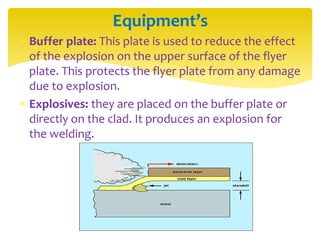
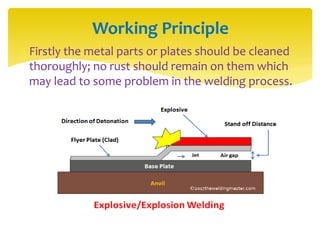
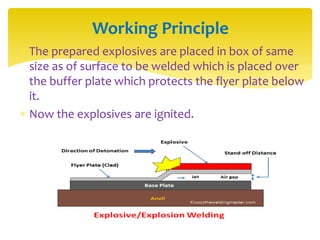
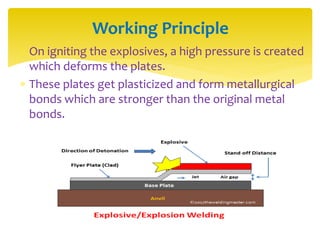
Explosion welding is a solid state welding process that joins metals through high-velocity impact using controlled explosions. It does not melt the metals. Explosion welding involves accelerating one metal part (the flyer plate) into another stationary part (the base plate) using explosives. When done correctly, the plates plastically deform and form metallurgical bonds without changing the properties of the original metals. Explosion welding can join dissimilar metals and produce large welds with complex geometries.