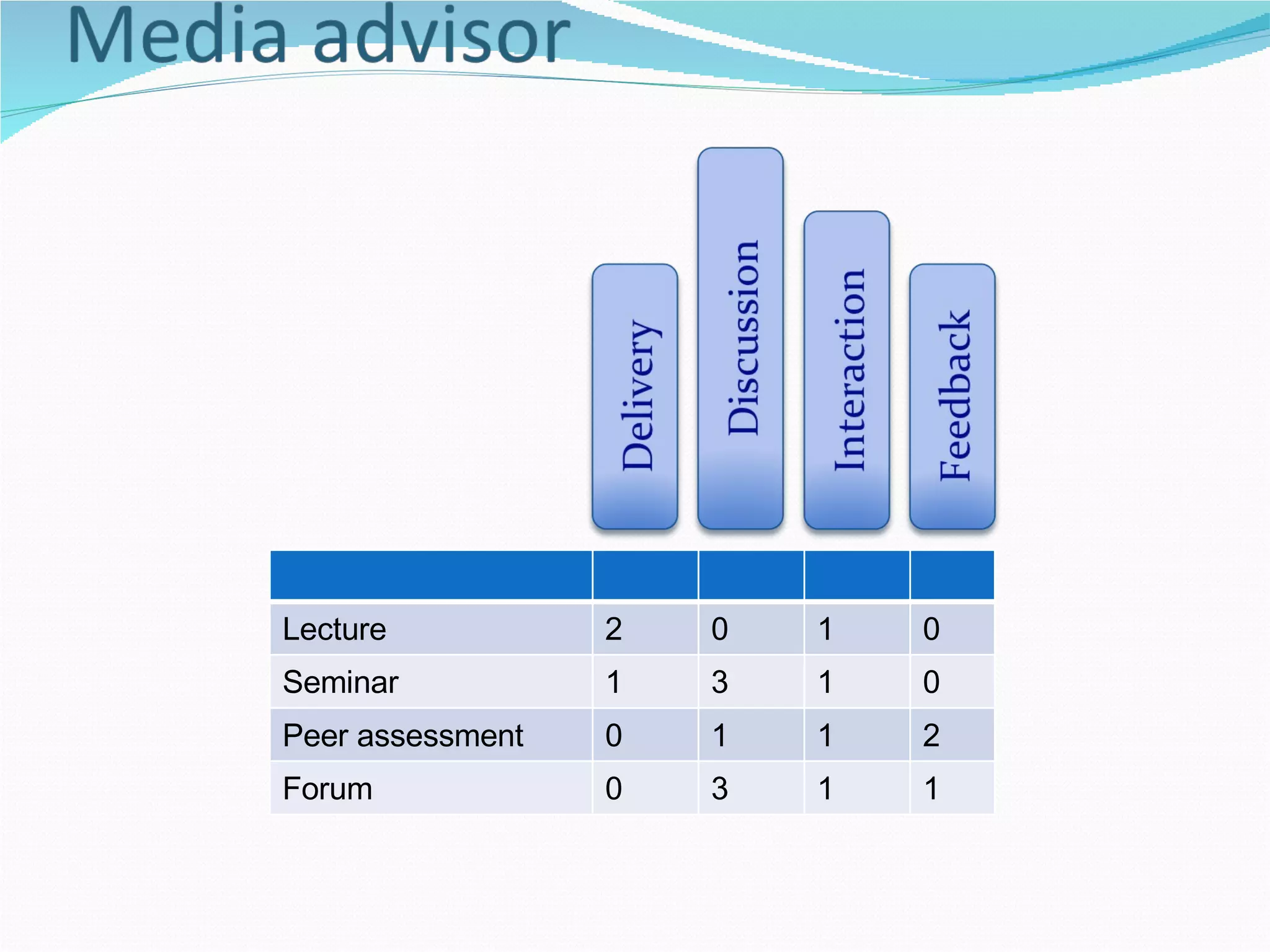
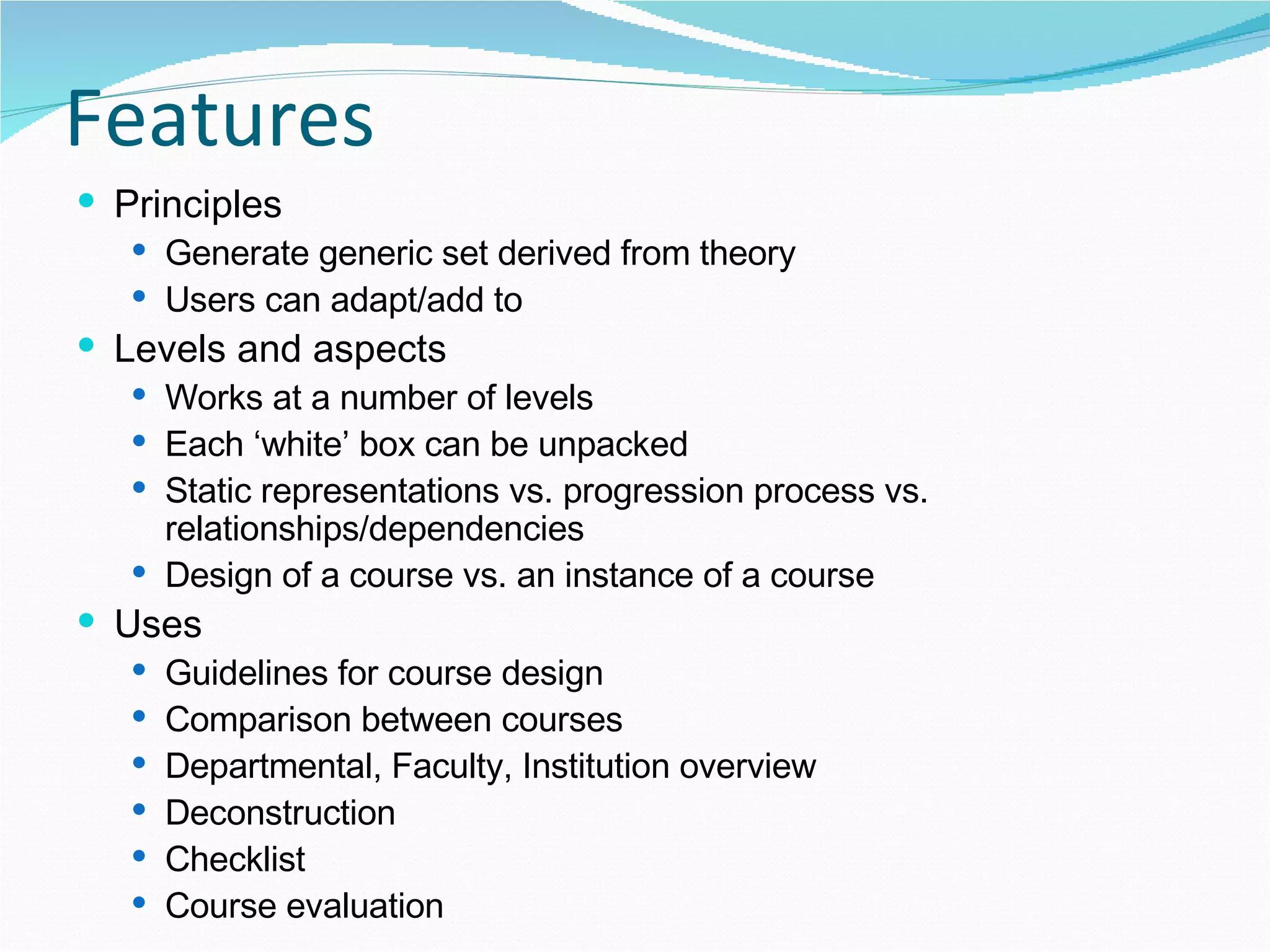
1. The document discusses potential representations for curriculum design from a meeting between three universities collaborating on curriculum design projects.
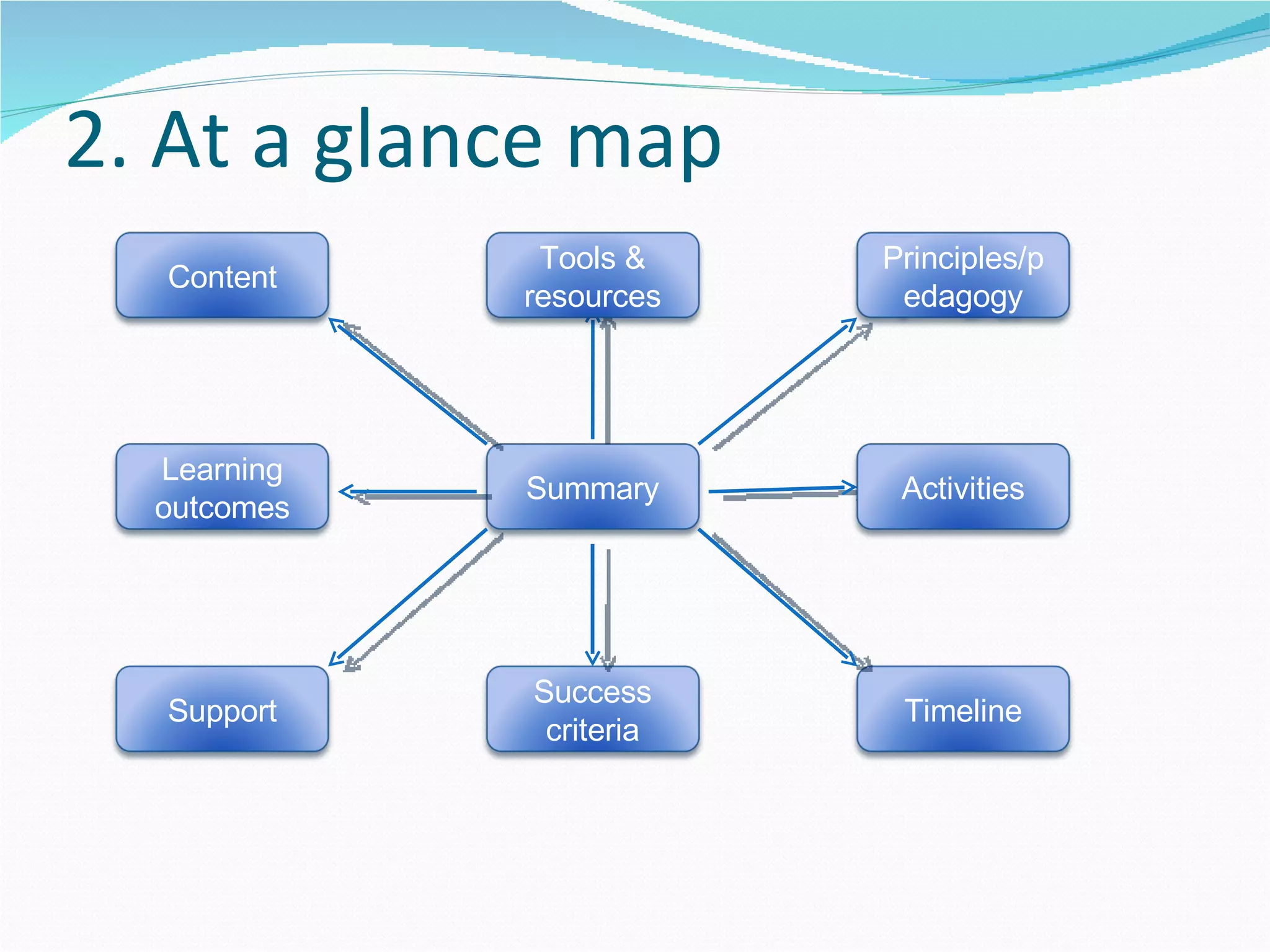
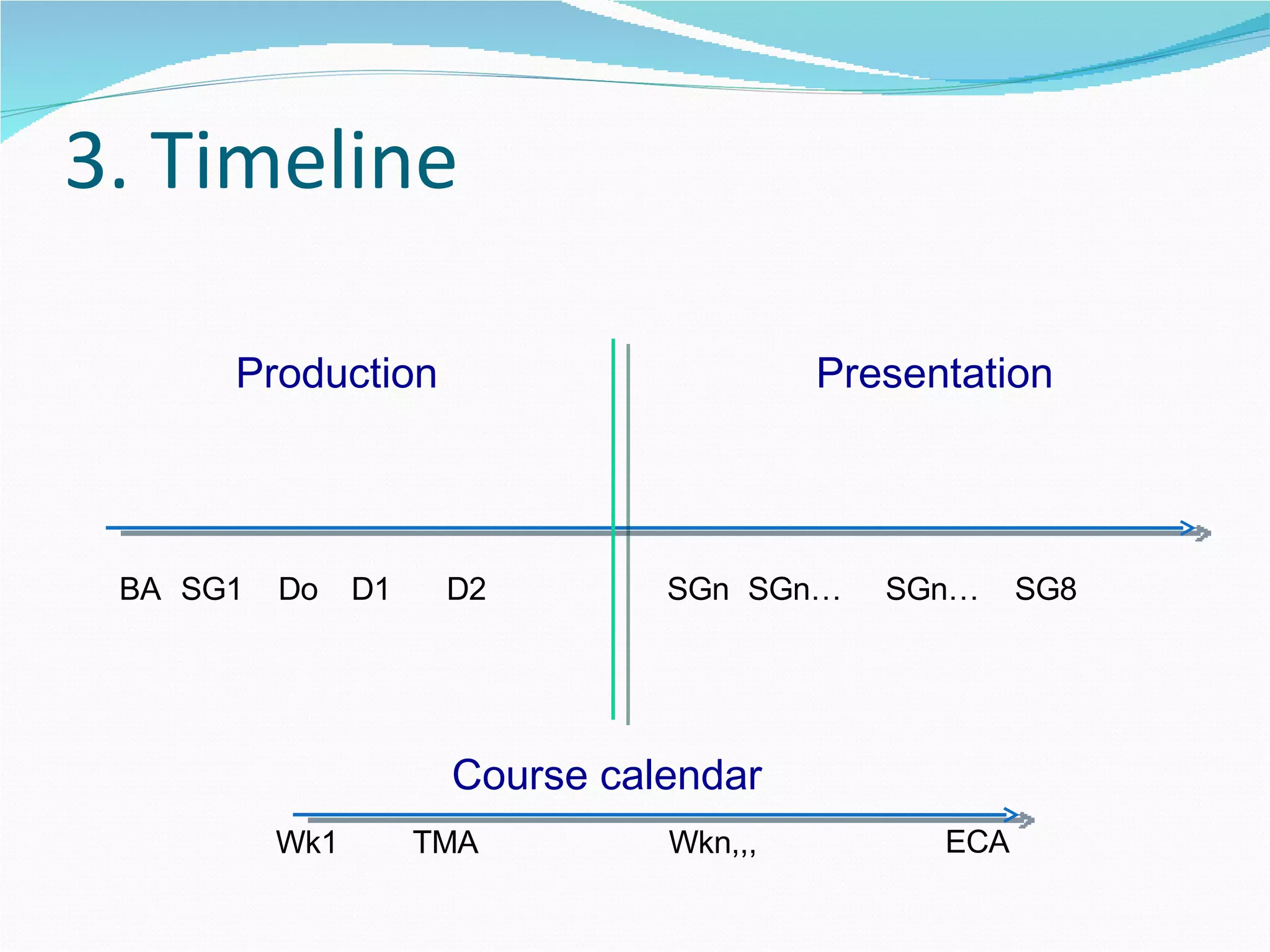
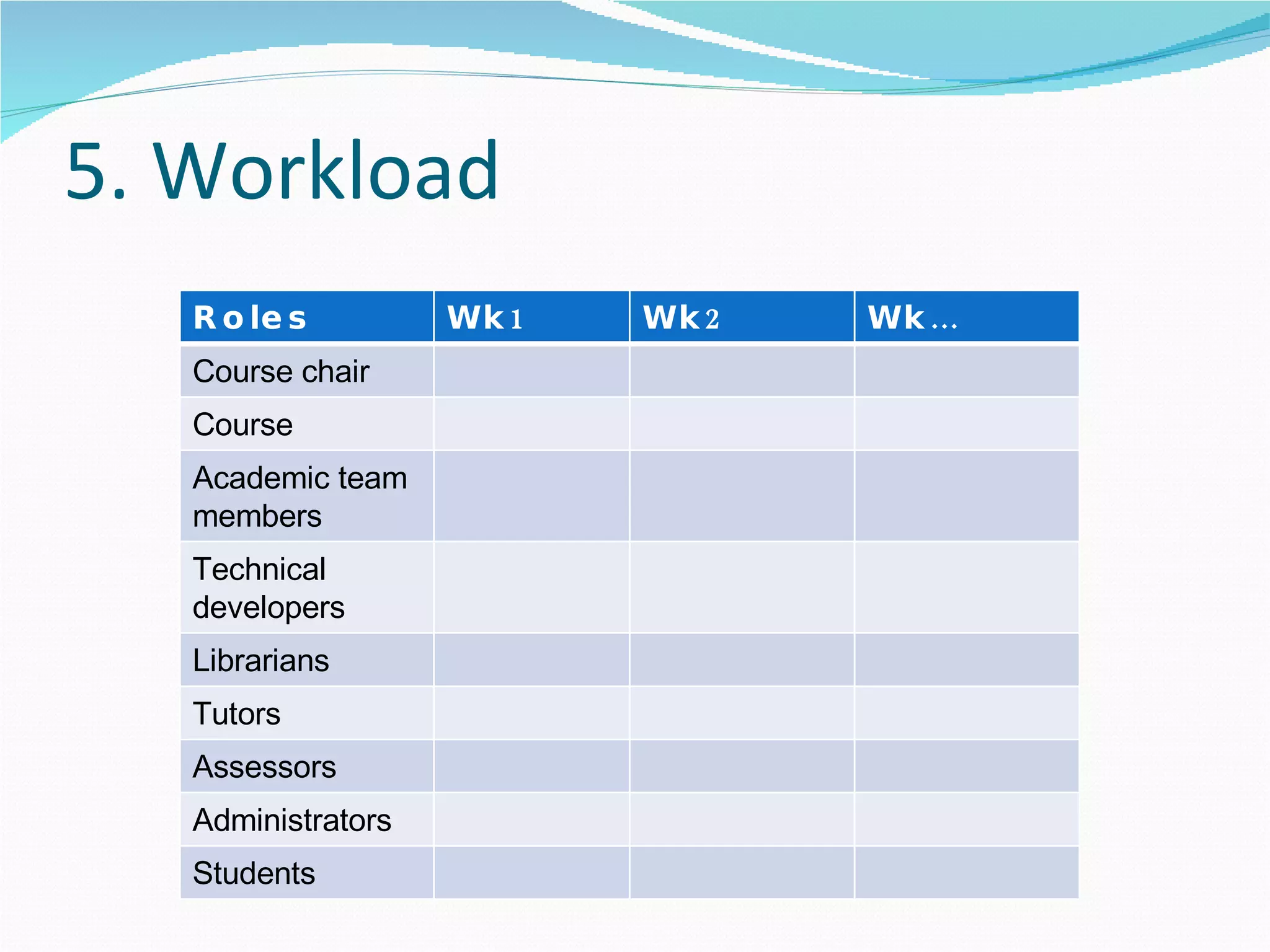
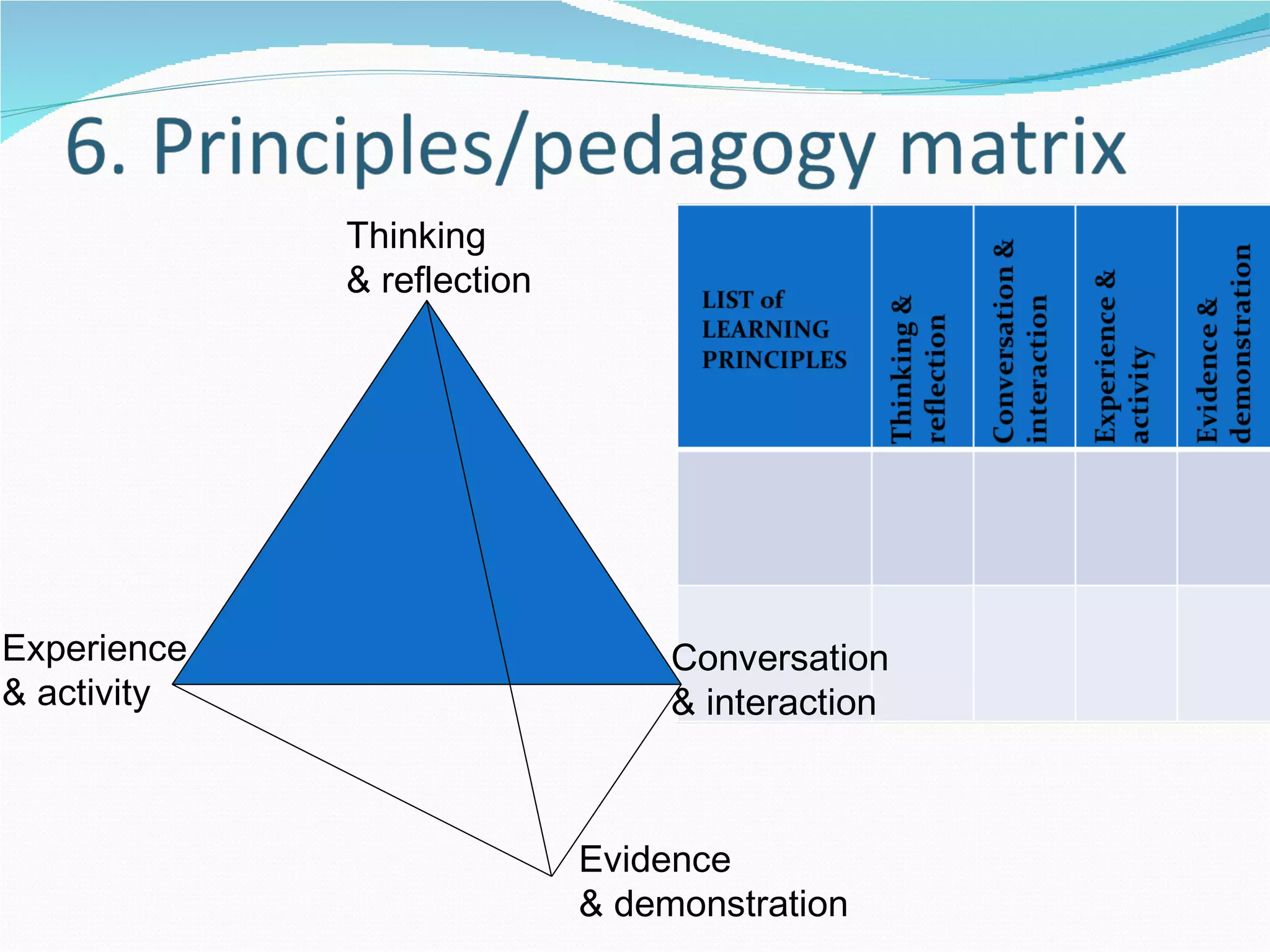
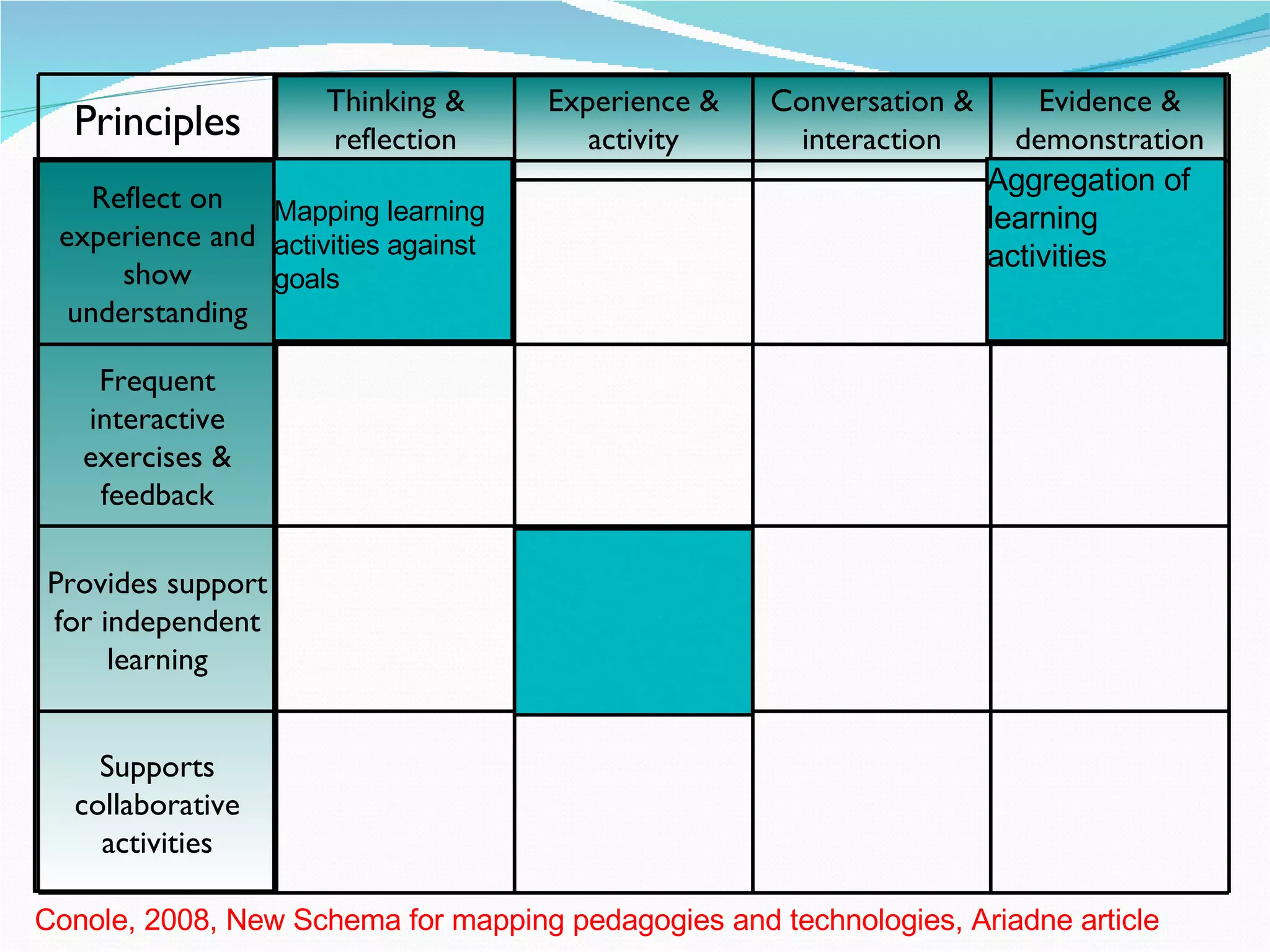
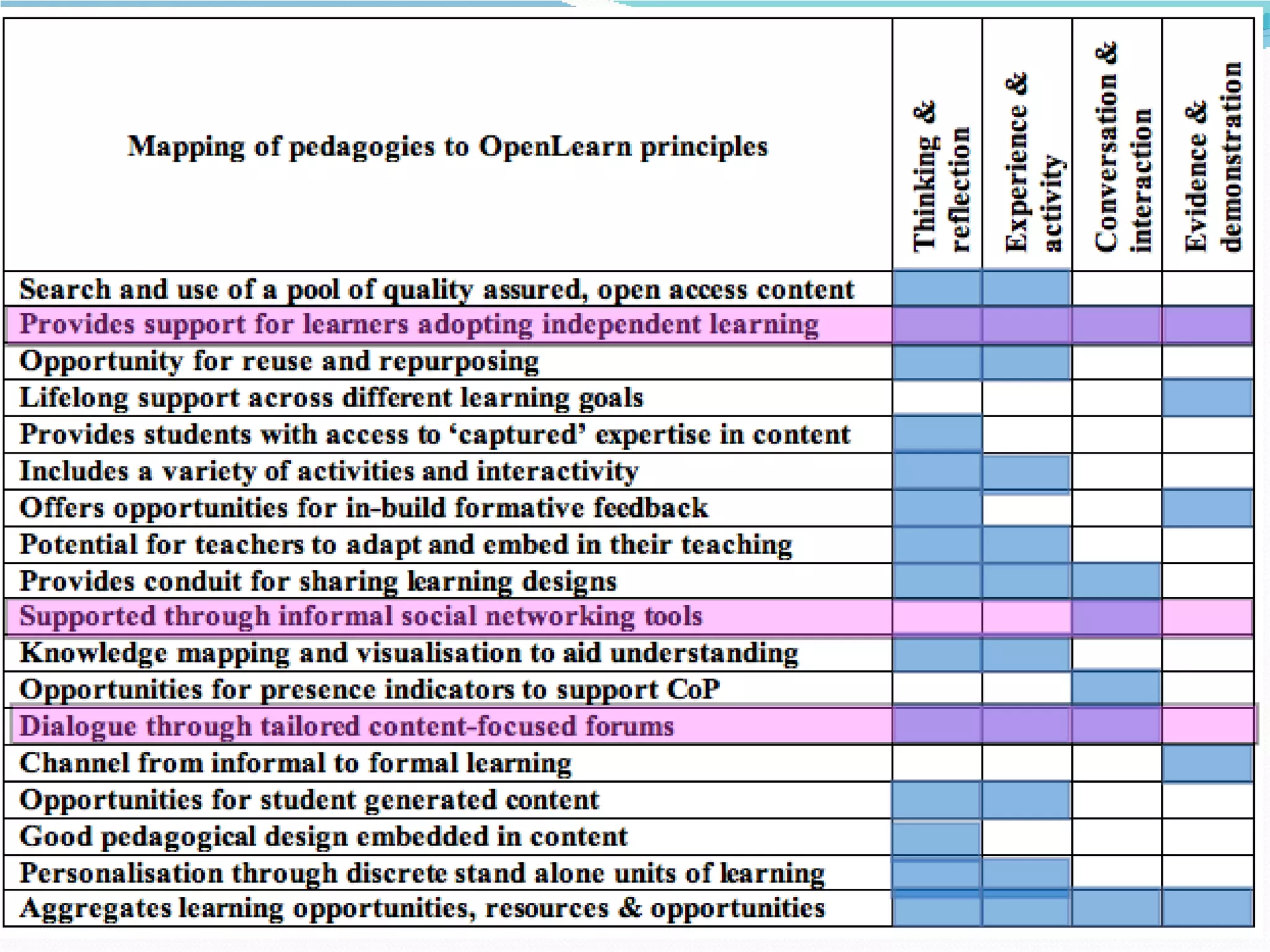
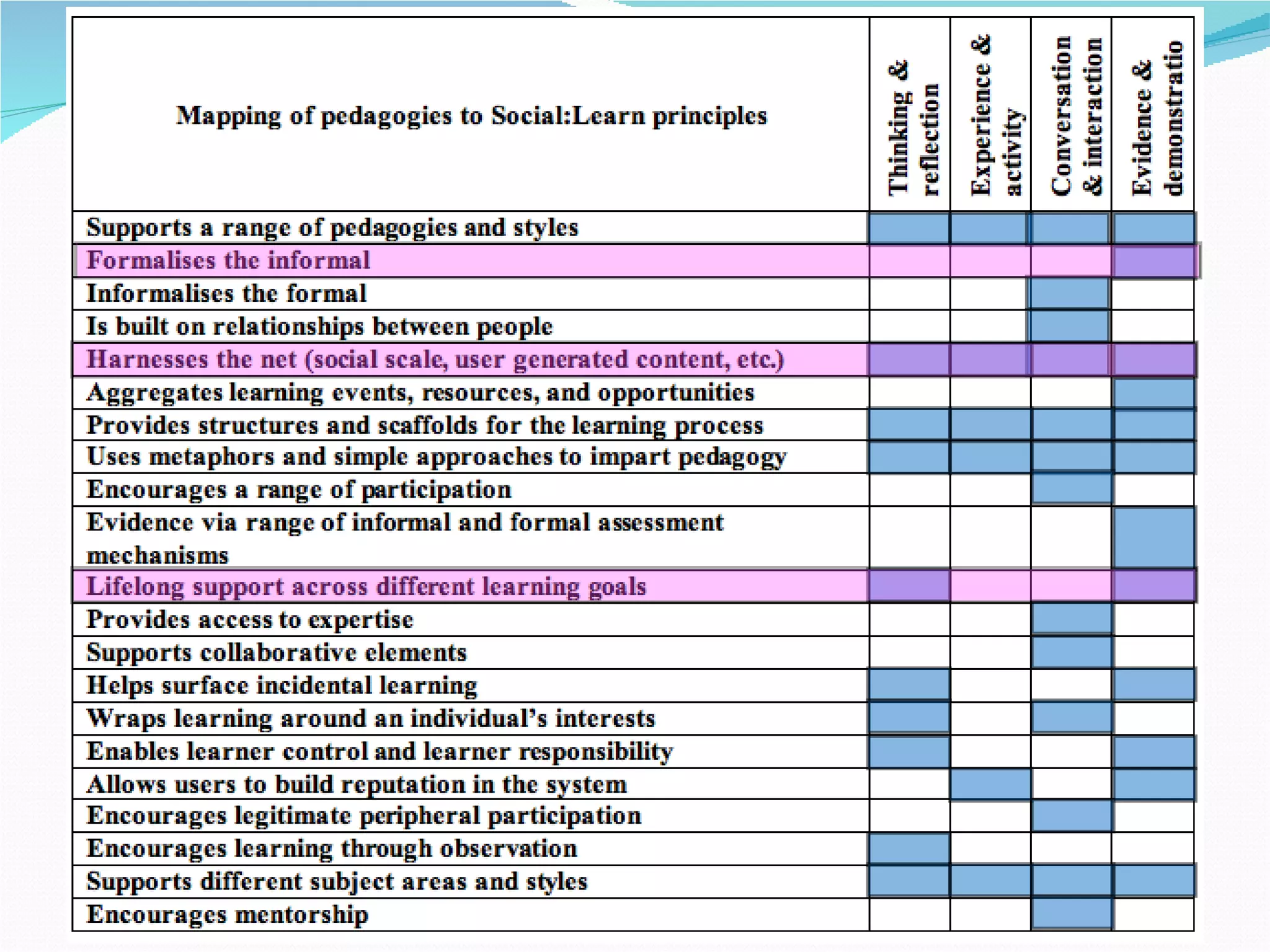
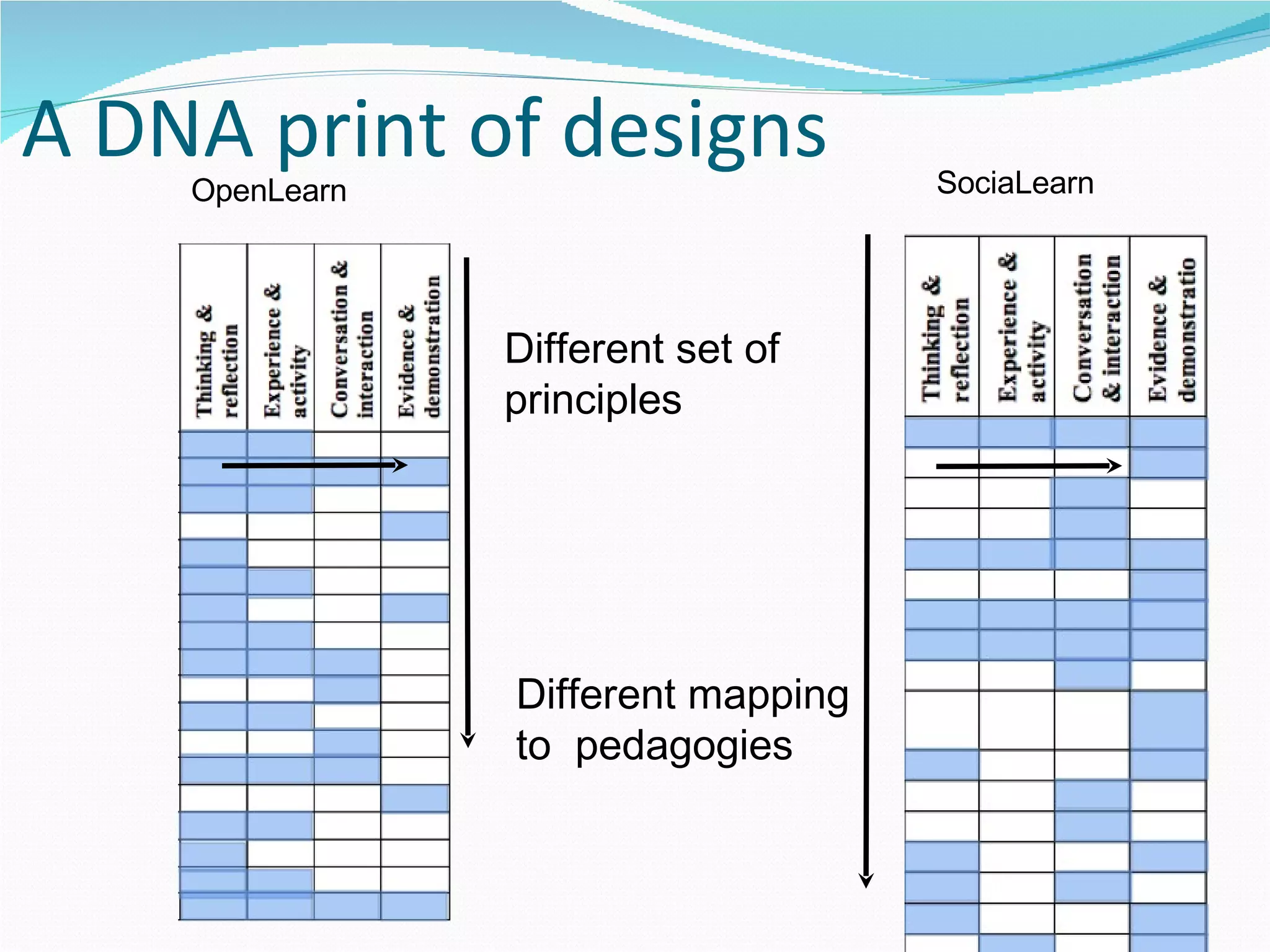
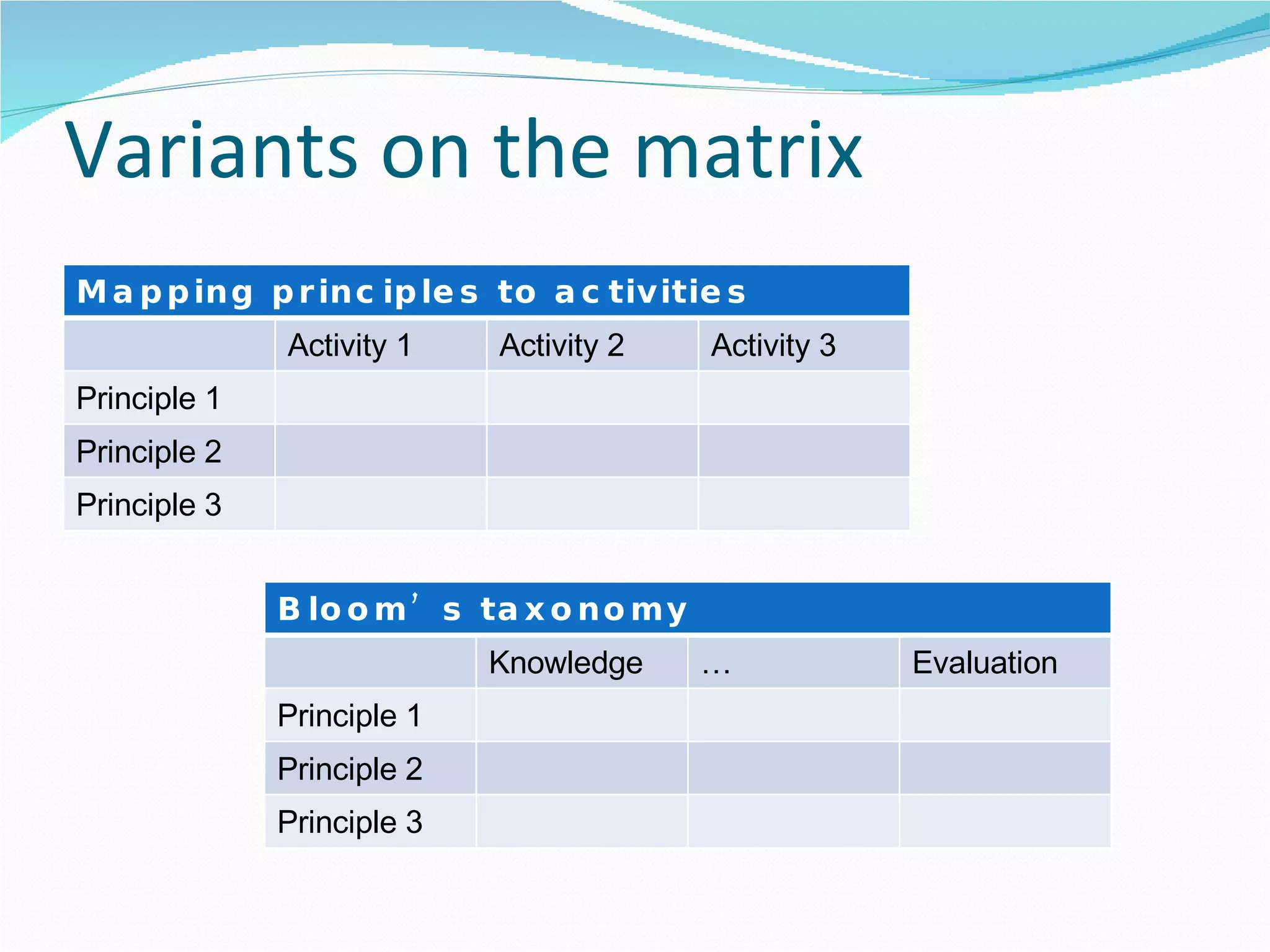
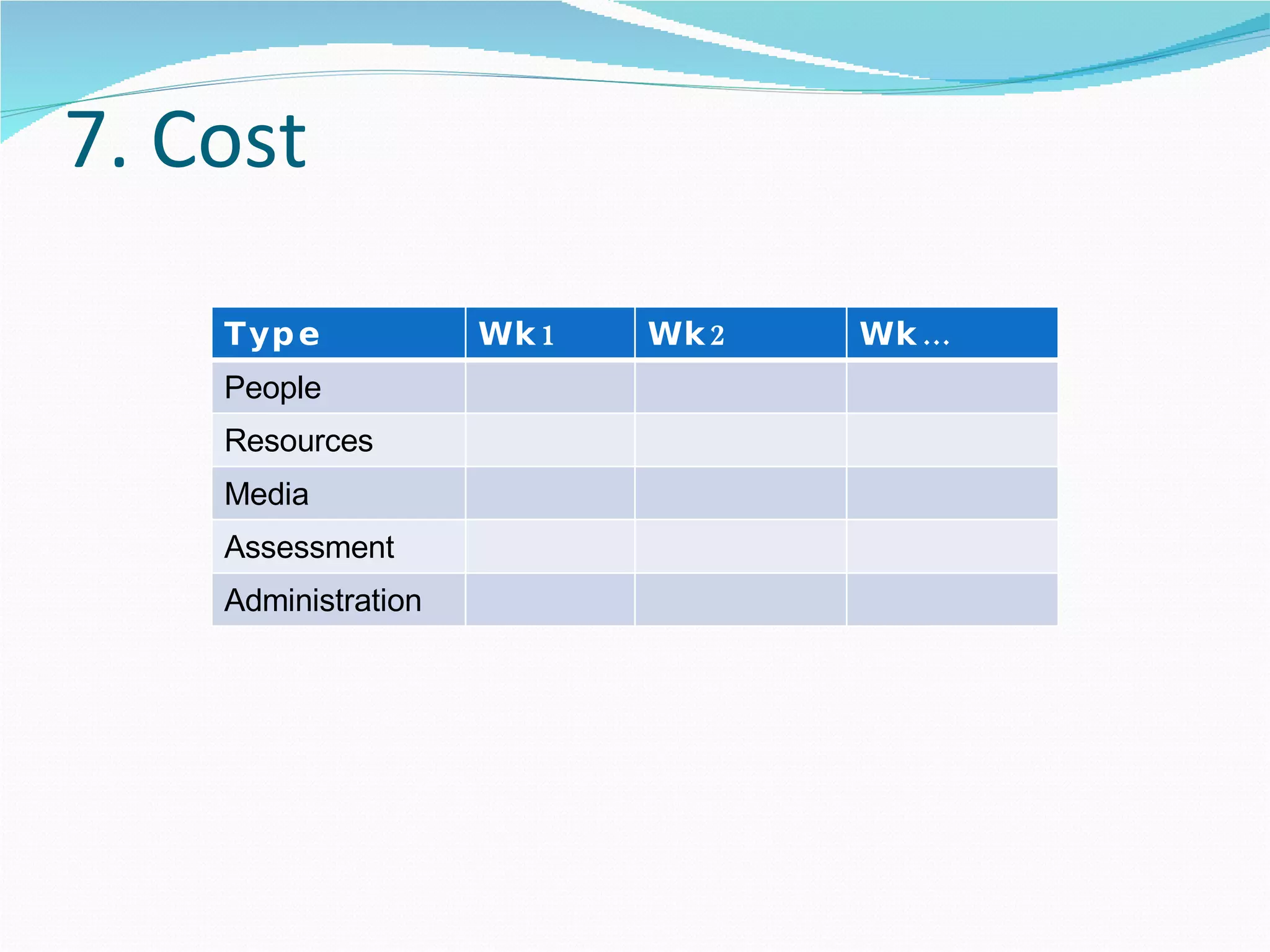
2. It proposes several representations including textual summaries, maps, timelines, matrices, and cost breakdowns to capture different aspects of curriculum design.
3. The goal is to develop a shared set of curriculum design representations and taxonomy across the universities.
![Gráinne Conole, The Open University [email_address] JISC Curriculum Design, Cluster meeting Strathclyde University 21/4/09](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/april2109-090423031426-phpapp02/75/JISC-Curriculum-Design-Cluster-C-meeting-1-2048.jpg)