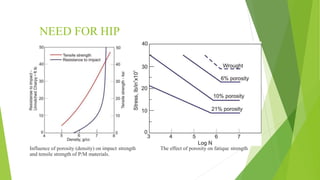
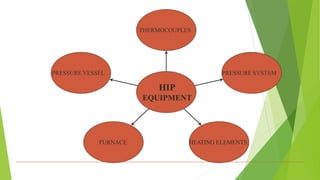
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a powder metallurgy technique that uses high temperature and pressure to reduce porosity and increase the density of metals and ceramics, enhancing their mechanical properties. It is widely applicable in the production of high-performance materials for industries such as aerospace and biomedical, producing fully dense components with a uniform grain structure. While HIP offers advantages in terms of performance and cost-efficiency, it is also subject to limitations depending on the material and application.