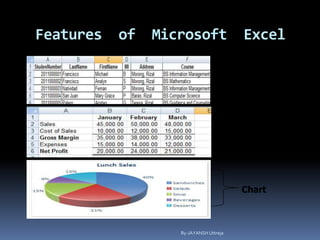
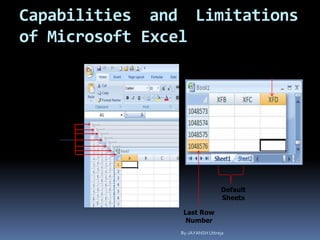
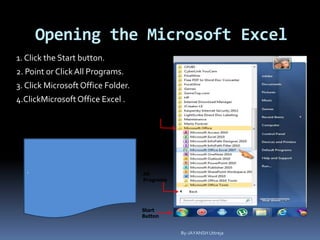
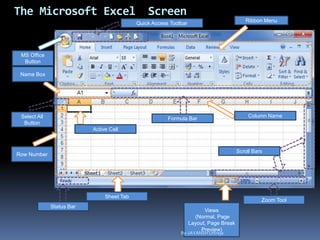
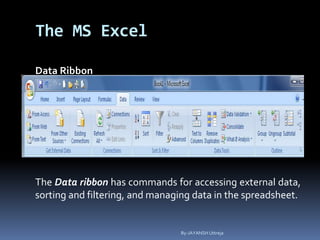
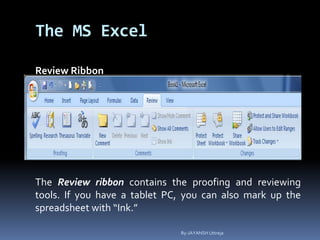
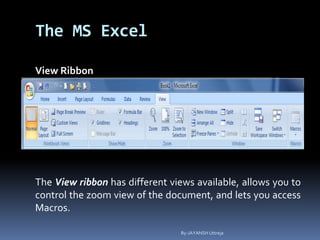
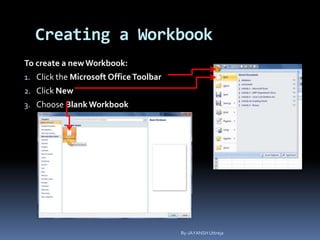
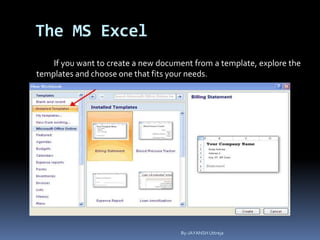
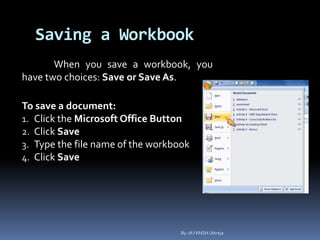
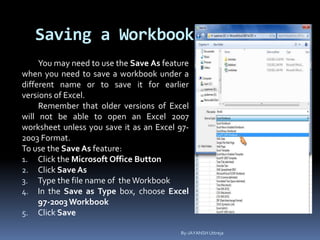
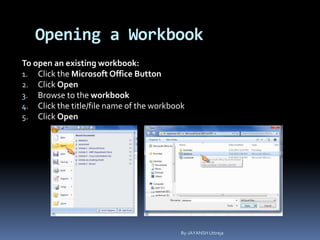
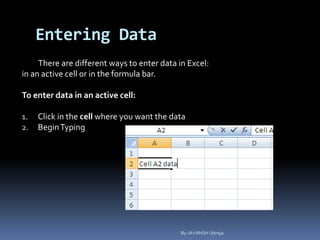
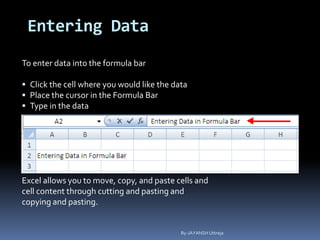
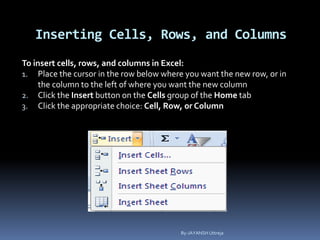
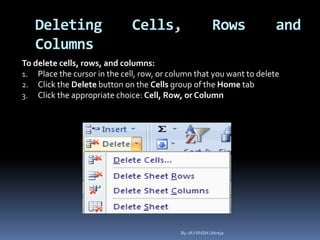
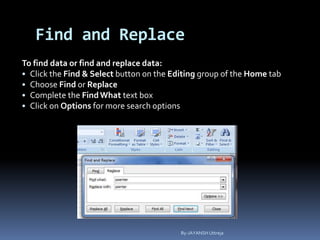
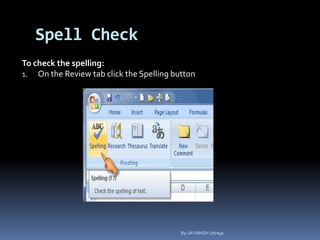
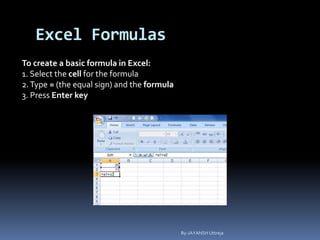
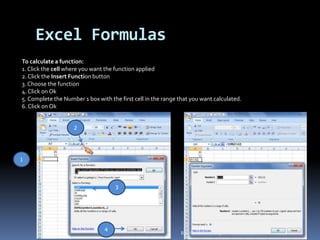
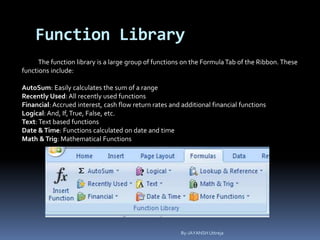
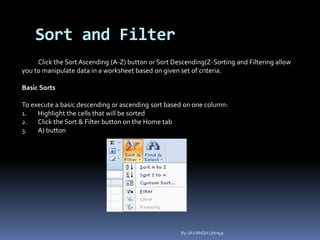
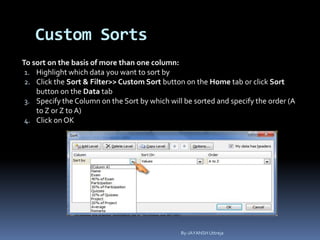
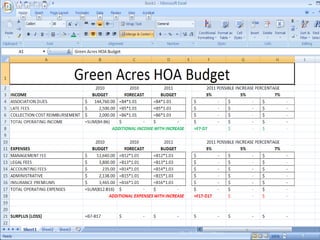
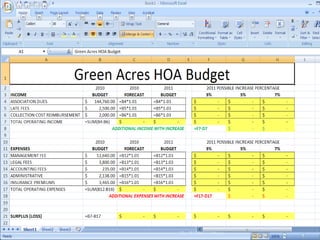
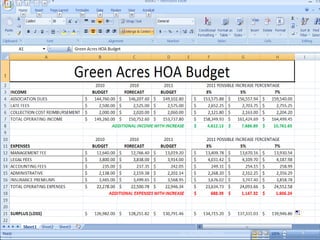
This document provides a tutorial on using Microsoft Excel. It discusses how Excel is used for tasks like number crunching, creating charts and graphs, organizing lists, and automating complex tasks. The tutorial describes the basic functions and features of Excel including opening and saving workbooks, entering and formatting data, using formulas and functions, sorting and filtering data, and linking worksheets. It provides step-by-step instructions on how to perform common Excel functions and demonstrates how to create and format a basic budget spreadsheet using formulas.