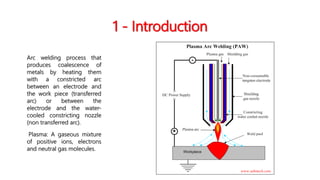
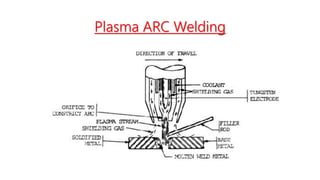
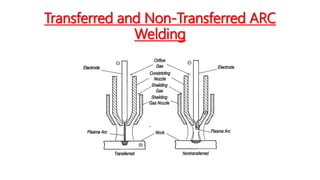
Plasma Arc Welding (PAW) is an advanced arc welding process that utilizes a highly ionized gas (plasma) to melt and fuse metals, either through a transferred arc between an electrode and the workpiece or a non-transferred arc to a nozzle. The technique offers several advantages, including faster metal deposition, high weld quality, and the ability to weld a variety of materials, but it also requires specialized equipment and safety precautions due to high power needs and radiation emissions. Applications of PAW span various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and construction.